
In addition, tissue cultures are useful for several other purposes listed below:
- To study the respiration and metabolism of plants.
- For the evaluation of organ functions in plants.
- To study the various plant diseases and work out methods-for their elimination.
- Single cell clones are useful for genetic, morphological and pathological studies.
- Embryonic cell suspensions can be used for large scale clonal propagation.
Why is tissue culture helpful for plants?
Tissue culture technology has made it possible for farmers to have access to the following:
- large quantities of superior clean planting materials that are early maturing (12-16 months compared to the conventional banana of 2-3 years)
- bigger bunch weights (30-45 kg compared to the 10-15 kg from conventional material)
- higher annual yield per unit of land (40-60 tons per hectare against 15-20 tons previously realized with conventional material
What plants can be propagated by tissue culture?
Tissue culture is used to store a large number of plants in a small space and also reduces labor. The types of plants that are being propagated by this method include cut flowers, foliage plants, perennials, and ornamental plants. Got a question on this topic?
What is tissue culture and its advantages?
What is tissue culture and its advantages class 10? Tissue culture is a practice of propagating organisms under sterile conditions, often to produce clones of a organism. Here, new organisms are grown by removing a tissue or separating cells from the growing tip of an organism. It can be plant tissue culture or animal tissue culture. Advantages.
How is vascular tissue in plants important?
What are Vascular Plants?
- Table of Content:
- Vascular Plants. Vascular plants are those plants, which have specialised vascular tissues for the transport of water, minerals and food.
- Classification and Examples. Vascular plants are also known as tracheophytes. ...
- Vascular Tissues. Vascular plants contain specialized conducting tissues known as xylem and phloem. ...
What is tissue culture and why is it important?
tissue culture, a method of biological research in which fragments of tissue from an animal or plant are transferred to an artificial environment in which they can continue to survive and function. The cultured tissue may consist of a single cell, a population of cells, or a whole or part of an organ.
What are 3 uses for tissue culture?
Applications include: micropropagation using meristem and shoot culture to produce large numbers of identical individuals. screening programmes of cells, rather than plants for advantageous characters. large-scale growth of plant cells in liquid culture as a source of secondary products.
What are the four types of plant tissue culture?
Types of Plant tissue cultureSeed Culture.Embryo Culture.Callus Culture.Organ Culture.Protoplast Culture.Anther Culture.
What is the process of plant tissue culture?
Tissue culture involves the use of small pieces of plant tissue (explants) which are cultured in a nutrient medium under sterile conditions. Using the appropriate growing conditions for each explant type, plants can be induced to rapidly produce new shoots, and, with the addition of suitable hormones new roots.
What is tissue culture mention any four applications?
ADVERTISEMENTS: The five applications of the tissue culture are: (1) Rapid Clonal Propagation (2) Soma-clonal Variation (3) Transgenic Plants (4) Induction and Selection of Mutations and (5) Resistance to Weedicides.
What is an example of tissue culture?
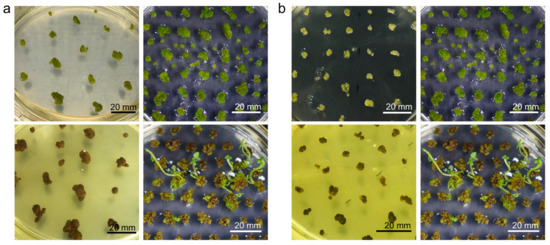
A- leaf-derived calli of Ginkgo biloba ; B- micropropagated shoots of Elatine hungarica ; C- embryogenic callus of Phragmites australis from axillary buds of plants from Tihany, Lake Balaton.
How is tissue culture used in agriculture?
Tissue culture in agriculture Tissue culture allows the production and propagation of genetically homogeneous, disease-free plant material [37]. Cell and tissue in vitro culture is a useful tool for the induction of somaclonal variation [38].
What is plant tissue culture and its applications?
Plant Tissue Culture is a technique of growing and multiplication of the cells, tissues and. organs of the plant in a controlled environment of light, temperature, pH etc. under. aseptic conditions.German botanist Haberlandt is recognized as the father of the plant.
Why is tissue culture important in biotechnology?
Plant tissue culture is one of the most rapidly growing areas of biotechnology because of its high potential to develop improved crops and ornamental plants. With the advances made in the tissue culture technology, it is now possible to regenerate species of any plant in the laboratory.
What is tissue culture?
Plant tissue culture broadly refers to the in vitro cultivation of plants, seeds and various parts of the plants ( organs, embryos, tissues, single cells, protoplasts). The cultivation process is invariably carried out in a nutrient culture medium under aseptic conditions. ADVERTISEMENTS:
What are the advantages of plant cells over animal cells?
the ability of change to meristematic state and differentiate into a whole plant.
What are the cells in an adult plant?
42.1). Both the stem and root are characterized by the presence of apical growth regions which are composed of meristematic cells. These cells are the primary source for all the cell types of a plant.
How are explants sterilized?
The requisite explants (buds, stem, seeds) are trimmed and then subjected to sterilization in a detergent solution. After washing in sterile distilled water, the explants are placed in a suitable culture medium (liquid or semisolid form) and incubated. This results in the establishment of culture.
How does tissue culture help the green revolution?
The techniques of plant tissue culture have largely helped in the green revolution by improving the crop yield and quality.
Which cell is responsible for the absorption of nutrients?
