What does the upward slope of the supply curve reflect?
This upward slope represents increasing marginal costs with an increase in production. When prices are low, quantity is low, but as price and profits increase, supply increases, as well, creating an upward curve. Supply curves can also be flat or even vertical.
Why does supply curve have a positive slope?
Why Does Supply Curve Have A Positive Slope? The Supply Curve has a positive slope because as the selling price of the product increases, the willingness of producers to create that product increases as well. With the greater incentive (profit) to make that product, production will rise in direct proportion to how much price increases.
Why are demand curves generally negatively sloped?
Demand Curve is Negatively Sloped: The demand curve generally slopes downward from left to right. It has a negative slope because the two important variables price and quantity work in opposite direction. The consumer, therefore, will purchase more units of that commodity only if its price falls.
Why AFC curve is downward sloping?
a. The average fixed costs AFC curve is downward sloping because fixed costs are distributed over a larger volume when the quantity produced increases.
Why does a long run supply curve slope upwards?
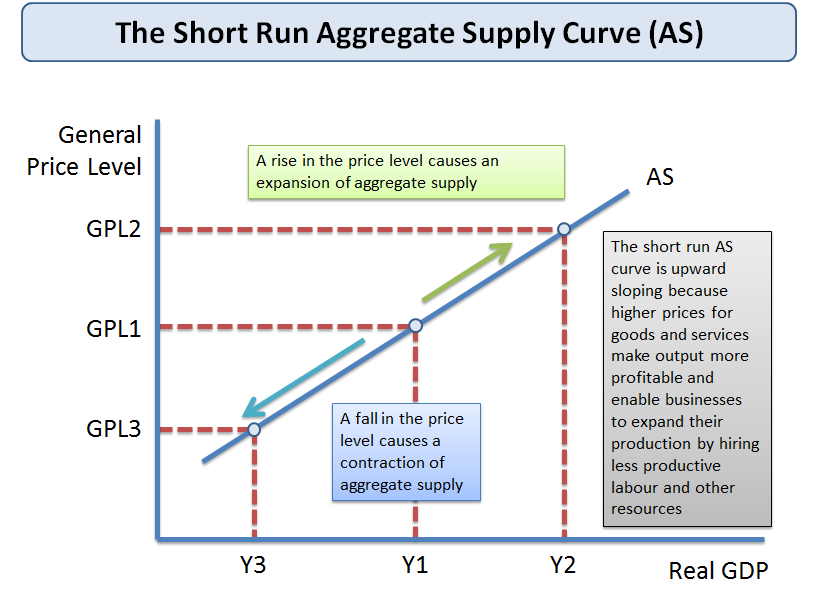
🤔 Understanding the Supply Curve The supply curve slopes upward because as a product's price rises, the business would tend to be more willing to make it. Also, since businesses are efficient and would exhaust the cheapest production inputs first, the cost of production tends to rise as output increases.
Why is the long run supply curve downward sloping?
In a decreasing cost industry, the long run supply curve is downward sloping since as output increases and new firms enter, production costs decline. The computer industry is an example of a downward sloping supply curve, since as the number of computers produced increased, the price of inputs, such as chips, decline.
Why is the supply curve upward sloping quizlet?
The supply curve is upward sloping because it reflects the higher price needed to cover the higher marginal cost of production.
Why the long run supply curve is horizontal?
All firms have identical cost conditions. Hence, in the case of a constant cost industry, the long-run supply curve LSC is a horizontal straight line (i.e., perfectly elastic) at the price OP, which is equal to the minimum average cost. This means that whatever the output supplied, the price would remain the same.
What does a downward sloping supply curve mean?
The downward shift represents the fact that supply often increases when the costs of production decrease, so producers don't need to get as high of a price as before in order to supply a given quantity of output. (Note that the horizontal and vertical shifts of a supply curve are generally not of the same magnitude.)
When the long run average cost curve is downward sloping?
The Long Run Average Cost Curve shows how the average costs of a firm evolve over time. As the curve slopes down the cost per unit shrinks as seen in the change from point A to point B. The downward sloping portion of the curve is an economy of scale, the average cost rises proportionately less to output.
