What is an incidental retroaortic left renal vein?
The retroaortic left renal vein (RLRV) is a malformation characterized by the presence of a vessel that drains the left renal blood up to the inferior vena cava (IVC) crossing behind the aorta.
Is left renal vein ligation benign?
Ligation of the left renal vein (LRV) has been felt to be a relatively benign maneuver with renal venous outflow maintained through existing venous branches. LRV has shown to be of negligible long-term renal function in the setting of aneurysm repair with dual kidneys; the effect of LRV in the setting of solitary left kidney however are less ...
What does incidental circumaortic left renal vein mean?
What does incidental Circumaortic left renal vein mean? Circumaortic left renal vein , also known as circumaortic renal collar is an anomaly of left renal vein when a supernumerary or accessory left renal vein passes posterior to the aorta, apart from the normal renal vein passing anterior to the aorta.
What veins that join to form the renal vein?
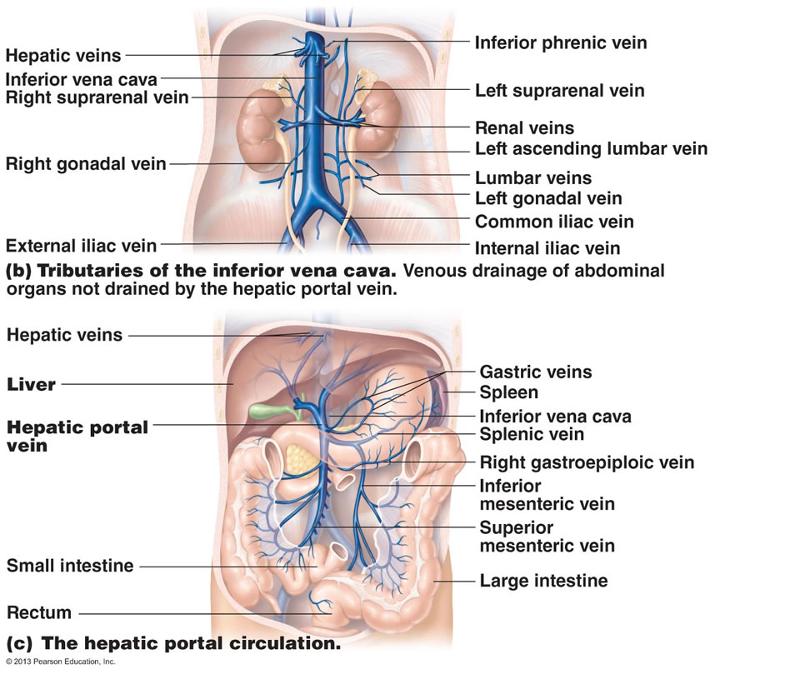
- left inferior phrenic vein
- left suprarenal vein
- left gonadal vein ( left testicular vein in males, left ovarian vein in females)
- left 2nd lumbar vein

Is the left renal vein longer?
The main renal veins empty into the inferior vena cava; the left renal vein is three times longer than the right (7.5 cm versus 2.5 cm). The left renal vein traverses behind the splenic vein and body of the pancreas before it crosses in front of the aorta near its termination in the inferior vena cava.
What is the difference between the left and right renal vein?
The right renal vein receives tributaries exclusively from the kidney, while the left renal vein receives several tributaries from other organs, including the left gonadal (ovarian/testicular) vein, left inferior phrenic vein and left adrenal veins. This article will discuss the anatomy and function of the renal vein.
Are the left and right renal veins the same length?
Gross anatomy The left renal vein is much longer, at 6-7 cm, than the right renal vein, at 3-4 cm, but they have a similar caliber (~1.2 cm). The left renal vein courses anteriorly to the abdominal aorta.
Which of the two renal veins is longer?
Because the inferior vena cava is on the right half of the body, the left renal vein is generally the longer of the two.
What is the function of left renal vein?
