Adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate is a complex organic chemical that provides energy to drive many processes in living cells, e.g. muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, and chemical synthesis. Found in all forms of life, ATP is often referred to as the "molecular unit of currency" of i…
Why was mitochondria give the nickname Powerhouse?
May 07, 2020 · Mitochondria are known as the powerhouse of the cell because it is responsible for the extracting energy from food through cellular respiration. The energy is released in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). It is an energy currency of the cell.
Why are mitochondria called the energy center of the cell?
Apr 05, 2020 · The mitochondria is called the powerhouse of the cell because it is responsible for producing most of the cell’s energy, or adenosine tri-phosphate (ATP). Mitochondria are able to multiply in response to the energy needs of a cell, so that cells requiring more energy to function are powered by more mitochondria than cells with lower energy needs.
Why is mitochondria called Strange organelle?
Aug 31, 2019 · Mitochondria are often called the “powerhouses” or “energy factories” of a cell because they are responsible for making adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the cell’s main energy-carrying molecule.
Why mitochondria is the organelle of the moment?
Aug 11, 2021 · Mitochondria are often called the “powerhouses” or “energy factories” of a cell because they are responsible for making adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the cell’s main energy-carrying molecule. ATP represents the short-term stored energy of the cell.
Why is the mitochondria called the powerhouse of the cell?
The mitochondria is called the powerhouse of the cell because it is responsible for producing most of the cell's energy, or adenosine tri-phosphate (ATP). Mitochondria are able to multiply in response to the energy needs of a cell, so that cells requiring more energy to function are powered by more mitochondria than cells with lower energy needs.
How did mitochondria form?
Mitochondria are thought to have been created early in the evolution of organisms when a cell containing a nucleus absorbed an aerobic prokaryote. The two cells entered into a mutually productive relationship, in which the surrounding cell provided protection to the prokaryote, and the prokaryote provided energy for the surrounding cell. ...
Why are free radicals used in the mitochondria?
Scientists believe that some free radicals are actually used by mitochondria as a measuring stick to sense whether the level of ATP production in a cell needs to be adjusted. Antioxidants also have the ability to defend the body against free radicals.
How does the mitochondria convert digestive products into ATP?
These substances are then transformed by the mitochondria into additional ATP for the cell to use as energy. The initial process that changes digestive products to ATP within the cell is called glycosis, and produces two ATP per glycogen molecule. After the waste product of glycosis, called pyruvate, enters the mitochondria, ...
What are the free radicals that mitochondria can destroy?
Luckily, mitochondria have their own internal defense system against free radicals, called antioxidant enzymes, that block any damage the free radicals could do to the cell. Scientists believe that some free radicals are actually used by mitochondria as a measuring stick ...
How does lack of exercise affect mitochondria?
Mitochondria play a key role in determining the overall health of an individual. Lack of exercise decreases the efficiency and amount of mitochondria in muscle cells, making it more likely for free radicals to do cell damage. Excess consumption of sugar-heavy foods and beverages also decreases the efficiency of mitochondria.
What are the similarities between prokaryotes and mitochondria?
This explains the many similarities seen today between mitochondria and prokaryotes, such as the presence of electron transport proteins in the membranes of both. While prokaryotes are able to synthesize their own proteins, mitochondria have lost this ability over time, and rely heavily on the nucleus of the host cell for this function.
Why mitochondria is called Power House of cell?
Mitochondria are often called the “powerhouses” or “energy factories” of a cell because they are responsible for making adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the cell’s main energy-carrying molecule.
Is ATP the powerhouse of the cell?
The mitochondria, often labeled the powerhouse of the cell, are the organelle responsible for energy production within the cell. Playing an important role in cellular respiration, the mitochondria are the main location for ATP production.
Is brain power house of human body?
The power house of the Human Body is the brain. It has billions of nerves connected to it that carry trillions of electrical impulses throughout your body.
What is the power source of the body?
Carbohydrates are the main energy source of the human diet. The metabolic disposal of dietary carbohydrates is direct oxidation in various tissues, glycogen synthesis (in liver and muscles), and hepatic de novo lipogenesis.