Phloem is responsible for the absorption of nutrients while xylem absorbs water. The meristematic cells of the shoot apex divide leading to the growth of stem. Some of the stem cells differentiate and develop into leaf primordia, and then leaves.
Why is tissue culture important?
Importance of Tissue Culture. Tissue culture is very important in biology due to its wide range of applications. Both plant and animal tissues can be used for culturing. For eg., animal tissue culture helps in preserving an organ or tissue.
What are the advantages of tissue culture?
Following are the various advantages of tissue culture technique: 1 The plantlets are obtained in a very short time with a small amount of plant tissue. 2 The new plants produced are disease-free. 3 The plants can be grown throughout the year, irrespective of the season. 4 A large space is not required to grow plants by tissue culture technique. 5 The production of new varieties in the market place speeds up. 6 This technique is being used for the production of ornamental plants such as dahlia, chrysanthemum, orchids, etc.
Why do explants need to be sterilized?
The explant should be sterilized to prevent it from tissue damage.
What is callus in explants?
A callus is an unorganized, dividing mass of cells. When the explants are cultured in a proper medium, the callus is obtained. The growth of callus is followed by organ differentiation. The culture is grown on a gel-like medium composed of agar and specific nutrients required for the growth of the cells.
What is tissue culture?
Tissue culture is a technique in which fragments of plants are cultured and grown in a laboratory. Many times the organs are also used for tissue culture. The media used for the growth of the culture is broth and agar. This technique is also known as micropropagation. It has proved beneficial for the production of disease-free plants ...
What is protoplast culture?
Protoplast Culture. It is a cell without a cell wall. A protoplast can be cultured using the hanging-drop method, or micro-culture chambers. In protoplast culture, a number of phases can be observed: development of cell wall, cell division, regeneration of a whole plant.
What are some examples of plants that have been produced by tissue culture?
Oil palm, banana, eggplant, pineapple, rubber tree, tomato, sweet potato have been produced by tissue culture in the developing countries.
Why is plant tissue culture important?
Along with the totipotent potential of plant cell, the capacity of cells to alter their metabolism, growth and development is also equally important and crucial to regenerate the entire plant [ 1 ]. Plant tissue culture medium contains all the nutrients required for the normal growth and development of plants.
What is the science of plant tissue culture?
The science of plant tissue culture takes its roots from the discovery of cell followed by propounding of cell theory. In 1838, Schleiden and Schwann proposed that cell is the basic structural unit of all living organisms. They visualized that cell is capable of autonomy and therefore it should be possible for each cell if given an environment to regenerate into whole plant. Based on this premise, in 1902, a German physiologist, Gottlieb Haberlandt for the first time attempted to culture isolated single palisade cells from leaves in knop’s salt solution enriched with sucrose.The cells remained alive for up to one month, increased in size, accumulated starch but failed to divide. Though he was unsuccessful but laid down the foundation of tissue culture technology for which he is regarded as the father of plant tissue culture. After that some of the landmark discoveries took place in tissue culture which are summarized as under:
How long to sterilize potato tubers?
Five days old sprouts were used as explants for direct proliferation. The explants were surface sterilized in detergent for 10 minutes, later with 0.1 % mercuric chloride solution for 5 minutes followed by three times washing with sterilized-distilled water. The sprouts were aseptically cut into 10 mm sections containing one node and inoculated in medium. The Espinosa medium plus vitamin B5 supplemented with different concentrations of BAP and GA3 alone and in combinations was utilized. Highest shoot length of shoots was observed in presence of 0.5 mg/l BAP and 0.4 mg/l GA3 with the ability to produce maximum plantlets per explant. For root induction the same medium was used with different concentrations of NAA and IBA. NAA at2.0 mg/l induced the highestroot development. The rooted plantlets were successfully acclimatized and delivered to the company for cultivation.
What is plant cell culture?
The technique depends mainly on the concept of totipotentiality of plant cells [ 9] which refers to the ability of a single cell to express the full genome by cell division.
Why are orchids grown?
Orchids are usually grown for the beauty, exoticism and fragrance of their flowers. They are cultivated since the times of Confucius (ca. 551 - 479 BC). Some orchids are commercialized not for their beauty, but for uses in food industry. They are also used medicinally as a treatment for diarrhea and as an aphrodisiac. The vegetative propagation of phalaenopsis is difficult and time consuming. In addition, the desired characteristics of seedlings and uniformity are not attained.
Why is in vitro cell culture important?
In vitro cell and organ culture offers an alternative source for the conservation of endangered genotypes [ 40 ]. Germplasm conservation worldwide is increasingly becoming an essential activity due to the high rate of disappearance of plant species and the increased need for safeguarding the floristic patrimony of the countries [ 41 ]. Tissue culture protocols can be used for preservation of vegetative tissues when the targets for conservation are clones instead of seeds, to keep the genetic background of a crop and to avoid the loss of the conserved patrimony due to natural disasters, whether biotic or abiotic stress [ 42 ]. The plant species which do not produce seeds (sterile plants) or which have ‘recalcitrant’ seeds that cannot be stored for long period of time can successfully be preserved via in vitro techniques for the maintenance of gene banks.
How does plant tissue culture affect agriculture?
As an emerging technology, the plant tissue culture has a great impact on both agriculture and industry, through providing plants needed to meet the ever increasing world demand. It has made significant contributions to the advancement of agricultural sciences in recent times and today they constitute an indispensable tool in modern agriculture [ 5 ].
