What is the intrinsic pacemaker of the heart?
To coordinate these two tasks, the heart has an intrinsic pacemaker–i.e the sinus node –and an electrical conduction system composed of specialized myocardial cells. Conduction cells form bundles of fibers that spread the action potential rapidly and sequentially to the contractile myocardium.
Why would I need a pacemaker?
You might need a pacemaker if:
- Your heart beats too slow or unevenly and other treatments haven't helped.
- You have an ablation procedure. This burns off tiny areas of your heart that trigger abnormal electrical impulses. ...
- You take certain heart medicines. Beta-blockers and some other heart medications can slow your heartbeat. You might need a pacemaker to speed up the beat.
What you should know about pacemakers?
Yes, the types of pacemakers include the following:
- Transvenous: The traditional type of pacemaker, it can be single-lead or double-lead. ...
- Biventricular: This type also sends pulses to both of the heart's ventricles (bottom chambers) and one of the heart's atria (upper chamber).
- Epicardial: The electrodes attach to the surface of the heart instead of within its chambers.
Why do people get pacemaker?
Pacemakers have been saving lives for more than 50 years. Quite different from the original device, today’s pacemakers are smaller than a deck of playing cards, externally programmable, and can last up to 10 years. While the most common uses are to manage arrhythmias, there are several cardiac disorders that can be improved by a pacemaker.
See 7 key topics from this page
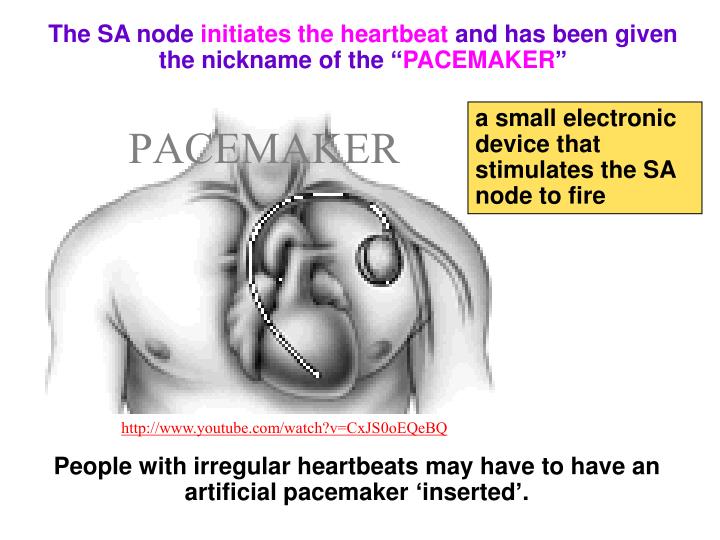
Why is the SA node the main pacemaker?
The sinus node continuously generates electrical impulses, thereby setting the normal rhythm and rate in a healthy heart. Hence, the SA node is referred to as the natural pacemaker of the heart.
Why is the SA node the usual pacemaker in the heart of many sites in the heart can become pacemakers?
The SA node is often referred to as a natural pacemaker because it generates a series of electrical pulses at regular intervals. The pulse is then sent to a group of cells known as the atrioventricular node (AV node). The AV node relays the pulse to the 2 lower chambers of the heart (the ventricles).
Why is the SA node called the pacemaker quizlet?
SA node establishes: -the basic rhythm and rate of the heartbeat. For this reason, its known as the natural pacemaker of the heart.
What is the role of pacemaker in the heart?
A pacemaker is a small device that's placed (implanted) in the chest to help control the heartbeat. It's used to prevent the heart from beating too slowly. Implanting a pacemaker in the chest requires a surgical procedure.
What is the role of pacemaker cells?
The cells that create these rhythmic impulses, setting the pace for blood pumping, are called pacemaker cells, and they directly control the heart rate. They make up the cardiac pacemaker, that is, the natural pacemaker of the heart.
What is considered to be the pacemaker of the heart quizlet?
