What does the olfactory bulb do?
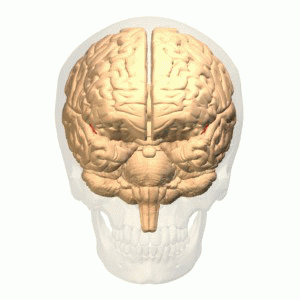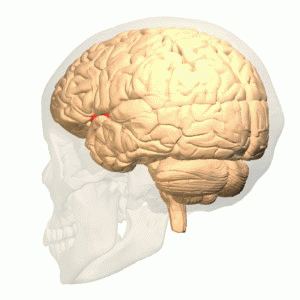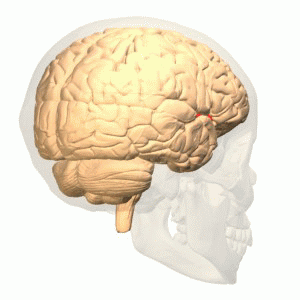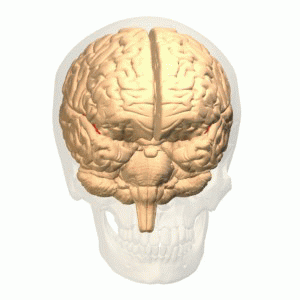
The olfactory bulb (Latin: bulbus olfactorius) is a neural structure of the vertebrate forebrain involved in olfaction, the sense of smell. It sends olfactory information to be further processed in the amygdala, the orbitofrontal cortex (OFC) and the hippocampus where it plays a role in emotion, memory and learning.
What does olfactory bulb mean?
Olfactory bulb, structure located in the forebrain of vertebrates that receives neural input about odours detected by cells in the nasal cavity. The axons of olfactory receptor (smell receptor) cells extend directly into the highly organized olfactory bulb, where information about odours is processed.
What is the main function of the olfactory membrane?
olfactory system, the bodily structures that serve the sense of smell. The system consists of the nose and the nasal cavities, which in their upper parts support the olfactory mucous membrane for the perception of smell and in their lower parts act as respiratory passages.
Is the human olfactory bulb necessary?
Typical olfactory bulbs might not be necessary for smell, case study suggests. by Cell Press. A scan of a person with olfactory bulbs (upper left) is visibly different from the brain scans of ...
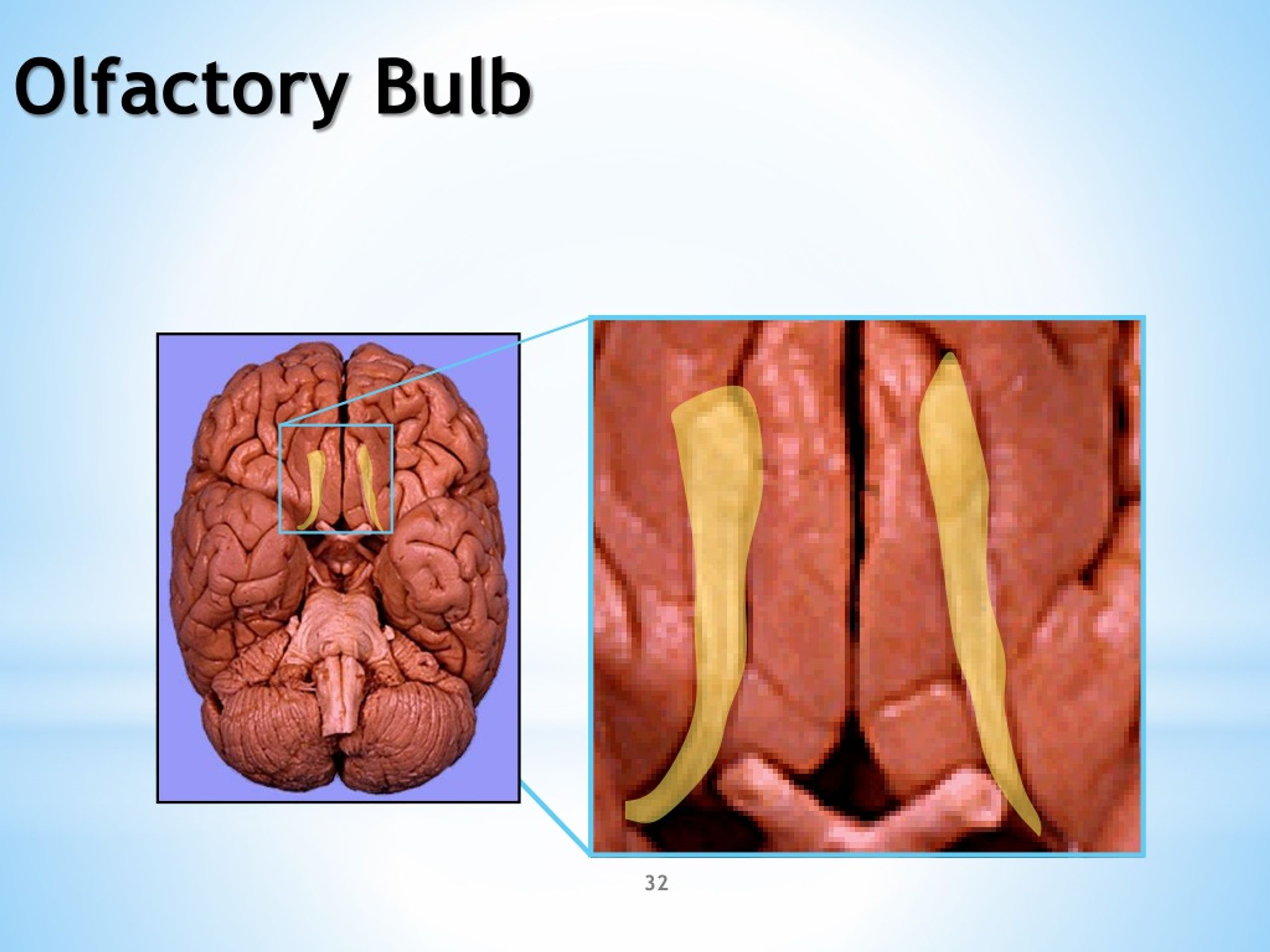
What is the purpose of the olfactory bulb?
The olfactory bulb (OB) plays the central role in the processing of olfactory information. It is the only relay between periphery and the central nervous system; it also processes olfactory information.
Why is the olfactory important?
