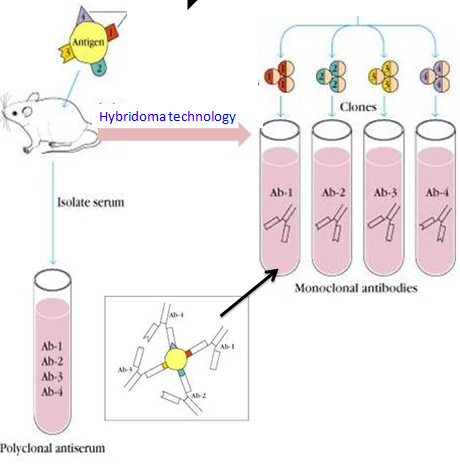
Hybridoma technology is a method for producing large numbers of identical antibodies (also called monoclonal
Monoclonal antibody
Monoclonal antibodies are antibodies that are made by identical immune cells that are all clones of a unique parent cell. Monoclonal antibodies can have monovalent affinity, in that they bind to the same epitope. In contrast, polyclonal antibodies bind to multiple epitopes and are usually made b…
How is hybridoma technology used in the workup of multiple myeloma?
After cell fusions between B cells and myeloma cells, protocols of hybridoma technology include multistep screening and cloning processes to identify antigen-specific hybridomas, which is labour-intensive and time-consuming. However, recent advances in robotic screening methods have alleviated this to some extent [88].
What are the characteristics of hybridomas of multiple myeloma (MM)?
Hybridomas possess two important properties of B cells, production of antibodies, and immortalization of myeloma cells. MAbs are monospecific antibodies that are produced by a clone of B cells.
How do B cell-myeloma hybrids survive myeloma?
In this way, only the B cell-myeloma hybrids survive, since the HGPRT gene coming from the B cells is functional. These cells produce antibodies (a property of B cells) and are immortal (a property of myeloma cells). The incubated medium is then diluted into multi-well plates to such an extent that each well contains only one cell.
Why is hybridoma the best method of antibody generation?
Even with the recent development of high throughput mAb generation technologies, hybridoma is the most favoured method due to its indigenous nature to preserve natural cognate antibody pairing information and preserves innate functions of immune cells.

Why are myeloma cells used in monoclonal antibodies?
A typical monoclonal antibody production process Preparation of myeloma cells - Myeloma cells are immortalized cells that, once fused with spleen cells, can result in hybridoma capable of unlimited growth.
Why is myeloma used in hybridoma?
Fusing antibody-producing spleen cells, which have a limited life span, with cells derived from an immortal tumor of lymphocytes (myeloma) results in a hybridoma that is capable of unlimited growth.
Why can't myeloma cells used in hybridoma technology survive in HAT medium?
However, these myelomas are unable to do so since they are deficient in an enzyme called HGPRT, which is required for the salvage pathway. Hence, myelomas are unable to replicate in culture. Only hybridomas survive.
Why is a Tumour cell used to form a hybridoma?
Formation of monoclonal antibodies The spleen cells are fused with human cancerous white blood cells called myeloma cells to form hybridoma cells which divide indefinitely. These hybridoma cells divide and produce millions of monoclonal antibodies specific to the original antigen.
What are myeloma cells?
Myeloma is a type of blood cancer that develops from cells in the bone marrow called plasma cells. Bone marrow is the spongy tissue found inside the inner part of some of our large bones. The bone marrow produces different types of blood cells. Diagram showing the skeleton and the bone marrow in the hip and thigh bone.
Why are spleen cells fused with myeloma cells during monoclonal antibody production?
The two cells (spleen cells and myeloma cells) are fused together to produce a hybrid cell (hybridoma) that has the best properties of both cells – the hybridoma grows in culture and makes antibody. Hybridoma cells are cloned to ensure that all cells in the culture are making exactly the same mAbs.
Why aminopterin is added in HAT medium?
Fused cells are incubated in the HAT medium. Aminopterin in the medium blocks the de novo pathway. Hence, unfused myeloma cells die, as they cannot produce nucleotides by the de novo or salvage pathway.
Which one of the following properties of the myeloma cells is used in the hybridoma technology to generate monoclonal antibody?
They discovered a hybrid cell that has the property of a B-cell to produce immorality of myeloma cells. Due to this feature, it can produce numerous monoclonal antibodies. This is called hybridoma technology.
Which medium is used for the selection of hybridoma?
HAT mediumHAT medium is used for selection of fused (hybridoma) cells.
Why are Tumour cells used to make monoclonal antibodies?
Monoclonal antibodies can be designed to bind specifically with these antigens. When injected into a person's body, the monoclonal antibodies will bind with these cancer cells and clump them together. This makes it easier to identify a cancerous tumour , which can then be treated or removed.