Is the supply curve ever downward sloping?
Supply curves from profit-maximizing firms can be vertical, horizontal or upward sloping. While it is possible for industry supply curves to be downward sloping, supply curves for individual firms are never downward sloping.
What is the supply curve in the long run?
An enterprise's long-run supply curve is the increasing part of the LRMC curve from and above the minimum LRAC, together with the zero output for all the cost prices less than the minimum LRAC. This was the concept of the long-run supply curve of a firm.
Why do supply curves slop?
Supply curves are traditionally shown on a graph as sloping upwards from left to right. There are a number of reasons for this. First and foremost, there is the profit motive. An increase in demand for a particular product in the market will cause the price of that product to rise. In turn, this will encourage firms to increase their output in ...
What happens to the supply of a product when production increases?
Once the production of a specific good has increased, in most cases this means an increase in the costs of production. It's not hard to see why. If firms increase their production, then of course it will cost them more to produce additional units. Inevitably, this additional production will increase supply, which, as we have seen, is illustrated on a graph by an upward sloping curve.
Why do firms have to keep their marginal revenues equal to their marginal costs?
This is an economic law because that is the way to maximize profit or minimize loss. Because of the law of diminishing marginal returns, marginal costs tend to increase as a firm produces more of a thing.
Why is it important for a supplier to produce or supply a commodity?
As a result of this increase in potential profit, it is more valuable for a supplier to produce or supply this commodity, because they will receive more money per unit supplied. Because of this, they will inherently create and furnish more of that good in order to profit off of it.
Why does a higher price mean higher profit?
This makes sense because a higher price will bring (all other things being equal) a higher profit. As the sale price of the good rises, the profit gained by selling it increases and the producer has a greater incentive to produce and sell a higher quantity.
Why is the price of a product higher?
The higher the price of a product—or, more accurately, the more a customer is willing to pay for it —the more incentive a producer has to supply the product, because they will receive a higher profit.
What is the effect of increased profitability on the market?
The prospect of increased profitability will inevitably tempt new entrants to come into the market. As they enter, they will produce more of the goods that can command a high price in the market. The main consequence of this additional production will be an increase in the overall level of supply. And as we've already seen, this increased level of supply is illustrated on a graph by an upward sloping curve.
How is supply determined in the long run?
In the long run, the supply of a commodity is determined by the minimum point of long run AC curve where optimum output is obtained . This results in a change not only in the size of the industry, but also in the supply of output. The change in scale of production in the long run brings about (external) economies and (external) diseconomies of production.
How will the long run AC curve of an individual firm shift as industry output expands?
How wills the long run AC curve of an individual firm shift as industry output expands depends on whether the industry operates under constant cost condition, or increasing cost condition, or decreasing cost condition. Consequently, the shapes of the long run industry supply curve will be horizontal, increasing, and decreasing—depending on the cost condition on which the industry operates.
What happens at OP 3?
At the new price OP 3, the firm earns normal profit after producing OQ 3 output. Further, entry of new firms in the industry leads to a rightward shift in the supply curve to S 1 S 1. Finally, equilibrium is achieved at point W. The industry output is now OQ 3 and equilibrium price is OP 3. Now by joining these equilibrium points (‘M’ and ‘N’), we get an upward rising long run industry supply curve, labelled as LRS.
How to find output of industry?
If we assume that there are 10,000 identical firms in the industry, then the industry output would be Oq × 10,000 firms = OQ ( shown in panel b). Since these firms are making only normal profit at the price OP, the industry is in equilibrium with an output OQ.
Why does an expansion in industry output cause costs to rise in the long run?
Thus as industry expands, external diseconomies outweigh external economies leading to a net increase in costs. As industry expands , demand for inputs rise and costs rise since the industry operates under increasing cost condition.
Why does variation in cost occur in a competitive industry in the long run?
That is why variation in cost occurs in a competitive industry in the long run. In other words, as industry output expands in the long run, a perfectly competitive industry may experience constant cost or decreasing or increasing cost.
What is LRS curve?
Thus, under constant cost industry, the LRS curve is a horizontal straight line or perfectly elastic even though the short run supply has a positive slope.