Olfactory sense is, in terms of evolution, one of the oldest senses, allowing the organisms with receptors for the odorant to identify food, potential mating partners, dangers and enemies. For most living creatures and for mankind smell is one of the most important ways of interaction with the environment.
Why is the olfactory bulb important in the sensation of smell?
Smells are handled by the olfactory bulb, the structure in the front of the brain that sends information to the other areas of the body's central command for further processing. Odors take a direct route to the limbic system, including the amygdala and the hippocampus, the regions related to emotion and memory.
Can you live without olfactory bulb?
Researchers have discovered a small group of people that seem to defy medical science: They can smell despite lacking "olfactory bulbs," the region in the front of the brain that processes information about smells from the nose.
Why is olfaction important for taste?
Neural activity created by this stimulation passes to the primary olfactory cortex at the back of the underside, or orbital, part of the frontal lobe. Olfactory information then passes to adjacent parts of the orbital cortex, where the combination of odor and taste information helps create the perception of flavor.
Why smell is the most powerful sense?
Because the olfactory bulb and cortex are so close physically to the hippocampus and amygdala (huge factors in memory retention), smell is considered the strongest and quickest memory inducer.
How do olfactory detect smell?
Each olfactory neuron has one odor receptor. Microscopic molecules released by substances around us—whether it's coffee brewing or pine trees in a forest—stimulate these receptors. Once the neurons detect the molecules, they send messages to your brain, which identifies the smell.
What is the function of olfactory cells?