Why do monoclonal antibodies need to be humanised?
A type of antibody made in the laboratory by combining a human antibody with a small part of a mouse or rat monoclonal antibody. The mouse or rat part of the antibody binds to the target antigen, and the human part makes it less likely to be destroyed by the body's immune system.
What antibodies are produced by hybridoma cells?
Hybridoma cells resulting from the fusion of B lymphocytes and myeloma cells produce specific monoclonal antibodies. As more monoclonal antibodies are being used in clinical applications, e.g. Muromonab-CD3 (OK3) to prevent acute rejection of organs (Shapiro et al., 2003), Rituximab™ to treat B-cell lymphoma, etc. (Coiffier et al., 2002, Raderer et al., 2003), a logical extension would be to encapsulate hybridoma cells to deliver monoclonal antibodies in vivo. Hence, anti-VE (vascular endothelium)-cadherin secreting 1B5 hybridoma cells were entrapped into alginate–agarose capsules ( Orive et al., 2001). The antibody was detectable in the medium during the 9 days of culture. The secreted antibody was able to inhibit microtube formation in an in vitro angiogenesis Matrigel assay. However, encapsulated hybridoma cells generated large aggregates in some beads, leading to breakdown of the microcapsules and release of the cells at day 15 (Orive et al., 2003). Hence, uncontrolled proliferation is a serious problem that would limit the use of hybridoma cells in microencapsulation.
What is hybridoma culture?
Hybridoma is a culture of hybrid cells that results from the fusion of B cells and myeloma cells. Hybridoma technology produces hybridomas. This technology was developed to produce mAbs. Hybridomas possess two important properties of B cells, production of antibodies, and immortalization of myeloma cells.
What is master cell bank?
The master cell bank is derived from the OKT3 hybridoma initially generated in 1978 by the technique of Kohler and Milstein. Both master and working cell banks have undergone extensive characterisation to ensure their safety and consistency. Each is tested for absence of murine viruses, bacteria, mycoplasma and fungi.
What are the cell banks used for OKT3?
The hybridoma cell banks provide the critical starting material for the OKT3 process. There are two categories of cell banks: the master cell bank and the working cell bank. The master cell bank is used to generate working cell banks, which in turn are used to generate the monoclonal antibody. Working cell banks are typically composed of approximately 100–200 vials. The use of this master cell bank/working cell bank concept assures a consistent, high quality supply of the OKT3 monoclonal antibody well into the twenty-first century.
What is a hybrid cell?
Hybridomas are hybrid cells produced by the fusion of an antibody-producing lymphocyte with a tumor cell and used to culture continuously a specific monoclonal antibody. From: Encyclopedia of Toxicology (Third Edition), 2014. Download as PDF.
How can B cells be immortalized?
Using hybridoma technology, B cells of interest can be immortalized by fusing them with cancer cells (myeloma) to produce hybridomas that are immortal. Methods such electrofusion and chemical fusion can be used to fuse B cells with myeloma cells.
What is a mAb?
MAbs are monospecific antibodies that are produced by a clone of B cells. Therefore, an mAb is understood to be an antibody for a unique epitope. This technology was invented by Cesar Milstein and Georges J. F. Kohler in 1975.
Who developed the hybridoma cell?
To develop a similar long-lasting cell that secreted antibodies of known specificity, he began to work alongside George and Kohler. The pair devised the idea of the hybridoma cell an antibody-producing B-cell fused with immortal myeloma cells.
How long does it take for a hybridoma to grow?
When the cells are cultured in HAT media, only the hybridoma cells grow, while rest will slowly disappear (unfused cells). This process is complete within 7-10 days in the culture. It is very important to the selection of single antibodies producing hybrid cells.
Why are monoclonal antibodies used?
Monoclonal antibodies widely used in diagnostics and for the detection of a key protein. The major demand for monoclonal antibodies in research and therapy has allowed the industry to flourish. It has developed into an exciting and competitive market, generating the highest-earning of any biology drug.
Why are antibodies used in medicine?
Antibodies are used as tools for locating or identifying antigens. For many years, antiserum extracted from human and animal blood was the main source of antibodies for test and therapy, but the basic problem of antiserum is contained polyclonal antibodies. It is a mixture of different antibodies because it starts dozens ...
Why is B-cell clone a mixture?
It is a mixture of different antibodies because it starts dozens of immune reactions from a wide verity of B-cell clones. This characteristic is to be expected because several immune reactions may be occurring simultaneously and even a single species of microbe can stimulate different types of antibodies.
Who made the first monoclonal antibody?
