What is ultrafiltration’s role in water treatment?
What Is Ultrafiltration’s Role in Water Treatment? Ultrafiltration removes particulates and macromolecules, an important role in the production of potable water. Ultrafiltration (UF) is a water purification process in which water is forced through a semipermeable membrane.
What is the application of ultrafiltration in dairy industry?
In the dairy industry, ultrafiltration is used for a wide range of applications such as protein standardization of cheese milk, fresh cheese production, protein concentration, and decalcification of permeates, as well as lactose reduction of milk.
How is the rate of ultrafiltration determined?
The ultrafiltration rate, as well as length of dialysis treatment time, control the amount of fluid to be removed. Your dialysis staff will set the ultrafiltration rate of your treatment based on your fluid weight gain since your last treatment. The goal is to get to your target or “dry weight”.
What are the clinical benefits of ultrafiltration profiling?
The clinical benefits of ultrafiltration profiling are under debate; in the absence of clear evidence-based recommendations, we suggest that ultrafiltration profiling be considered in patients prone to intradialytic complications, such as hypotensive episodes. John Feehally DM, FRCP, in Comprehensive Clinical Nephrology, 2019

Why do we need ultrafiltration?
Ultrafiltration is the removal of fluid from a patient and is one of the functions of the kidneys that dialysis treatment replaces. Ultrafiltration occurs when fluid passes across a semipermeable membrane (a membrane that allows some substances to pass through but not others) due to a driving pressure.
What is the role of UF in water purification?
It eradicates suspended solids, larger particles, and molecules from water through a hollow membrane. UF water purifiers can kill and eliminate bacteria and microorganisms but cannot get rid of dissolved solids. Unlike the RO water purifier, it cannot convert hard water to soft water.
What is ultrafiltration explain in short?
Definition of ultrafiltration : filtration through a medium (such as a semipermeable capillary wall) which allows small molecules (as of water) to pass but holds back larger ones (as of protein)
What does ultrafiltration not remove?
However, this means that an ultrafiltration system does not remove salts, fluoride, or TDS dissolved in water. An ultrafiltration system also operates on low water pressure, but a reverse osmosis system needs a booster pump to increase water flow.
What is the principle of ultrafiltration?
Ultrafiltration (UF) is a variety of membrane filtration in which hydrostatic pressure forces a liquid against a semi permeable membrane. Suspended solids and solutes of high molecular weight are retained, while water and low molecular weight solutes pass through the membrane.
What can ultrafiltration remove?
Ultrafiltration removes bacteria, protozoa and some viruses from the water. Nanofiltration removes these microbes, as well as most natural organic matter and some natural minerals, especially divalent ions which cause hard water. Nanofiltration, however, does not remove dissolved compounds.
What is ultrafiltration give an example?
Ultrafiltration is a process in the kidney by which urea, salt, water and glucose etc. is extracted from the blood. When blood passes through the top of the nephron, it enters a structure called the glomerulus which is a network of tiny capillaries.
Where does ultrafiltration occur?
Bowman's capsuleIn renal physiology, ultrafiltration occurs at the barrier between the blood and the filtrate in the glomerular capsule (Bowman's capsule) in the kidneys.
What is the other name for ultrafiltration?
In this page you can discover 5 synonyms, antonyms, idiomatic expressions, and related words for ultrafiltration, like: fractionation, flocculation, adsorbent, solubilization and desorption.
What is a major factor affecting ultrafiltration?
Factors Affecting the Performance of Ultrafiltration Flow velocity if especially critical for liquids containing emulsions or suspensions. Higher flow also means higher energy consumption and larger pumps. Increasing the flow velocity also reduces the fouling of the membrane surface.
Is UF water good for health?
UF water purifier also terminates all bacteria, viruses, and germs present in the water. A UF water purifier not only kills the microbes but also flushes out their dead body through the drain. Thus making sure to free your drinking water from microbial contamination.
Does ultrafiltration remove potassium?
As the patient's blood volume is reduced by ultrafiltration, the potassium level is not affected because the ultrafiltrate potassium levels will always be in equal concentration to the plasma.
What does a UF membrane remove?