Once the cells detect the molecules they send messages to our brains, where we identify the smell. Olfactory, or smell nerve cells, are stimulated by the odors around us--the fragrance of a gardenia or the smell of bread baking.
What is unique about the olfactory system?
The olfactory system is thus unique among the sensory systems in that it does not entail a thalamic relay en route to the primary cortical region that processes the sensory information. The olfactory tract also projects to a number of other targets in the forebrain, including the hypothalamus and amygdala.
What happens if the olfactory bulb is injured?
Lesions to the Olfactory Nerve and/or to the Olfactory Pathway can lead to the following symptoms: Anosmia- loss of sense of smell. Hyposmia- decrease ability to detect smell. Hyperosmia- increased sensitivity to the sense of smell.
Can you smell without olfactory bulb?
But now researchers have stumbled upon people who can still enjoy coffee's fragrance even though they lack an olfactory bulb. Scientists had thought that people without olfactory bulbs could not detect odours.
Can you taste without olfactory bulbs?
"When you lose your sense of smell, your whole sense of food flavor is distorted and diminished," Cowart says. "You can still taste the basic tastes which are sweet, salty, sour, bitter, and umami or savory.
What is the importance of olfactory in animals?
Olfaction is a major sense in animals. The detection of volatile chemical compounds is an important attribute for any animal to survive and reproduce in the natural environment. Different animals utilize different types of olfactory organs.
Why are olfactory sensations long lasting and an important part of our memories and emotions?
Scents bypass the thalamus and go straight to the brain's smell center, known as the olfactory bulb. The olfactory bulb is directly connected to the amygdala and hippocampus, which might explain why the smell of something can so immediately trigger a detailed memory or even intense emotion.
How does the olfactory system work in humans?
Each olfactory neuron has one odor receptor. Microscopic molecules released by substances around us—whether it's coffee brewing or pine trees in a forest—stimulate these receptors. Once the neurons detect the molecules, they send messages to your brain, which identifies the smell.
Why is the olfactory system unique among human senses?
The olfactory system is thus unique among the sensory systems in that it does not entail a thalamic relay en route to the primary cortical region that processes the sensory information. The olfactory tract also projects to a number of other targets in the forebrain, including the hypothalamus and amygdala.
Where are olfactory bulbs located?from thoughtco.com
Olfactory bulbs: bulb-shaped structures in the forebrain where olfactory nerves end and the olfactory tract begins.
What is the olfactory system?from thoughtco.com
This sense, also known as olfaction, is one of our five main senses and involves the detection and identification of molecules in the air. Once detected by sensory organs, nerve signals are sent to the brain where the signals are processed.
How many different odors can humans detect?from journals.physiology.org
Thus far, it has generally been accepted that humans can discriminate ~10,000 different odorants. In a recently published study, however, it was proposed that there may be even more than one trillion different odors that can be discriminated by the combinatorial activation of different ORs ( 23 ). However, the authors postulated this conclusion after making just 260 comparisons of 2 smells, of which only half could be discriminated. Reanalysis of the experiments by another group showed controversial data arguing for errors in the mathematical logic ( 123 ). At the molecular level, however, only ~10% of the ~400 intact human ORs have been deorphanized to date ( 3, 24, 49, 53, 58, 64, 75, 79, 91, 105, 112, 113, 120, 132, 134, 155, 159, 161, 168, 173, 178, 179, 182, 191, 198 ). Because of the potential of exogenous chemicals to activate ectopically expressed ORs, it will be interesting to elucidate how tissue accessibility is guaranteed. Moreover, the question arises as to whether endogenous ingredients may be recognized by specific tissue-expressed ORs.
