Why are covalent radii smaller than van der Waal radii?
Covalent Radii are smaller than Van Der Waal radii. Since Covalent forces are stronger than Van Der Waals forces, the atoms or molecules will be held relatively closer by Covalent forces than Van Der Waal forces. Thus, decreasing the separation and the radius itself.
Is van der Waals radius greater than metallic radius?
It was written that if any atom can possess all the three types of radius, then van der Waals radius will be greater than metallic radius. However from the above diagram, it appears that the van der Waals radius and metallic radius are equal.
What is the difference between Vander Wall radius and covalent radius?
Hint: Vander wall radius can be measured when there is no bonding between two atoms while covalent radius is measured when two atoms are bonded with each other by a covalent bond. The bonding between atoms in covalent bond is stronger as compared to Vander wall.
What is the difference between Van der Wal forces and radii?
Don't compare both the situations using above diagrams. The radii are calculated in two different situations. As in case of metallic bond, the atoms are bonded tightly so their shells can overlap, but in case of van der wal forces the bond is weak.

Why is the van der Waals radius larger than the covalent radius?
Thus when two atoms of the same element do not form any bond with each other but they are close enough to each other then we measure the distance between their nucleus which is known as Vander waal radius. Thus, we can say that van der Waals radius is greater than covalent radius for covalent compounds.
Why van der Waals radius is stronger than metallic and covalent radius?
So Metallic radii are smaller than the van der Waals' radii, since the bonding forces in the metallic crystal lattice are much stronger than the van der Waal's forces and Values of van der Waals' radii are larger than those of covalent radii because the van der Waals' forces are much weaker than the forces operating ...
What is the difference between covalent radius and van der Waals radius?
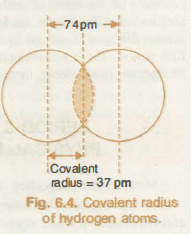
Covalent radius is half of the internuclear separation between the nuclei of two single-bonded atoms of the same species (homonuclear). While van der Waals radius is used to define half of the distance between the closest approach of two non-bonded atoms of a given element.
Why van der Waals radius of chlorine is greater than the covalent radius of chlorine?
The van der Waals radius of chlorine is defined as half that distance or 184 pm. The covalent radius of chlorine is half the distance (one-half AB or A′B′) between two chlorine nuclei in the same molecule. This is smaller than the van der Waals radius because of the covalent bond in each Cl2 molecule.
Why covalent radius is less than van der Waals radius?
The overlap that exists between the two electron clouds is what causes the covalent radius to be smaller than the van der Waals radius.
Is van der Waals radius or ionic radius greater?
Its van der Waals radius is 0.154 or 0.160 nm (depending on which source you look the value up in) - bigger than the fluoride ion. You can't really sensibly compare a van der Waals radius with the radius of a bonded atom or ion....vdW radius (nm)ionic radius of X- (nm)Br0.1850.196I0.1980.2202 more rows
Which is greater ionic radius or covalent radius?
Correct among the following van der Waal's radius is larger than covalent radius Covalent radius is larger than ionic radius Ionic radius is larger than metallic radius All of these.
What is the difference between covalent radius and metallic radius?
Covalent radii is defined as one-half the distance between the nuclei of two covalently bonded atoms of the same element in a molecule. Metallic radii : Metallic radii is defined as one - half the internuclear distance between the two adjacent metal ions in the metallic lattice .
Why does covalent radii decrease across a period?
Covalent radius mostly decreases as we move left to right across a period because the effective nuclear charge experienced by the electrons increases, and the electrons are pulled in tighter to the nucleus.
Why covalent radius is smaller than metallic radius?
In a metallic lattice, the valence electrons are mobile, therefore, they are only weakly attracted by the metal ions or kernels. In a covalent bond, a pair of electrons is strongly attracted by the nuclei of two atoms. Thus, a metallic radius is always longer than its covalent radius.
Why crystal radius is larger than covalent radius?
Expert-verified answer Covalent radius is smaller than crystal radius because the contraction of the nucleus makes the covalent radius smaller. For crystal radius, the metal ions are not overlapping are just touching the electrons. So the metallic radii are greater than the corresponding covalent radii.
What determines the van der Waals radius for an atom?
The Van der Waals radius is equal to one half the distance between two unbonded atoms when the electrostatic forces between them are balanced. In other words, it is half of the closest distance between two atoms that aren't bonded or within the same molecule.
Why the metallic radius is greater than covalent radius?
In a metallic lattice, the valence electrons are mobile, therefore, they are only weakly attracted by the metal ions or kernels. In a covalent bond, a pair of electrons is strongly attracted by the nuclei of two atoms. Thus, a metallic radius is always longer than its covalent radius.
What is the difference between covalent radius and metallic radius?
Covalent radii is defined as one-half the distance between the nuclei of two covalently bonded atoms of the same element in a molecule. Metallic radii : Metallic radii is defined as one - half the internuclear distance between the two adjacent metal ions in the metallic lattice .
Why crystal radius is larger than covalent radius?
Expert-verified answer Covalent radius is smaller than crystal radius because the contraction of the nucleus makes the covalent radius smaller. For crystal radius, the metal ions are not overlapping are just touching the electrons. So the metallic radii are greater than the corresponding covalent radii.