SA node (sinoatrial node) - known as the heart's natural pacemaker The impulse starts in a small bundle of specialized cells located in the right atrium, called the SA node.
What node is the pacemaker of the heart quizlet?
The actual structure that serves as the heart's primary pacemaker is called the sinoatrial node (SA node). As described above, the SA node is a little bundle of cells located in the wall of the right atrium, the small upper chamber on the right side of the heart.
What is the role of pacemaker cells quizlet?
Pacemaker cells, sets the pace for contractions of the heart because of the conductivity.
Which location of the heart is normally the pacemaker site and usually has the fastest firing rate quizlet?
Primary pacemaker-Sinoatrial (SA) node. The sinoatrial (SA) node normally depolarizes faster than any other part of the heart's conduction system. As a result, the SA node is normally the heart's primary pacemaker. Sinus rhythm is the name given to a normal heart rhythm.
What is the normal pacemaker of the heart quizlet?
SA node (sinoatrial node) - known as the heart's natural pacemaker The impulse starts in a small bundle of specialized cells located in the right atrium, called the SA node.
What is the pacemaker that sets the rate of the heart beat quizlet?
The pacemaker cells set the pace (or rate) of the heartbeat. The actual structure that serves as the heart's primary pacemaker is called the sinoatrial node (SA node).
What are the pacemaker cells of the heart and their normal heart rates quizlet?
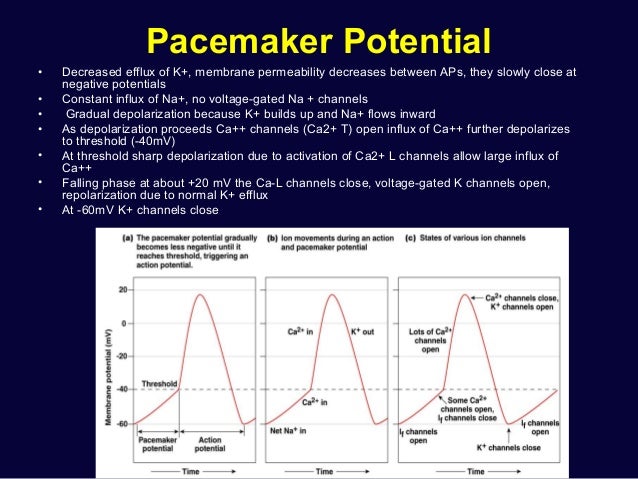
The SA node is the normal pacemaker of the heart. The pacemaker cells of the SA node exhibit progressive depolarization during phase 4 of the action potential, generating the "pacemaker potential." Cells in SA node are intrinsically leaky to Na+, generating the normal cardiac rhythm of 60-100 beats per minute.
What is the SA node?
It replaces the heart's defective natural pacemaker functions. The sinoatrial (SA) node or sinus node is the heart's natural pacemaker. It's a small mass of specialized cells in the top of the right atrium (upper chamber of the heart). It produces the electrical impulses that cause your heart to beat. A chamber of the heart contracts ...
How do pacemakers work?
What is a pacemaker? 1 The generator is a small battery-powered unit. 2 It produces the electrical impulses that stimulate your heart to beat. 3 The generator may be implanted under your skin through a small incision. 4 The generator is connected to your heart through tiny wires that are implanted at the same time. 5 The impulses flow through these leads to your heart and are timed to flow at regular intervals just as impulses from your heart's natural pacemaker would. 6 Some pacemakers are external and temporary, not surgically implanted.
What is the process of the heart contracting?
It produces the electrical impulses that cause your heart to beat. A chamber of the heart contracts when an electrical impulse or signal moves across it. For the heart to beat properly, the signal must travel down a specific path to reach the ventricles (the heart's lower chambers).
Is a pacemaker surgically implanted?
The impulses flow through these leads to your heart and are timed to flow at regular intervals just as impulses from your heart's natural pacemaker would. Some pacemakers are external and temporary, not surgically implanted. View an animation of a pacemaker.