Ultrafiltration membrane filtration (UF) is a low pressure membrane process for water treatment that is designed to remove turbidity causing particles including those comprised of suspended solids, bacteria, colloidal matter and proteins.
Does UF purifier waste water?
The UltraGuard ultrafiltration (UF) membrane cartridge delivers purified water with 100% efficiency while providing protection against bacteria, cysts, viruses and turbidity. Unlike reverse osmosis (RO) membranes, the UF membrane does not produce wastewater, nor does it require electricity or additional components.
Does UF Water Purifier reduce TDS?
It cannot remove the dissolved solids or reduce the TDS level. So, UF purifiers are not suitable for the purification of high TDS water or hard water. As the name suggests, Ultraviolet or UV purification uses ultraviolet rays for the purification of water.
Does UF filter chlorine?
Ultrafiltration only filters out solid particulate matter, but it does so on a microscopic level. Because it has such a fine micron reduction capacity, ultrafiltration will filter out the vast majority of contaminants like sediment, chlorine, and cysts.
What is the purpose of ultrafiltration?
Ultrafiltration processes have proved successful for the treatment of effluents, the treatment of black liquor, bleaching effluents and paper machine wash waters.
Who is the author of Ultrafiltration and Microfiltration Handbook?
Source: Cheryan, Copyright® 1998 from Ultrafiltration and Microfiltration Handbook by M. Cheryan. Reproduced by permission of Routledge/Taylor & Francis Group, LLC.
How are MF membranes prepared?
MF membranes are prepared by sintering, track-etching, stretching or by phase inversion. They are usually symmetric unlike UF membranes. MF membranes with well-defined pores are now manufactured in inorganic materials such as alumina and zirconia. α-Alumina-based ceramic membranes are available in multi-tube sheet and monolith honeycomb modules [ 17, 18, 26 ]. Ceramic MF membrane modules cost three to four times the polymer membrane modules. Some of this high initial cost is off-set by the lower operating costs because of much longer life of ceramic membranes. Characteristics of some commercial ceramic membranes are given in Table 6.13.
What is MF in filtration?
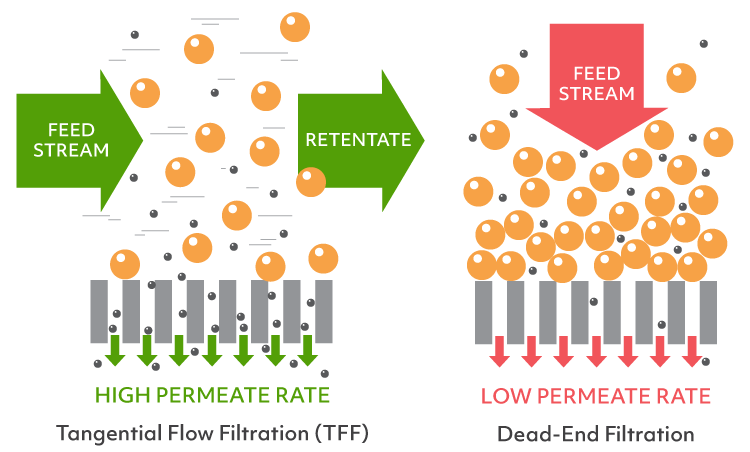
MF is the oldest membrane process ( Table 1.2) and historically operated in dead-end mode in small volume applications, which remains a very important application ( Figure 1.4 ). In dead-end filtration the feed solution flows perpendicular to the membrane surface. Unlike cross-flow (tangential flow) filtration, there is no reject stream, only a feed stream and a permeate stream, as shown in Figure 1.12. The permeate drags all the solids in the feed solution to the membrane surface resulting in adsorption and deposition of solutes on the membrane surface. The pore size of MF membrane is in the range of 0.05–10 μm ( Table 1.3 ). In cross-flow membrane processes (e.g., RO, NF, conventional UF), the feed solution flows tangentially across the membrane surface. The cross-flow or tangential velocity continuously removes particles from the membrane surface by shear forces especially when operating in a turbulent regime. The net effect is reduced cake build-up and less fouling [ 18, 31 ].
What is UF membrane?
