Proper Thoracic Extension is important not only for proper posture, but also to prevent neck, shoulder, upper back, lower back and even hip pain.
What is thoracic extension of the spine?
When the term “extension” is used about the thoracic spine, the meaning is a reduction in relative flexion. While there may not be true extension of the thoracic spine, this reduction in flexion is important for movement of the scapula and arm.
Why does the thoracic spine need to be moved?
The thoracic spine is built for rotation, flexion, and extension. It is highly mobile – or, rather, it has the potential for lots of mobility. Because of its mobility, the thoracic spine must be used, must be moved. But it has to be known.
Do thoracic extension exercises work your back?
Many of the exercises you need to include to improve your Thoracic Extension don’t actualy work on your back or spine. Actually a huge reason you may lack Thoracic Extension is because your chest is tight. So these moves will address many of the areas of tightness that perpetuate your forward flexion.
Why is thoracic rotation important?
Rotation through the thoracic spine facilitates both stability of the cervical spine and cranium along with optimal function of the lumbar spine. Since thoracic rotation is so important, a rotation deficit may contribute to a lack of extension and impede shoulder movement during functional actives such as running, throwing, and swimming.
Why is thoracic mobility important?
How to increase thoracic mobility?
How many vertebrae are in the thoracic spine?
Why does my lower back arch backwards?

What is thoracic extension good for?
A thoracic extension exercise is a correctional exercise that improves the thoracic extensor muscle strength and chest muscle stretch to maintain an optimal postural kinetic chain [16,17]. Thoracic correction exercise also improves kyphosis, pain, and scapular forward distance [14].
Why is the thoracic important?
The thoracic spine is the middle portion of the spinal column that connects the neck to the lower back region. It consists of 12 separate segments that serve as connections for the ribs, which protect many vital organs including the heart and lungs.
How important is thoracic rotation?
The thoracic spine also plays an important role in assisting with the movement of the neck. The thoracic spine contributes 33% of neck flexion movements and 21% of neck rotation. Therefore a lack of movement in the thoracic spine can contribute to the development of pain in the neck.
What muscles do thoracic extensions work?
Thoracic extensions target your upper and mid-back, both of which are problem areas for many people. If you feel tight in those areas, try adding T-spine extensions to your stretching routine to improve mobility.
How do you increase thoracic extension?
0:082:50Exercises to increase thoracic extension and rotation - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipInside line for thoracic extension. And rotation that you can do we use foam rolls to support theMoreInside line for thoracic extension. And rotation that you can do we use foam rolls to support the head and neck and to lock out the lower lumbar spine.
How do you increase your thoracic mobility?
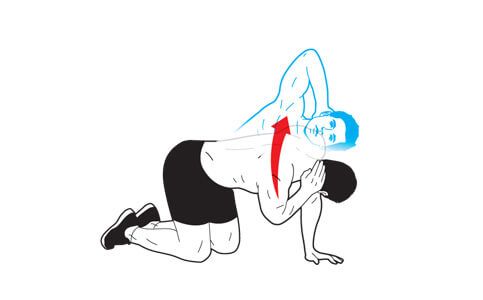
Below are a number of exercises that have proven effective in increasing thoracic extension and rotation.Thoracic Extension w/ Roller & Bar. This is a great drill to improve thoracic extension. ... Cat-Camel Drill. ... Deep Squat + Thoracic Rotation. ... Spiderman w/ Thoracic Rotation. ... Side-Lying Thoracic Windmill.
Why is my thoracic spine so tight?
The causes of thoracic spine syndrome can vary significantly. The most common reason is poor posture and not moving enough. Both of these are often caused by prolonged sitting at your desk with your back rounded, especially if your arms are stretched forward for things like computer work.
Why Is spinal flexibility important?
The spinal cord is a column of nerves that connects our brain with the rest of the body, allowing control our movement and bodily function. This is why keeping spine flexible is vital for healthy and active life and also important for optimum nervous system function.
Why is it important to move your spine?
The facts are simple; the more you purposely move your spine, the better range of motion you will have and the less chance you'll have of developing back pain. Ensuring your spine gets the movement it needs will enable it to get the nutrients it requires to stay healthy.
What does thoracic extension mean?
Thoracic extension is the ability for the t-spine to move from its normally kyphotic or forward rounded position to a flat or event arched back position. Lack of thoracic extension is one of the most common mobility restrictions we see.
What limits thoracic extension?