Which is greater ionic radius or covalent radius?
Correct among the following van der Waal's radius is larger than covalent radius Covalent radius is larger than ionic radius Ionic radius is larger than metallic radius All of these.
Which bond is stronger, covalent or van der Waals?
So covalent bond is stronger than van der waals force.
Which forces are stronger, van der Waals or covalent?
Since Covalent forces are stronger than Van Der Waals forces, the atoms or molecules will be held relatively closer by Covalent forces than Van Der Waal forces. Thus, decreasing the separation and the radius itself.
What is covalent bond?
Covalent bonds are the bonds between atoms created when the atoms share electrons. These bonds create such stability in the atoms, that they tend to be difficult to break, subsequently making them very strong.
What is the ionic radius of Na+?
For example, the ionic radius of Na+ is about 0.095 nm, while the ionic radius of Cl- is about 0.181 nm. So with that information, we can estimate that in NaCl, the separation between the nucleus of Na+ and Cl- is about 0.095 + 0.181 = 0.276 nm.
Why does the boiling point increase as the size of the atom increases?
An example would be that of the noble gases where the boiling point increases as size of the atom increases; this is due to the increased Van Der Waal forces between the gas atoms.
What is van der Waal force?
Van Der Waal forces are the forces that are generated due to temporary charges that are formed around the atom due to movement of electrons.
Why do dipoles occur?
Momentary dipoles occurring due to uneven electron distributions in neighboring molecules as they approach one another.
What is van der Waals radius?
And van der Waals radius is half of the internuclear distance of two non-bonded atoms of the same element in the closest possible distance.
Is van der Waals radius greater than metallic radius?
It was written that if any atom can possess all the three types of radius, then van der Waals radius will be greater than metallic radius. However from the above diagram, it appears that the van der Waals radius and metallic radius are equal.
Is van der Waal stronger than metallic bond?
As in case of metallic bond, the atoms are bonded tightly so their shells can overlap, but in case of van der wal forces the bond is weak. Therefore, in case of van der waal force, the internuclear distance will be higher as compared to metallic bond.
What is the volume of a Van der Waals atom?
Therefore, the Van der Waals volume of a single atom Vw = 39.36 Å 3, which corresponds to rw = 2.11 Å (≈ 200 picometers). This method may be extended to diatomic gases by approximating the molecule as a rod with rounded ends where the diameter is 2rw and the internuclear distance is d. The algebra is more complicated, but the relation
What is the Van der Waals volume?
The Van der Waals volume, Vw, also called the atomic volume or molecular volume, is the atomic property most directly related to the Van der Waals radius. It is the volume "occupied" by an individual atom (or molecule). The Van der Waals volume may be calculated if the Van der Waals radii (and, for molecules, the inter-atomic distances, ...
How are molecules held together in a crystal?
The molecules in a molecular crystal are held together by Van der Waals forces rather than chemical bonds. In principle, the closest that two atoms belonging to different molecules can approach one another is given by the sum of their Van der Waals radii. By examining a large number of structures of molecular crystals, it is possible to find a minimum radius for each type of atom such that other non-bonded atoms do not encroach any closer. This approach was first used by Linus Pauling in his seminal work The Nature of the Chemical Bond. Arnold Bondi also conducted a study of this type, published in 1964, although he also considered other methods of determining the Van der Waals radius in coming to his final estimates. Some of Bondi's figures are given in the table at the top of this article, and they remain the most widely used "consensus" values for the Van der Waals radii of the elements. Scott Rowland and Robin Taylor re-examined these 1964 figures in the light of more recent crystallographic data: on the whole, the agreement was very good, although they recommend a value of 1.09 Å for the Van der Waals radius of hydrogen as opposed to Bondi's 1.20 Å. A more recent analysis of the Cambridge Structural Database, carried out by Santiago Alvarez, provided a new set of values for 93 naturally occurring elements.
What is the refractive index of helium?
The refractive index of helium n = 1.000 0350 at 0 °C and 101.325 kPa, which corresponds to a molar refractivity A = 5.23 × 10−7 m3/mol. Dividing by the Avogadro constant gives Vw = 8.685 × 10−31 m3 = 0.8685 Å 3, corresponding to rw = 0.59 Å.
What is the density of helium at 1.1 K and 66 atm?
The density of solid helium at 1.1 K and 66 atm is 0.214 (6) g/cm3, corresponding to a molar volume Vm = 18.7 × 10−6 m3/mol. The Van der Waals volume is given by
Is the Van der Waals volume smaller than the sum of the Van der Waals volumes of the constituent atom?
The Van der Waals volume of a molecule is always smaller than the sum of the Van der Waals volumes of the constituent atoms: the atoms can be said to "overlap" when they form chemical bonds .
Is Van der Waals volume the same as atomic polarizability?
When the atomic polarizability is quoted in units of volume such as Å 3, as is often the case, it is equal to the Van der Waals volume. However, the term "atomic polarizability" is preferred as polarizability is a precisely defined (and measurable) physical quantity, whereas "Van der Waals volume" can have any number of definitions depending on the method of measurement.