What are the 4 types of energy do humans have?
In the body, thermal energy helps us to maintain a constant body temperature, mechanical energy helps us to move, and electrical energy sends nerve impulses and fires signals to and from our brains.
How do the energy system works in our body?
Energy is made up of carbohydrates, proteins and fats which are broken down during digestion to become glucose, amino acids and fatty acids respectively. These are then absorbed into the blood cells where they become adenosine triphosphate (ATP) our body’s fuel.
Do humans run on electricity?
Electricity is everywhere, even in the human body. Our cells are specialized to conduct electrical currents. Electricity is required for the nervous system to send signals throughout the body and to the brain, making it possible for us to move, think and feel.
Why the mitochondria is called the powerhouse of the cell?
Mitochondria are often called the “powerhouses” or “energy factories” of a cell because they are responsible for making adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the cell’s main energy-carrying molecule. ATP represents the short-term stored energy of the cell.
Why are mitochondria called the powerhouse of the cell quizlet?
Terms in this set (12) Why are mitochondria called the powerhouse of the cell? It is called the powerhouse because they burn and break the chemical bonds of glucose to release energy to do work in a cell.
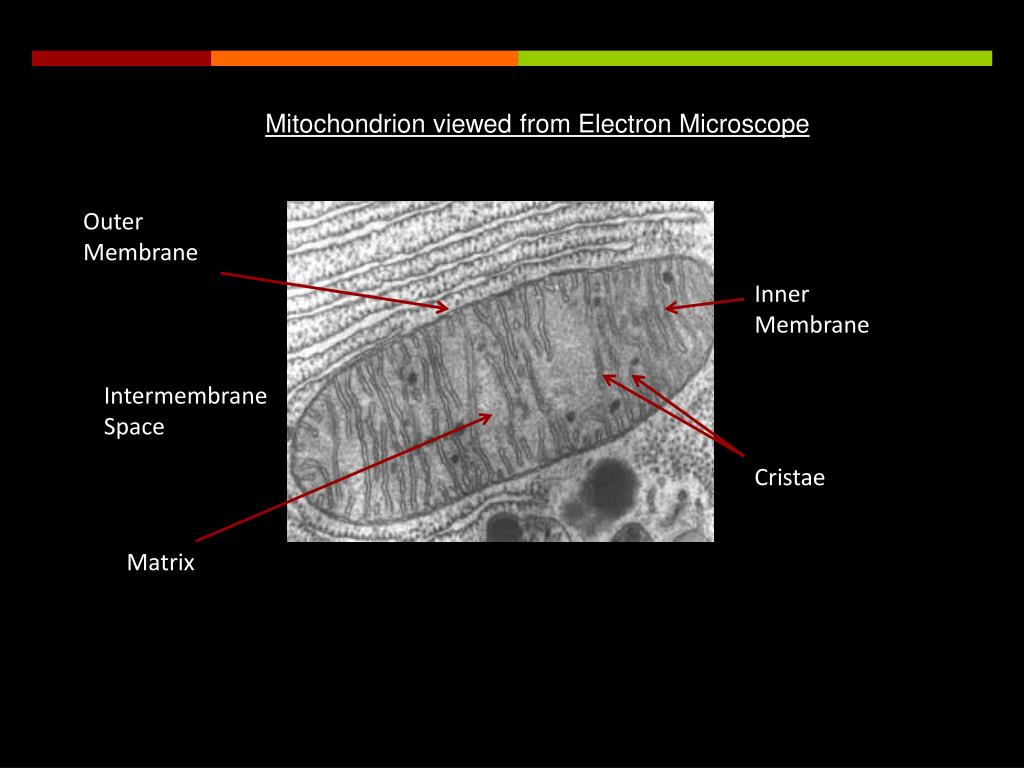
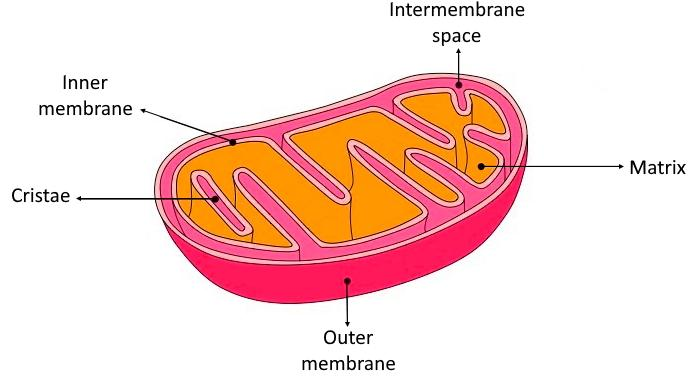
What is the diagram of mitochondria?