The positioning of the ribs and spinous processes greatly limits flexion and extension of the thoracic vertebrae.
How do thoracic muscles work?
2:524:384 Exercises to IMPROVE Your Stiff Mid-Back (Thoracic Spine Mobility)YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipHere's a thoracic bridge where mike is bridging up but the key here is to rotate his chest towardsMoreHere's a thoracic bridge where mike is bridging up but the key here is to rotate his chest towards the floor. So he's rotating towards the right if he keeps his chest open this becomes more of a peck
What organs does the thoracic cage protect?
The rib cage surrounds the lungs and the heart, serving as an important means of bony protection for these vital organs.In total, the rib cage consists of the 12 thoracic vertebrae and the 24 ribs, in addition to the sternum.
What is the clinical significance of the thoracic organs being in separate compartments?
It is very important to separate "the lung" into those functionally different subunits to understand the development and the course of immune responses and inflammatory diseases within this organ.
What is the thoracic?
Your thoracic spine is the middle section of your spine. It starts at the base of your neck and ends at the bottom of your ribs. It consists of 12 vertebrae. Your thoracic spine is especially rigid and stable, making it the least common area of injury along your spine.
What does thoracic mean?
Definition of thoracic : of, relating to, located within, or involving the thorax.
Why Should You Care About Thoracic Spine Mobility?
What Is the Thoracic Spine? From its name, you probably know that your thoracic spine is on located in your (drum roll please)... spine. Your spinal column has three sections (cervical, thoracic, and lumbar), and the thoracic spine is the middle section located in your upper back, starting at the base of the neck and extending down to the abdomen, explains Nichole Tipps, a sports medicine ...
Why is a thoracic extension important?
Proper Thoracic Extension is important not only for proper posture, but also to prevent neck, shoulder, upper back, lower back and even hip pain. If you don’t have proper Thoracic Extension, your body is going to take the path of least resistance ...
How to improve thoracic extension?
The first step to improving your Thoracic mobility and extension is to roll out all the muscles that get tight from sitting in flexion for most of the day. That means you really need to focus on rolling out and loosening up your chest and lats.
What stretch to do for a thoracic extension?
Half Wall Hang – A great stretch for your lats that will also work on your Thoracic Extension is the Half Wall Hang. With this stretch, you’ve got to make sure to focus on extending your upper and mid back as you relax over. It is very easy with this stretch to simply extend your low back instead of your Thoracic spine, especially if your Thoracic Extension is limited, so really focus on keeping your abs engaged as you extend.
What is the best way to stretch your bicep?
These stretches will loosen tight muscles caused by sitting in flexion for most of the day and will even start to put your spine through extension. Standing Chest Stretch – The Standing Chest Stretch is a great way to stretch your chest, shoulders and bicep.
What happens if you don't have a thoracic extension?
If you don’t have proper Thoracic Extension, your body is going to take the path of least resistance and seek out extra extension from other areas – areas that may not have the ability to provide the extension needed and therefore become overworked and injured.
Why is it important to do extension exercises?
This causes poor posture and often poor extension, which can lead to improper movement patterns, compensations and eventually pain and injury. That is why it is important to include Extension Exercises in our workouts. These exercises open us up after sitting in flexion all day. And one of the more important areas to include Extension Exercises ...
What exercises can help with back extension?
No one move alone will solve your problem. You must included Foam Rolling, Stretching, Activation and Strength Training in your workout routine.
Is Thoracic Spine Extension Work Necessary? – Part 1
Today’s guest post comes from my friend and colleague, physical therapist Eric Schoenberg. Eric is an integral part of our Elite Baseball Mentorships, and here, he kicks off a three-part series that I think you'll find very educational – even if it is a bit "geeky" along the way.
Not every individual – especially in baseball populations – needs thoracic extension and rotation mobility drills!
In fact, to take it a step further, I would argue that in some cases, performing these types of exercises will actually make the athlete worse.
How to treat a stiff thoracic spine?
Treatment for a stiff thoracic spine can include joint mobilisations, soft tissue massage, postural exercises, strength exercises and self stretching. Self stretching is very important and something that should be included in a regular stretching program for all athletes but more so for people at risk of problems such as desk workers, cyclists, swimmers, kaykers and other sports that require good thoracic mobility and posture.
Why does the lower back tilt in the reverse?
Below the thoracic spine the pelvis often ends up in an anterior (forwards) tilt and the lower back more rounded in the reverse direction (lordotic) to compensate for the thoracic spine posture. This is associated with lower back pain especially in people with previous lumbar disc injuries.