The main blood vessel that carries blood from the kidney and ureter to the inferior vena cava (a large vein that carries blood to the heart from the lower part of the body).
What is the significance of the orientation of the left renal vein to the superior mesenteric artery?
Clinical Significance Constriction of the left renal vein between the superior mesenteric artery and the aorta leads to compression ischemia in a condition known as Nutcracker syndrome. The normal pressure gradient is 1 mmHg between the renal vein and the inferior vena cava.
Why is the renal vein bigger than the renal artery?
Answer and Explanation: The renal artery is thicker than the renal vein because D. arteries have more smooth muscle. Arteries have more smooth muscle because they are subjected to higher levels of blood pressure.
How did you distinguish between the renal artery and the renal vein?
Our blood circulates through our kidneys frequently....Complete answer.Renal arteryRenal veinThe amount of urea in the blood of the renal artery is high.The amount of urea in the blood of the renal vein is low.The concentration of salts in the blood is higher.The concentration of salts in the blood is lower.8 more rows
Why is the right kidney lower in the abdominal cavity than the left kidney?
The right kidney usually is slightly lower than the left because the liver displaces it downward. The kidneys, protected by the lower ribs, lie in shallow depressions against the posterior abdominal wall and behind the parietal peritoneum. This means they are retroperitoneal.
Does renal vein carry deoxygenated blood?
Oxygenated blood comes to the kidneys from the right and left renal arteries off the abdominal aorta. Deoxygenated blood leaves the kidneys via the right and left renal veins that run into to the inferior vena cava.
What does blood in the renal vein contain?
Blood in the renal vein (i.e. after the kidney) will have: Less urea (large amounts of urea is removed via the nephrons to form urine) Less water and solutes / ions (amount removed will depend on the hydration status of the individual)
What does the right renal vein drain?
Each renal vein drains into a large vein called the inferior vena cava (IVC), which carries blood directly to the heart.
How did you distinguish between the renal artery and the renal vein?
Our blood circulates through our kidneys frequently....Complete answer.Renal arteryRenal veinThe amount of urea in the blood of the renal artery is high.The amount of urea in the blood of the renal vein is low.The concentration of salts in the blood is higher.The concentration of salts in the blood is lower.8 more rows
Is the right renal artery longer or shorter?
longerThe Cardiovascular System The right renal artery is longer than the left, because it has to pass behind the inferior vena cava to reach the right kidney (see Chapter 17: Urinary Tract). The adrenal arteries arise either from the renal arteries or directly from the aorta.
How is the left renal vein related to the left renal artery?
Left Renal Artery: The left renal vein separates the left renal artery from the body and tail of the pancreas and the splenic vessels. Posteriorly, its proximal part is related to the left crus of the diaphragm, left psoas major muscle, left sympathetic trunk, and the body of the second lumbar vertebra.
How does the renal vein terminate?
It terminates by draining into the inferior vena cava at a right angle. The left renal vein is more than three times longer than its right counterpart (about 7 cm). It courses posterior to the splenic vein and pancreas.
Which veins receive tributaries from the kidney?
The right renal vein receives tributaries exclusively from the kidney, while the left renal vein receives several tributaries from other organs, including the left gonadal (ovarian/testicular) vein, left inferior phrenic vein and left adrenal veins. This article will discuss the anatomy and function of the renal vein.
What is the name of the vessel that carries blood from the kidney to the inferior vena cava?
Renal vein (Vena renalis) The renal vein is an asymmetrically paired vessel that carries the deoxygenated blood from the kidney to the inferior vena cava. Both left and right veins run anterior to their corresponding renal arteries. The right renal vein receives tributaries exclusively from the kidney, while the left renal vein receives several ...
What is the name of the vein that drains into the interlobar veins?
Further, the arcuate veins drain into the interlobar veins that merge to form a single renal vein. The right renal vein is a short vein (about 2-3 cm long) that runs anterior to its corresponding artery. It courses retroperitoneally, passing posterior to the descending segment of the duodenum.