UF membranes have been widely tested in removal of virus and bacteria from water. UF membranes made of polyethersulfone, cellulose, and polyvinylidine have been found quite effective in separation of bacteria, bacteriophages and viruses such as poliovirus types 1 and 3, Vesicular stomatitis virus, and leukemia virus.
How does reverse osmosis work?
By applying pressure to the more concentrated solution, the flow direction can be reversed so that water passes through the membrane, hence the name, reverse osmosis. The pressures required for this process are typically 2,000–7,000 kPa (300–1,000lb/in. 2 ).
When were UF membranes used?
UF membranes have been used industrially in oily wastewater applications since the early 1980's. These early systems successfully concentrated oily wastewaters to reduce the volume of wastewater to be disposed of off-site and to produce an effluent suitable for sewer discharge.
Why is ultrafiltration important?
Ultrafiltration with semipermeable membranes can play an important role in water purification because of its compactness and efficiency. Ultrafiltration (UF) is a water purification process in which water is forced through a semipermeable membrane.
When was ultrafiltration first used?
UF was first described at the end of the 19th century, but the practical start of ultrafiltration as a separation process came in 1963, coming on the heels of the discovery of the asymmetric cellulose acetate reverse osmosis membrane in the 1950s, and MIT’s discovery of polyelectrolyte complex hydrogels at the beginning of the 1960s.
Why do ultrafiltration membranes need cleaning?
The membranes used in ultrafiltration require maintenance cleaning to prevent fouling with solids, scaling, and microbiological agents such as microbes and algae. Separated contaminants condensed in the UF retentate must be disposed of.
What is the pore size of an ultrafiltration membrane?
The pore size of ultrafiltration membranes ranges from 0.1 to 0.01 microns , but “molecular weight cut-off” (MWCO) is now one of the best ways to describe UF membranes. MWCO is the molecular weight at which 90% of a macromolecular solute does not pass through the membrane. UF’s range of filtration lies between microfiltration and nanofiltration.
How big is the ultrafiltration market?
In 2019, the global ultrafiltration membrane market size was $5.3 billion. While the pandemic put a damper on investment in 2020, the market is projected to recover in 2021 and grow substantially moving forward, with efficiency advancements and increasing water safety regulations expected to drive adoption.
Which side of the membrane does suspended solids filter?
Suspended solids and high-molecular-weight solutes remain on one side of the membrane, the retentate side, while water and low-molecular-weight solutes filter through the membrane to the permeate side. UF can remove most organic molecules and viruses, as well as a range of salts.
What is UF pretreatment?
UF pretreatment can extend the life of reverse-osmosis membranes in the treatment of high-silt density index (SDI) waters. They require lower investment, deliver reduced operating costs, use no coagulants, and require little chemical use.
Why is ultrafiltration important?
Ultrafiltration is an important parameter for assessing adequacy of dialysis, and ultrafiltration has been found to be associated with survival in anuric APD patients;
How does ultrafiltration work?
Ultrafiltration removes plasma water from whole blood across a semipermeable membrane in response to a pressure gradient. Different from loop diuretics, which produce hypotonic urine, the fluid removed by ultrafiltration is isotonic with plasma. Thus a relatively larger amount of sodium is removed with ultrafiltration, compared with loop diuretics.78 Despite initial favorable results, the largest trial to date, the Cardio-Renal Rescue Study in Acute Decompensated Heart Failure (CARRESS-HF), failed to show efficacy over an intense pharmacological regimen. 71 In this trial, 188 patients with AHF and worsening renal function were randomized to ultrafiltration, at a fixed rate of 200 mL/hr, versus a stepped care regimen of pharmacologic therapy. The reduction in body weight was similar with ultrafiltration, compared with pharmacological treatment, though with higher serum creatinine values at 96 hours and with more side effects. 71 The interpretation of the results is, however, complicated by the relatively high crossover rate. In a subsequent per protocol analysis, ultrafiltration was associated with greater fluid loss compared with pharmacologic therapy. 79 Another trial comparing ultrafiltration with standard therapy was prematurely stopped for slow enrollment. 80 Another trial, the Peripheral Ultrafiltration for the Relief from Congestion in Heart Failure (PURE-HF), is ongoing ( ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT03161158 ). In the current guidelines, ultrafiltration is indicated when diuretic strategies are unsuccessful. 13,28
What is ultrafiltration in a CRRT filter?