What changes the lower limb mechanics?
Changes to lower limb mechanics due to thoracic spine stiffness can be more subtle than seen in upper limb. An increased thoracic curve leading to increased lumbar spine lordosis (arch) and an anterior pelvic tilt changes the forces on the lower limb which can have particularly detrimental effects in any sports that involve running.
What is a physio assessment?
A physio is trained to assess all vertebra movements and posture. A thorough assessment should involve thoracic spine movements such as extensions, rotation, side bending and rib expansion. Other things may include shoulder movements such as streamline in swimmers, neck movements and lumbar spine movements as well. Sitting and standing posture will also be assessed. If there are specific sports positions that require assessing such as time trial position or boat position this should be assessed as well.
Why is it important to develop thoracic mobility?
In sum, it is important to develop thoracic mobility in a precise way that allows healthy spinal architecture and movement and not in a wanton way that threatens your skeletal integrity or scaffolding. Loosening up the thoracic spine and then using that extra mobility to round or distort the spine further while sitting or standing is in some ways worse than being inflexible. It is therefore crucial to be conscious of posture as well, so that your whole spine is well-aligned throughout your day, and any extra mobility you create in your thoracic spine works to your advantage and towards making you straighter and taller.
Why is the lumbar spine important?
The lumbar spine is built for stability. It’s supposed to support the weight of the body (plus any added weights) and resist excessive rotation and twisting. It remains stable and acts as a conduit for power generated by the hips and fed to the mobile thoracic spine. It is not meant to twist and bend and do all sorts of the acts that active, thoracically-immobile folks expect it to. It can move, obviously, but it’s not meant to be wildly mobile. It’s meant to be solid, reliable.
Why does my upper back bow?
Lack of kyphosis – The bowing of the upper back, endemic in offices across the country, is almost entirely due to poor thoracic mobility. Improve your mobility, try to cut back on all the sitting, and your posture will improve and your pain will go away.
Is thoracic immobility bad?
Because thoracic spine immobility is so commonplace, people don’t notice that anything is wrong. Nearly everyone slumps when they sit, and very few people perform the type of exercises that require full range of motion in the spine. You can get away with poor mobility if all you’re doing is isolation exercises on machines, just as millions of people “get away with” the SAD. How many times have you told people who balk at your eating habits to just “try it for thirty days and see how you feel”? If you’re (they’re) lucky, they’ll ditch the sugar and the grains and notice an incredible difference. But you’ll never know the difference until you give the other side a fair shot. You’ll never know how beneficial a mobile thoracic spine can be without developing its mobility. C’mon – you trusted me on grains, sugars, and vegetable oils, didn’t you?
Can you have poor thoracic mobility?
If you answered “yes” to any of those (and most people will answer yes to at least one), you may have poor thoracic spine mobility. Even if you don’t notice any of the symptoms leaping out at you, it never hurts to get more mobility, especially in the thoracic spine. And establishing good habits by actively maintaining and training mobility, as opposed to being content with what you have (even if it’s not optimum), is always a good move. Scoff at the prospect of thoracic spine mobility all you want; you still gotta have it.
Is a thoracic spine immobile?
You’ll find that an immobile thoracic spine isn’t just bad for the vertebrae themselves. It’s bad for your lower back and your shoulders, too. In fact, you’ll rarely feel actual pain along the twelve vertebrae that comprise your thoracic spine. Instead, your lower back will take over work for which it’s really not designed, getting chronic pain for its troubles, and your scapula (shoulder blades) will compensate by moving away from the spine, making overhead shoulder work difficult, dangerous, and painful, and a rotator cuff injury nearly inevitable. Everything in the body is linked, remember, and you can’t remove a major player from the equation without seriously affecting the balance.
What is the function of the thoracic spine?
When the thoracic spine is operating optimally, it allows you to move in basically all directions. "It's built for mobility and movement, bending and twisting. It's designed for flexion, extension, and rotation," explains Medhat Mikhael, M.D., a pain management specialist for Spine Health Center at Memorial Care Orange Coast Medical Center in Fountain Valley, California. It's what allows you to safely execute basically all the movements you use in everyday activities.
What Is the Thoracic Spine?
Your spinal column has three sections (cervical, thoracic, and lumbar), and the thoracic spine is the middle section located in your upper back, starting at the base of the neck and extending down to the abdomen, explains Nichole Tipps, a sports medicine-certified personal trainer and lead trainer with V Shred.