What is the drainage of blood in the kidney?
Anatomy and course. In the kidney, the blood drainage starts with the peritubular plexuses that give off fine venules that form the interlobular veins. The interlobular veins anastomose with each other and drain into the arcuate veins.
Which vein empties into the inferior vena cava?
left adrenal vein. capsular veins of the left kidney. Similar to the right, the left vein is accompanied by its corresponding artery and empties into the inferior vena cava. Occasionally, there can be two left renal veins present.
What are the tributaries of the left vein?
The tributaries of the left vein include: left gonadal vein. left inferior phrenic vein. left adrenal vein.
Where is the left renal vein?
The left renal vein lays posterior to the inferior margin of the tail of the pancreas (Fig. 36-1 ). The left adrenal vein enters the superior surface of the renal vein, and the adrenal gland can sometimes be adherent to the posterior capsule of the pancreas, making this mobilization of the pancreas more difficult. During the course of medial reflection, the left renal vein, adrenal gland, or adrenal vein may be inadvertently injured.
Which vein is longer, the left or the right?
The renal veins lie ventral to the renal arteries. The left is longer than the right and passes in front of the aorta, just inferior to the origin of the superior mesenteric artery. The renal veins enter the vena cava around the level of L1-L2. The left renal vein is usually slightly more cephalad than the right.
What is the most common procedure for transposition of the renal vein?
Left renal vein transposition: Because the basic pathology responsible for NCSs is compression of the renal vein, direct procedures on the LRV are likely to be most efficacious with least risk to other structures. This is the most common and most effective procedure in which the LRV is transposed distally onto the IVC at an area where the aortomesenteric space is wider ( Fig. 22.7 ). Through a transabdominal, transperitoneal minilaparotomy, the small bowel is retracted to the right and in part toward the distal abdomen. The retroperitoneum is opened between the fourth part of the duodenum and the inferior mesenteric vein, in front of the infrarenal abdominal aorta. The LRV is mobilized, and the left adrenal and descending left lumbar vein are ligated and divided to facilitate adequate mobilization. The left gonadal vein is preferably preserved for subsequent coiling to treat unresolved pelvic congestion or as a conduit for bailout secondary procedures. Intraoperative measurement of the pressure gradient can be performed before transecting the LRV. Following systemic heparinization, the IVC is controlled with a side-biting Satinsky clamp across the LRV confluence. The LRV is then transected and a tension-free end-to-side reanastomosis to the IVC at a more distal location is performed. The original insertion site on the IVC is oversewn. Following restoration of flow, patency may be documented with intraoperative DUS, IVUS, or venography.
What are renal vein anomalies?
All anomalies are variations of the embryologic development and persistence of portions of the paired longitudinal channels, the subcardinal and supracardinal veins, which form a ladder-like collar around the aorta. Normally, only the anterior components persist, becoming the renal veins, which course anterior to the aorta. Persistence of the whole collar results in a circumaortic renal vein, which is depicted in this graphic. This anomaly is more common than an isolated retroaortic renal vein.
What veins do renal veins drain from?
It receives drainage from the left gonadal, left inferior phrenic, and left adrenal veins. Renal vein anomalies are common. Multiple renal veins can arise from one or both kidneys; there can be circumaortic or retroaortic left renal veins, and rarely the renal veins can arise from the iliac vessels. View chapter Purchase book.
What vein is below the kidney?
Persistence of the left supracardinal vein below the kidney results in a “duplicated” inferior vena cava.
How many accessories does the right renal vein have?
In another study, the right renal vein was found to have one to three accessories (18% of 203 cases) and the left renal vein to have one or two accessories (9% of 203 cases). Poynter pointed out that the renal veins show a tendency to form two or more trunks as the arteries do, but in the veins the frequency is only about 7%.