Ultrafiltration describes the transport of plasma water (solvent) through a semipermeable membrane driven by a pressure gradient between blood and dialysate/ultrafiltrate compartments. (The non-blood chamber of a CRRT filter typically is designated as the effluent compartment, and the rate at which fluid exits the filter from this space is equal to the sum of the dialysate flow rate and/or replacement fluid rate along with the patient's net fluid removal rate.) Quantitatively, ultrafiltration is defined by the ultrafiltration rate:
How does ultrafiltration help with heart failure?
Ultrafiltration removes excess plasma volume without causing a significant change in electrolytes. In patients with chronic heart failure and diuretic resistance, ultrafiltration improves symptoms, neurohormones, and hemodynamics without hypotension.102 Reductions in peripheral and pulmonary edema, and a subsequent increase in diuretic efficacy have been reported. Recent pilot studies in acute decompensated heart failure suggest that early ultrafiltration is associated with greater fluid removal and symptom relief than medical therapy alone, 103 and may decrease length of stay and readmission rates. 104 The effects of ultrafiltration on renal function and outcomes were tested in a large, multicenter randomized trial (UNLOAD). Preliminary data from UNLOAD suggest that ultrafiltration removes more fluid and reduces readmission rates compared with standard diuretic therapy in patients with acute decompensated heart failure. 104a Additional data on safety and cost effectiveness are needed.
What is ultrafiltration in pediatrics?
Ultrafiltration is a method of removal of fluid and high-molecular-weight solutes and inflammatory mediators across a semipermeable membrane after or during CPB. There are numerous types of ultrafiltration, but the most common in pediatrics is modified ultrafiltration.
Is ultrafiltration a dialysis?
Ultrafiltration and other forms of dialysis may be useful for patients with refractory heart failure, and they have been advocated by some experts for even more widespread use. In contrast to conventional hemodialysis, ultrafiltration removes water, sodium, and non-protein-bound small and medium-sized molecular solutes. One system makes it possible to perform this with peripheral catheters.
Can you change the ultrafiltration rate during dialysis?
The ultrafiltration rate is usually kept constant but can be changed during the dialysis session in a preprogrammed manner (ultrafiltration profiling). It may be advantageous to remove a large proportion (e.g., two thirds) of the ultrafiltration volume in the first half of the HD session. Because of a high initial plasma refilling rate, severely overhydrated patients may tolerate a higher ultrafiltration rate in the early stages, and dry weight may be reached more easily. In some machines, predefined ultrafiltration profiles are incorporated, for example, triangular ultrafiltration ramps and exponential profiles; in most instances, the ultrafiltration rate is initially high and then turned down. The clinical benefits of ultrafiltration profiling are under debate; in the absence of clear evidence-based recommendations, we suggest that ultrafiltration profiling be considered in patients prone to intradialytic complications, such as hypotensive episodes.
Why use an ultrafiltration system?
Whether for potable drinking water or the treatment of waste water, ultrafiltration systems provide numerous benefits due in part to the simplicity behind the physics and chemistry of the operations, but also in the low energy costs that are associated with operating a UF system. While there are numerous other types of filtration such as nanofiltration and microfiltration, ultrafiltration systems usually are compared to reverse osmosis, both processes for purifying water. Of course, both utilize different methods, have much different results, and seek to gain vastly different end products.
What are the advantages of ultrafiltration?
Another one of the advantages of ultrafiltration systems involves its ability to remove harmful colloids, bacterial species, bacterial cysts, and some viruses and parasites such as the cryptosporidium and giardia species from the water.
What are the chemicals used in water purification?
Some of the types of chemical agents used in water purification include antifoams, biocides, coagulants, disinfectants, flocculants, and oxidizers, just to name a few. While effective in their function, residues and other harmful byproducts are produced through the use of each of these.
What happens when minerals are removed from water?
When such essential minerals are removed from the water sources, the pH of the water drastically decreases to levels that can easily cause erosion and damage to pipes, potentially exacerbating already problems that might be apparent within piping systems.
What are the benefits of reverse osmosis?