How do ORs work?from journals.physiology.org
The processing of chemical cues following the activation of ectopically expressed ORs is based on a complex interplay of various signaling molecules, which greatly depends on the participating OR and the cellular system ( TABLE 1, FIGURE 3 ). The functional versatility of ORs is related to their substantial plasticity in the activation of different molecular and cellular mechanisms. For odorant detection, ORs elicit distinct signaling pathways in olfactory neurons, which leads to the production of electrical signals. Based on current knowledge, expressed ORs in somatic cells do not generate action potentials the way they do in olfactory neurons. In nonolfactory tissues, ORs can activate various signaling pathways. The specific pathway depends on the cellular phenotype regarding the expression of signaling components. Most likely, the most important decisive component is the type of involved heterotrimeric G protein.
Why is functional analysis of ectopic ORs important?from journals.physiology.org
The functional analysis of ectopic ORs in the cardiovascular system is of particular interest because they have an enormous potential to operate as the main carrier of endogenously and exogenously derived odorants throughout the entire human body.
Why are the functions of the majority of ORs in nonolfactory tissues uncertain?from journals.physiology.org
However, the function of the majority of ORs in nonolfactory tissues remains uncertain because their activating odorants are currently unknown. This review summarizes the occurrence of human ORs outside of the nose with a focus on their effects on various human tissues.
Why is the sense of smell and emotion different?from thoughtco.com
The connection between our sense of smell and emotions is unlike that of the other senses because olfactory system nerves connect directly to brain structures of the limbic system. Odors can trigger both positive and negative emotions as aromas are associated with specific memories.
The Evolutionary Importance of Senses
The five main senses are important for identifying danger and factors that could lead to the death of a human being.
Answer and Explanation: 1
The human body has five main senses that it depends on to gather information about the external environment and respond according to it. One of those senses is the sense of smell. It is important in identifying gases and differentiate between them.
The Olfactory Bulb
Not only does our sense of smell help us identify odors in the air around us, but it also plays a significant role in our ability to enjoy the taste of our food. (1)
Functions Of The Olfactory Bulb
To filter out multiple background odors to improve the transmission of a few specific ones.
The Olfactory Bulb Is Where Smell And Taste Collide
The olfactory bulb sends signals directly to the limbic system, including the hippocampus and the amygdala, areas of the brain related to memory and learning. But taste also plays a part.
The Cribriform Plate And the Olfactory Bulb
The bony plate in the nose, called the cribriform plate, connects to the olfactory bulb. It is very susceptible to injury. When a person experiences trauma to the cribriform plate, it could lead to olfactory dysfunction, like losing their sense of smell, septal hematoma, and also cerebrospinal fluid rhinorrhea. Infections could cause meningitis.
The Sense Of Smell
A fetus only has one fully developed sense in the womb: his sense of smell. It is also the most developed sense in a child up until age ten, when his sight becomes more advanced. We store smell and emotion as a single memory, and childhood tends to be the stage of life where you determine scents that you will love and hate for your lifetime. (4)
Smell Disorders
Parosmia is the condition of experiencing a changed perception of a smell. Parosmia can make something smell different from how it smelled before, or something that previously smelled good is now repulsive.
Strange Facts About The Olfactory Bulb And Smell
Here are some interesting facts about the olfactory bulb and our ability to smell:
Why is the olfactory sense important?
The importance of the olfactory sense in the human behavior and evolution. Not long ago it was believed that the human olfactory sense had a low importance, a vision which turned into the exploration of the environment.
What are the cortical areas of integration of the olfactory sensations?
Recent studies have shown that, despite the weak representation of the olfactory receptor common in other species too, the cortical areas of integration of the olfactory sensations are very large and have important interconnections with memory, language, and neuro-vegetative areas.
How are olfactory preferences explained?
These preferences were explained by the experiences (good or bad) that people had had and associated with particular odors. Despite the peculiarities of these individuals, it is possible to make some significant generalizations about olfactory preferences.
What is the olfactory memory?
The olfactory memory refers to memory of odors. Odors can bring us a lot of memories. This is because the olfactory bulb, which is a region of the central nervous system that processes sensory information from the nose, is part of the limbic system.
Why do smells trigger emotions?
Since the limbic system is an area closely associated with memory and emotions, smells can evo ke memories and trigger strong responses almost immediately.
Why do babies smell like tobacco?