The first monoclonal antibody was produced by Cesar Milstein and George Kohler in 1975. Cesar Milstein began researching somatic mutation in the 1960s, which he hypothesized was responsible for antibody diversity and specificity. He investigated this mechanism in antibodies produced by myeloma cells, which were readily available at the time. However, the exact antigen specificity of these cells was unknown, making it difficult to study their molecular mechanism. To develop a similar long-lasting cell that secreted antibodies of known specificity, he began to work alongside George and Kohler. The pair devised the idea of the hybridoma cell an antibody-producing B-cell fused with immortal myeloma cells. Milstein and Kohler hypothesized that by immunizing the host with a specific antigen and fusing host B-cells with myeloma cells, they would create an immortal hybridoma cell line with the ability to secrete antibodies of known specificity.
Can hybrid cells produce antibodies?
Thus these hybrid cells have got the ability to produce antibodies due to the B-lymphocyte genetic material and also the capacity to divide indefinitely in the culture due to the presence of tumor cells or myeloma cells involved in the production of hybrid cells. Therefore, these hybrid cells produced from hybridoma technology are cultured in ...
What is hybridoma technology?
Hybridoma technology. A general representation of the hybridoma method used to produce monoclonal antibodies. Hybridoma technology is a method for producing large numbers of identical antibodies (also called monoclonal antibodies ). This process starts by injecting a mouse (or other mammal) with an antigen that provokes an immune response.
Why is myeloma cell line used?
The myeloma cell line that is used in this process is selected for its ability to grow in tissue culture and for an absence of antibody synthesis. In contrast to polyclonal antibodies, which are mixtures of many different antibody molecules, the monoclonal antibodies produced by each hybridoma line are all chemically identical.
What is the next stage of the monoclonal antibody screening process?
The next stage is a rapid primary screening process , which identifies and selects only those hybridomas that produce antibodies of appropriate specificity.
Why do patients with metastatic tumors relapse?
One of the main reasons for metastatic relapse in patients with solid tumours is the early dissemination of malignant cells. The use of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) specific for cytokeratins can identify disseminated individual epithelial tumor cells in the bone marrow.
What is the process of fusion of B cells and myeloma cells?
The fusion of the B cells with myeloma cells can be done using electrofusion. Electrofusion causes the B cells and myeloma cells to align and fuse with the application of an electric field.
Why do unfused myeloma cells die?
Removal of the unfused myeloma cells is necessary because they have the potential to outgrow other cells , especially weakly established hybridomas.
What media is needed for hybridoma?
Supplemental media containing interleukin-6 (such as briclone) are essential for this step. Once a hybridoma colony is established, it will continually grow in culture medium like RPMI-1640 (with antibiotics and fetal bovine serum) and produce antibodies.
What is the purpose of hybridoma of murine B lymphocytes and myeloma cells
This hybridoma of murine B lymphocytes and myeloma cells is then screened to ascertain whether a potential therapeutic antibody is being expressed.
How do hybridoma cells work?
Hybridoma cell lines are widely used to create mAbs. This is achieved by immunizing a mouse with a target antigen, thereby eliciting an immune response. The B lymphocytes, taken from the immunized mouse spleen, produce anti-bodies to the antigen. Each B lymphocyte is then fused with an immortal myeloma cell line, ...
What is the purpose of Southern Blotting and DNA sequencing?
Several classical studies were published in 1980 in which Southern blotting, electron microscopy, and DNA sequencing were used to analyze the structure of Ig heavy chain genes in plasmacytomas and hybridoma cells lines. The data indicated that switching is effected by recombination between DNA sequences located in the intergenic regions upstream of C H genes, resulting in deletion of the chromosomal DNA residing between the recom-bining switch regions from the cell ( Coleclough et al., 1980; Cory and Adams, 1980; Davis et al., 1980a; Hurwitz et al., 1980; Rabbits et al., 1980; Sakano et al., 1980; Yaoita and Honjo, 1980 ). Data were later provided suggesting this deletion event also occurs in culture when mouse splenic B cells are induced with LPS to undergo class switching ( Hurwitz and Cebra, 1982; Radbruch and Sablitsky, 1983 ). These experiments also allowed a preliminary ordering of the C H genes in mice, which was confirmed when Shimizu et al. (1982) cloned the entire Ig C H locus in overlapping λ phage clones.
What is the main source of energy in CRL 1606 hybridomas?
Glutamine can be incorporated into biomass or oxidized via the TCA cycle. Glutamine has been found to be the major source of energy in many cell lines. For CRL 1606 hybridomas, glucose and glutamine are the major energy sources, with ammonia, lactic acid, and alanine as the major products.
Do mice produce antibodies?
The mice are modified so that they do not produce their own antibodies but instead generate totally human versions after being immunized with specific antigens. 25, 26 The B lymphocytes are again taken from the spleen and used to generate human hybridoma cell lines.