How to do a sit up on the thoracic spine?
For something easier to incorporate to your day-to-day, try this thoracic spine chair exercise: Sit on your chair with a flat back, engaged core, and put your hands behind your head like you're doing a sit-up, explains Dr. Mikhael. Then twist to side so right elbow lands on left armrest; right elbow pointing to the sky.
What are the muscles that help you stand up?
The muscles attached to the vertebrae (via ligaments) in that region are called the 'spinalis' and the 'longissimus.' These are the primary muscles involved in helping you stand up straight, maintain proper posture when you're sitting, and—most importantly—protect your spinal column, explains Allen Conrad, D.C., C.S.C.S. a doctor of chiropractic at the Montgomery County Chiropractic Center in North Wales, PA.
Where is the thoracic spine located?
Your spinal column has three sections (cervical, thoracic, and lumbar), and the thoracic spine is the middle section located in your upper back, starting at the base of the neck and extending down to the abdomen, explains Nichole Tipps, a sports medicine-certified personal trainer and lead trainer with V Shred.
Does thoracic mobility improve lung volume?
Need even more convincing to improve your thoracic spine mobility? Well, "when you have good mobility in the thoracic spine you usually have more lung volume and are better able to open up your chest and breathe," says according to Dr. Mikhael. Yep, thoracic mobility boosters are also your quick fix to improved cardiovascular capacity.
Does sedentary lifestyle affect thoracic mobility?
Trouble is , today's sedentary lifestyle lends itself to reduced thoracic spine mobility. "Like most things in the body, it's an 'if you don't use it you lose it' scenario," explains Dr. Mikhael. "A lack of thoracic spine mobility means that the lumbar spine, pelvis, shoulders and surrounding muscles all compensate to allow you to move how you want ...
How to do thoracic extension?
Try to emphasize thoracic flexion over the stability ball and then extend into a neutral position. Move slowly and don’t hyperextend the spine. Perform 12-15 reps.
What is the Thoracic Spine?
The thoracic spine is the twelve vertebrae of the middle segment of the vertebral column. While all vertebrae have rib components, they are usually small and make up the transverse processes in regions other than the thorax (Drake, Vogl & Mitchell, 2015).
How many thoracic vertebrae rotate?
In many cases, the last two to three thoracic vertebrae begin to demonstrate movement characteristics of the lumbar spine. On average, each thoracic vertebra can rotate approximately 3 °. Therefore, the entire thoracic spine should demonstrate between 30 -35 ° of total rotation to each side (Neumann, 2010).
How to get the thoracic spine to flex?
Move slowly and keep the spine neutral. Perform 12-15 repetitions. Overhead squat with tubing —this exercise will attempt to pull the arms and shoulders into extension and the thoracic spine into flexion.
What does "extension" mean in a scapula?
When the term “extension” is used about the thoracic spine, the meaning is a reduction in relative flexion. While there may not be true extension of the thoracic spine, this reduction in flexion is important for movement of the scapula and arm.
What is the articulation of the ribs?
In the thorax, the ribs articulate with each vertebra, at the vertebral bodies and transverse process es. A typical thoracic vertebra has two partial surfaces on each side of the vertebral body for articulation with the head of its rib and the head of the rib below. Each transverse process also has a smooth, flat surface for articulation with the connection of its rib.
Which vertebrae have the same characteristics as the thoracic vertebrae?
Each transverse process also has a smooth, flat surface for articulation with the connection of its rib. Thoracic vertebrae 2 -9 share the same characteristics whereas, thoracic vertebra 1 and 10 -12 are different. The first thoracic vertebrae have the body that resembles a cervical vertebra.
Why is thoracic mobility important?
Thoracic mobility is important because neglecting it could lead to poor posture and could predispose you to chronic neck, shoulder and back pain. Increasing your thoracic mobility with mobility tools, self care exercises and manual therapy will help reverse the process and prevent injuries from occurring.
How to increase thoracic mobility?
Being consistent with the self care exercises and practicing proper posture will also contribute to increasing your thoracic mobility.
How many vertebrae are in the thoracic spine?
The thoracic spine (middle back) is composed of 12 vertebrae and connects the cervical spine (neck) with the lumbar spine (lower back).
Why does my lower back arch backwards?
Your lower back has to “arch” backwards in order to keep your center of gravity. This means that it’s a possibility for neck and lower back pain to stem from poor posture (in this case, hunched forward) from the thoracic spine.