Children who have been exposed to alcohol, tobacco smoke or garlic in the womb of their mothers often show a preference for these odors. For them, smells that can bother other babies seem normal or even pleasurable.
What are the visual stimuli in perfume?
The visual stimuli included an image of the perfume that the participant had chosen and an image of an unmarked perfume. The olfactor y stimulus included the perfume chosen by the participant and the unmarked perfume.
Why is color important in perfume?
A note for perfume merchants: one of the studies showing our tendency to prefer fragrances that we can correctly identify also showed that the use of an appropriate color can help us to make a correct identification, increasing our taste for perfume.
What does it mean when you smell something?
When you smell something for the first time, you link it unconsciously to an event, a person, an object, a moment or a place . Your brain forges a link between the smell and a memory, associating, for example, the smell of chlorine with summer or the smell of lilies with funerals.
What are the two structures of the olfactory bulb?
The bulb is divided into two distinct structures: the main olfactory bulb and the accessory olfactory bulb. The main olfactory bulb connects to the amygdala via the piriform cortex of the primary olfactory cortex and directly projects from the main olfactory bulb to specific amygdala areas. Why Do Sheep have Olfactory Bulbs.
Where is the accessory olfactory bulb located?
The accessory olfactory bulb resides on the dorsal-posterior region of the main olfactory bulb and forms a parallel pathway. Destruction of the olfactory bulb results in ipsilateral anosmia while irritative lesion of the uncus can result in olfactory and gustatory hallucinations. In sheep, the brain’s olfactory bulb is two or three times ...
Why do sheep have olfactory bulbs?
It provides the sheep with a strong sense of smell which is key for survival. The Olfactory Bulbs help A mother can use her sense of smell to find her baby in a flock. A baby can smell its way back to its mother if it gets lost.
Why is the sense of smell important to sheep?
This reflects the importance of the sense of smell to the sheep. In addition to helping it understand its surroundings and avoid danger, a sense of smell also plays a crucial role in establishing the bond between mother and infant, known as imprinting.
Why filter out background odors?
filtering out many background odors to enhance the transmission of a few select odors
Do sheep have a sense of smell?
The sheep, like many mammals, have a more developed sense of smell, or olfaction, than humans do. The olfactory bulb is the part of the brain located underneath the frontal lobe that is responsible for relaying sensory information from the nose to the rest of the brain. The olfactory bulb in sheep is two to three times the size ...
How many square centimeters does the olfactory epithelium have?
There is a correlation across species between the surface area of the olfactory epithelium and olfactory abilities. Humans have around 10 square centimeters of this tissue lining the roof of the nasal cavity. Dogs have about 170 square centimeters of it.
Why do dogs have a olfactory lobe?
Canine Olfactory Structures. Dogs have a huge olfactory lobe that helps them process all of the scent-related information that they take in . The size and complexity of this structure in the brain is one reason that dogs have such an amazing sense of smell and can detect bombs, cancer, drugs, lost people and even the tiniest trace ...
What is the olfactory epithelium of a dog called?
The projections are bony structures called turbinates. A recent study explored the development of the canine olfactory epithelium and the turbinates.
What part of the brain is responsible for dogs' ability to smell?
The dog brain is only one part of the anatomy responsible for their extraordinary sniffing abilities. The canine nose also contains key features that contribute to dogs’ superior skill at smelling, but only recently have people studied how the structures in the nose develop.
What is the function of FGF20?
In a paper called “ FGF20-Expressing, Wnt-Responsive Olfactory Epithelial Progenitors Regulate Underlying Turbinate Growth to Optimize Surface Area ”, graduate student Lu M. Yang and several collaborators report that a recently discovered type of stem cell (FEP) controls the extent of the surface area of the olfactory epithelium. These stem cells signal the turbinates to grow by sending out a molecule specific to this purpose. The type and extent of this signaling regulates the final surface area of the olfactory epithelium. Without these molecular signals, the growth of the turbinate and the olfactory epithelium are stunted.