From the above topic, we can easily conclude that the single-phase induction motors are not self-starting because the produced stator The stator is the stationary part of a rotary system, found in electric generators, electric motors, sirens, mud motors or biological rotors. Energy flows through a stator to or from the rotating component of the system. In an electric motor, the stator provides a rotating magnetic field that driv…Stator
What is the starting torque of a single phase motor?
It is worth noting that a single phase motor is just as a three phase motor only that it runs on one phase. Each phase sets up an oscillating magnetic field whose movement is back and forth instead of rotary motion like the three phase. Because of this motion, the single phase will not have a starting torque.
Why single phase induction motor is not self-start?
It is not synchronously revolving (or rotating) flux, as in case of 3 phase stator winding, the fed cannot produce rotation. Hence single phase induction motor is not self-starting.
How does an induction motor respond to two magnetic fields?
The induction motor responds to each of the magnetic fields separately. The net torque in the motor is equal to the sum of the torque due to each of the two magnetic fields.
What is the difference between double revolving field theory and induction motor?
Both the theories are similar and explain the reason for the production of torque when the rotor is rotating. The double revolving field theory of a single phase induction motor states that a pulsating magnetic field is resolved into two rotating magnetic fields. They are equal in magnitude but opposite in directions.
Why does the single phase induction motor have no starting torque?
From the above topic, we can easily conclude that the single-phase induction motors are not self-starting because the produced stator flux is alternating in nature and at the starting, the two components of this flux cancel each other and hence there is no net torque.
Why single motors are not self-starting?
As discussed above, single phase induction motors are not self-starting because a single phase supply cannot produce a rotating magnetic field. We require a two phase or three phase supply for the production of rotating magnetic field. But we can create a rotating magnetic field by a two-phase construction.
Why the single phase induction motor is not self-starting motor explain in detail with the help of double field revolving theory?
When a single-phase AC supply is fed to the stator winding, a pulsating magnetic field (not the rotating) is produced. Under these conditions, the rotor does not rotate due to inertia. Hence, a single-phase induction motor is inherently not self-starting, but requires some auxiliary starting means.
How does a single phase induction motor start?
Starting Principle A single phase induction motor consists of a single phase winding on the stator and a cage winding on the rotor. When a 1 phase supply is connected to the stator winding, a pulsating magnetic field is produced. In the pulsating field, the rotor does not rotate due to inertia.
Why synchronous motor has no starting torque?
An ideal synchronous motor has no starting torque because the. Rotor is made up of salient poles. Relative velocity between the stator and rotor mmfs is zero. Relative velocity between stator and rotor mmfs is not zero.
Why synchronous motor has no net starting torque?
This will tend to rotate the rotor in the direction of the rotating magnetic field. But, before this happens stator poles again change their position reversing the direction of the torque exerted on the rotor. Hence the average torque on the rotor is zero. So, synchronous motor will not start itself.
Why does a single phase induction motor need two windings?
Adding aCapacitor in series with the start winding creates a larger phase shift and movement in the magnetic field which provides more starting Torque for applications where the motor must start under a load.
Why capacitor is used in single phase motor?
Some single-phase AC electric motors require a "run capacitor" to energize the second-phase winding (auxiliary coil) to create a rotating magnetic field while the motor is running. Start capacitors briefly increase motor starting torque and allow a motor to be cycled on and off rapidly.
What is the special feature of single phase induction motor?
1. What is the special feature of single phase induction motor? Explanation: The single phase induction motor has no inherent starting torque. Thus special means should be used to make it self starting.
Can a single phase motor run without a capacitor?
Answer: There are three common types of single-phase motors named capacitor motor, shaded pole motor and split phase motors. Shaded pole and split phase single-phase motors do not require a capacitor to run.
Which type of single phase motor is having very high starting torque?
Capacitor-start motorCapacitor-start motor: The capacitor-start motor develops a much higher starting torque, i.e. 3.0 to 4.5 times the full-load torque.To obtain a high starting torque, the value of the starting capacitor must be large, and the resistance of starting winding must be low.
Do single phase motors require starters?