One additional and surprising advantage of ultrafiltration lies in what is left over from filtrate. Reverse osmosis removes important and healthy minerals such as calcium and magnesium due to the greatly smaller pore diameter. When such essential minerals are removed from the water sources, the pH of the water drastically decreases to levels that can easily cause erosion and damage to pipes, potentially exacerbating already problems that might be apparent within piping systems .
Why is water filtration important?
Water filtration is very important to the world as a whole, as we need it in everyday life for drinking and cleanliness . Ultrafiltration provides important advantages over other methods for helping to clean and purify water. Depending on the application, ultrafiltration might require supplemental processes, as is the case with potable drinking water, but can stand alone for many other purposes. Through the use of ultrafiltration systems, harmful agents can be removed, energy costs can significantly be decreased, piping infrastructure can remain intact, and chemical pollution will never be an issue. There are numerous other ultrafiltration systems benefits to the use of UF systems and those are surely to increase as demand for cost effective measures and green campaigns ramp up in the coming years.
Is ultrafiltration the same as reverse osmosis?
While there are numerous other types of filtration such as nanofiltration and microfiltration, ultrafiltration systems usually are compared to reverse osmosis, both processes for purifying water. Of course, both utilize different methods, have much different results, and seek to gain vastly different end products.
What is ultrafiltration in dairy?
In the dairy industry, ultrafiltration is used for a wide range of applications such as protein standardization of cheese milk, fresh cheese production, protein concentration, and decalcification of permeates, as well as lactose reduction of milk. Specifically, UF allows the smaller lactose, water, mineral, and vitamin molecules to pass through ...
Why is UF technology important?
UF technology also will play an important role during the current COVID-19 pandemic, as it is effective for virus removal in the production of therapeutic proteins and vaccines, as well as for antibiotics recovery.
How to reduce fouling in UF?
They are more focused on the physical and chemical methods that are used at various stages of the UF system. During pretreatment, prefiltration can be used as a physical method to reduce fouling; precipitation, coagulation/flocculation, disinfectants, anti-scalants, and absorption can also be used as methods to reduce fouling. During design, vibrating or rotating membranes or turbulence promotors can be added to reduce fouling physically. Pulsed/reverse-flow and electric fields may also be employed. Chemical methods to reduce fouling in UF include membrane surface modification and the selection of specific membrane material. During operation, reducing trans-membrane pressure, maintaining high cross-flow, and periodic hydraulic or mechanical cleaning reduce fouling, as does selection of cleaning chemicals and frequency of cleaning.
Why should pore diameters of UF membranes be at least one-half that of the smallest solute?
Because of pore size distribution, the pore diameters of UF membranes should be at least one-half that of the smallest solute to be removed. There is a correlation between pore size and water flux through a UF membrane, but direct proportionality between flux and applied pressure is only true for water.
What are the three processes used in dairy filtration?
Within the dairy industry, three membrane filtration processes are used in addition to UF: microfiltration (MF), nanofiltration (NF), and reverse osmosis (RO). Figure 1 illustrates which milk and whey components can be concentrated by means of each process, depending on membrane density. RO is the tightest possible membrane process in liquid separation. It concentrates the total solids, and only water can pass through the membrane; all dissolved and suspended material is rejected. NF separates a range of minerals from a liquid, allowing only the fluid and certain monovalent ions to pass through the membrane. UF membranes separate the feed (e.g., skim milk) into two streams, allowing water, dissolved salts, lactose, and acids to pass through the filter in either direction, while retaining (and thereby concentrating) proteins and fat. MF uses the most open type of membrane, which is used to separate bacteria, spores, and fat globules from the stream, and for fractionation of skim milk.
What are the applications of UF in food?
Food UF applications include concentration of proteins (enzymes, milk proteins, egg whites), starch, and pectin; clarification/stabilization of fruit juices and wine (removal of haze components); removal of cellular debris and bacteria from beer; removal of polysaccharides, proteins, and colloidal impurities in sugar refining; and sterile filtration of biologicals (removal of bacteria and viruses). Additional food applications of UF are detailed in Table 1.
What is UF in chemistry?
Ultrafiltration (UF) is a selective separation step used to both concentrate and purify components of medium to high molecular weight, such as plant and dairy proteins, carbohydrates, and enzymes.