What factors will shift the inelastic long run aggregate supply?
For example an increase in population will mean more workforce in the economy, technological advancement will mean the country can produce more faster and efficiently and a war could destroy some capital assets.
What is long run aggregate supply?
As a model, Long Run Aggregate Supply is made up of consumer goods, capital goods and public goods. Essentially it represents the real GDP of a country. Intuitively, a country's GDP level is too large to be significantly affected by price changes.
What does shift LRAS to the right?
What does shift LRAS to the right (increases the real GDP at equilibrium) are increases in the amount of resources available and technological improvements.
Why is the LRAS vertical?
The LRAS is vertical because, when you reach the limits of the capital in place, you can’t produce more, at any price. So, price ceases to matter, it can’t increase GDP. Thus, the vertical line.
What happens if a firm does not increase its price?
Also, if a firm does not increase its price, it will have a relatively lower or cheaper priced good/service and production will need to increas. To understand why the long-run aggregate supply (LRAS) curve is verticle, it may help to understand why the short-run aggregate supply curve is positively sloped.
How does short run affect production?
However, in the short run you can increase the utilisation of existing factors of production, e.g. workers doing overtime. In the short run an increase in the price of goods, encourages firms to take on more workers, pay slightly higher wages and produce more.
When changes in the money supply (MV) are fully anticipated or if enough time passes then all consumers in the economy?
When changes in the money supply (MV) are fully anticipated or if enough time passes then all consumers in the economy update their expectations about price levels as monetary policy changes. We consider this to be true both in the long-run as well as in the short-run when monetary policy changes are being tracked closely by enough people that there is no nominal change in output (Y) when there are changes to monetary policy (MV).
Why is the supply curve upward sloping?
According to the misperceptions theory, the short-run aggregate supply curve is upward sloping because changes in the overall price level can temporarily mislead suppliers about what is happening in their individual market. That means, when the price level falls, many firms will notice a fall in the price of the goods and services they sell and reduce production because they believe their business has become less profitable. However, if the overall price level falls, the prices of other products ( including raw materials used for production) decrease as well. That means the relative price of the firms’ products doesn’t necessarily decline, and there is no actual reason to reduce the output.
Why is the aggregate supply curve upward?
According to the sticky wage theory, the upward slope of the aggregate supply curve in the short-run is due to the fact that nominal wages are slow to adjust to changes in the overall price level ( i.e., they are sticky ). That means when the price level falls, most firms cannot adjust wages immediately, which leads to an increase in real ...
Why does the sticky price curve slope upward?
The sticky price theory states that the curve slopes upward because the prices of some goods and services are slow to adjust to changes in the price level. Finally, the misperceptions theory states that the short-run aggregate supply curve is upward sloping because changes in the overall price level can temporarily mislead suppliers about ...
Why do sticky prices slope?
The sticky price theory states that the short-run aggregate supply curve slopes upward because the prices of some goods and services are slow to adjust to changes in the overall price level. That means when the overall price level falls, some firms may find it hard to adjust the prices of their products immediately. This causes sales to drop, which in turn leads to a decrease in the quantity of goods and services supplied. According to the sticky price theory, the primary reason for sticky prices is what we call menu costs. Menu costs describe all costs incurred by firms in order to change their prices ( e.g., printing new menus, distributing updated price lists, changing price tags on the shelves ).
What happens when the price level falls?
That means when the price level falls, most firms cannot adjust wages immediately, which leads to an increase in real production costs. As a consequence, the suppliers hire fewer workers and produce a smaller quantity of goods and services.
What are the three theories of supplier behavior?
There are three theories that try to explain why suppliers behave differently in the short run than they do in the long run: (1) the sticky wage theory, (2) the sticky price theory, and (3) the misperceptions theory . We will look at each of them in more detail below. 1. The Sticky Wage Theory.
What happens to the price of raw materials when the price level falls?
However, if the overall price level falls, the prices of other products ( including raw materials used for production) decrease as well. That means the relative price of the firms’ products doesn’t necessarily decline, and there is no actual reason to reduce the output.