Starting mechanism of single phase and three phase motor The single-phase motor does not start on its own and requires the use of auxiliary equipment such as motor starters.
Is a single-phase induction motor self starting?
Single-phase induction motors are not self-starting without an auxiliary stator winding driven by an out of phase current of near 90°. Once started the auxiliary winding is optional. The auxiliary winding of a permanent split capacitor motor has a capacitor in series with it during starting and running.
How does a single-phase motor operate?
Single phase motors work on the same principle as 3 phase motors except they are only run off one phase. A single phase sets up an oscillating magnetic field that goes back and forth rather than a rotating magnetic field (see bottom figure). Because of this a true single phase motor has zero starting torque.
What are the starting methods of induction motor?
The most commonly used starting methods of induction motor are given below.Direct Online Starting.Stator resistance/reactance starting.Auto-Transformer starter.Star-Delta starter.Rotor resistance control.
How does an induction motor run?
The conductors of the rotor are short-circuited either by the end rings or by the help of the external resistance. The relative motion between the rotating magnetic field and the rotor conductor induces the current in the rotor conductors. As the current flows through the conductor, the flux induces on it.
Why is there no starting torque in a single phase motor?
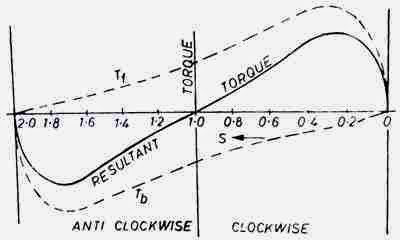
That explains why there is no starting torque in a single-phase motor. However, if the rotor is started somehow, say, in the clockwise direction, the clockwise torque starts increasing and, at the same time, the anticlockwise torque starts decreasing. Hence, there is a certain amount of net torque in the clockwise direction which accelerates ...
Why are induction motors not self-starting?
As discussed above, single phase induction motors are not self-starting because a single phase supply cannot produce a rotating magnetic field. We require a two phase or three phase supply for the production of rotating magnetic field.
How to Make Single Phase Induction Motor Self Starting?
We require a two phase or three phase supply for the production of rotating magnetic field.
What is a flux in a stator winding?
When fed from a single-phase supply, its stator winding produces a flux ( or field ) which is only alternating i.e. one which alternates along one space axis only.
How many fluxes are in an alternating flux?
That is why an alternating flux can be looked upon as composed of two revolving fluxes each of half the value and revolving synchronously in opposite directions.
What happens to flux after a quarter cycle of rotation?
After a quarter cycle of rotation, fluxes A and B will be oppositely directed as shown in Fig (c) so that the resultant flux would be zero.
How many revolving fluxes are there in sinusoidal flux?
So, an alternating sinusoidal flux can be represented by two revolving fluxes, each equal to half the value of alternating flux and each rotating synchronously in opposite directions.
What is a single phase induction motor?
A Single Phase Induction Motor consists of a single phase winding which is mounted on the stator of the motor and a cage winding placed on the rotor. A pulsating magnetic field is produced, when the stator winding of the single-phase induction motor shown below is energised by a single phase supply.
What are the two theories of induction motors?
The performance of the single phase induction motor is analysed by the two theories. One is known as the Double Revolving Field Theory, and the other is Cross Field Theory. Both the theories are similar and explain the reason for the production of torque when the rotor is rotating.
What happens when a 1 phase motor is rotated?
If the 1 phase stator winding is excited and the rotor of the motor is rotated by an auxiliary means and the starting device is then removed, the motor continues to rotate in the direction in which it is started.
Which direction does a single phase motor move?
The direction in which the single phase motor is started initially is known as the positive direction.
Is a single phase induction motor self-starting?
Under these conditions, the rotor of an induction motor does not rotate. Hence, a single phase induction motor is not self-starting. It requires some special starting means.
Is the net torque of a single phase induction motor zero?
Both are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction but at the same frequency. At the standstill condition, the induced voltages are equal and opposite as a result; the two torques are also equal and opposite. Thus, the net torque is zero and, therefore, a single phase induction motor has no starting torque.