Mitochondria are a double-membrane-bound cell organelle found in most eukaryotic organisms. In all living cells, these cell organelles are found freely floating within the cytoplasm of the cell. The diagram of Mitochondria is useful for both Class 10 and 12.
What are the functions of a mitochondria?
Known as the “powerhouses of the cell,” mitochondria produce the energy necessary for the cell’s survival and functioning. Through a series of chemical reactions, mitochondria break down glucose into an energy molecule known as adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used to fuel various other cellular processes.
Why is the mitochondria the most important organelle?
As the power plants in virtually every human cell (as well as animal, plant, and fungi cells), mitochondria play an essential role in creating energy to drive cellular function and basically all of our biological processes.
Where did mitochondria come from?
The origin and evolution of mitochondria and eukaryotes. Mitochondria evolved from an endosymbiotic al- phaproteobacterium (purple) within an archaeal- derived host cell that was most closely related to Asgard archaea (green).
What can we do in order to have more functioning mitochondria?
Strategies to Improve Mitochondrial Function Pick the right mother. Optimize nutrient status to limit oxygen and high-energy electron leakage in the ETC. Decrease toxin exposure. Provide nutrients that protect the mitochondria from oxidative stress. Utilize nutrients that facilitate mitochondrial ATP production.
Why mitochondria is known as the powerhouse of the cell explain?
Mitochondria are often called the “powerhouses” or “energy factories” of a cell because they are responsible for making adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the cell’s main energy-carrying molecule. ATP represents the short-term stored energy of the cell.
Why does the mitochondria need energy?
They produce energy in the form of a molecule called ATP (adenosine triphosphate) which gets used throughout the cell to power the different jobs it has to do. How mitochondria make energy is very important to us as it allows our cells to function and for us to move and be alive.
Why are mitochondria called the powerhouse of the cell quizlet?
Why are mitochondria called the powerhouse of the cell? It is called the powerhouse because they burn and break the chemical bonds of glucose to release energy to do work in a cell.
What process take place in mitochondria?
The process is called oxidative phosphorylation and it happens inside mitochondria. In the matrix of mitochondria the reactions known as the citric acid or Krebs cycle produce a chemical called NADH. NADH is then used by enzymes embedded in the mitochondrial inner membrane to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
What process makes ATP?
The process human cells use to generate ATP is called cellular respiration. It results in the creation of 36 to 38 ATP per molecule of glucose. The two ATP-producing processes can be viewed as glycolysis (the anaerobic part) followed by aerobic respiration (the oxygen-requiring part).
What is Cytoplasms?
Cytoplasm is a thick solution that fills each cell and is enclosed by the cell membrane. It is mainly composed of water, salts, and proteins. In eukaryotic cells, the cytoplasm includes all of the material inside the cell and outside of the nucleus.
What is the cristae in the mitochondria?
A crista (/ˈkrɪstə/; plural cristae) is a fold in the inner membrane of a mitochondrion. This aids aerobic cellular respiration, because the mitochondrion requires oxygen. Cristae are studded with proteins, including ATP synthase and a variety of cytochromes.
Mitochondria: Function
The main function of the mitochondria is to produce energy through the process of oxidative phosphorylation.
Mitochondrial Disease
Most of the mitochondrial diseases are due to mutations in nuclear DNA that affect products that end up in the mitochondria. These mutations can be inherited or spontaneous.