
Why was the Delian League formed?
(Show more) ... (Show more) Delian League, confederacy of ancient Greek states under the leadership of Athens, with headquarters at Delos, founded in 478 bce during the Greco-Persian wars. The original organization of the league, as sketched by Thucydides, indicates that all Greeks were invited to join to protect themselves from Achaemenian Persia.
Why was Athens the head of the Delian League?
Several Ionian cities joined together in the Delian League for mutual protection against the Persians. They placed Athens at the head (as hegemon) because of her naval supremacy.
What caused the formation of the Confederacy of Delos?
History - Several causes contributed to the formation of the first Confederacy of Delos. During the 6th century B.C. Sparta had come to be regarded as the chief power, not only in the Peloponnese, but also in Greece as a whole, including the islands of the Aegean.
Who was the real father of the Delian League?
Some say that the Athenian politician and military man, Themistocles, is the real father of the Delian League, because it was under his reign that the development of the Athenian navy made the League possible.
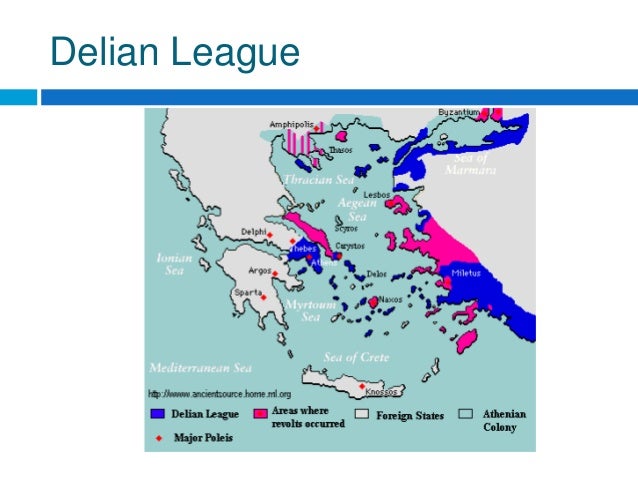
Who was in the Delian League and why?
The Delian League, founded in 478 BC, was an association of Greek city-states, with the number of members numbering between 150 and 330 under the leadership of Athens, whose purpose was to continue fighting the Persian Empire after the Greek victory in the Battle of Plataea at the end of the Second Persian invasion of ...
What were the aims of the Delian League?
Formed in 478 B.C., the Delian League was an alliance of mainly coastal and Aegean city-states against Persia at a time when Greece feared Persia might attack again. Its goal was to make Persia pay and to free the Greeks under Persian dominion.
Was the Delian League A Confederacy?
Delian League , Confederacy of ancient Greek states led by Athens and based on the island of Delos. Founded in 478 bc to combat Persia, its members included Aegean states and islands; Athens supplied commanders and assessed tributes of ships or money.
Why did city-states in the Delian?
Why did city-states in the Delian League revolt against Athens? They resented not having a say in the government. They wanted to establish a representative democracy. They feared that Athens could not protect them from Persia.
Why was the Delian League formed quizlet?
The Delian League was formed by the Athenians during the struggle of the Persian war to prevent a Persian take over. The Delian League consisted of other Greek subject that would contribute to the military naval power that was led by the Athenians by paying tribute in monetary form or sometimes with ships.
What was the purpose of the Delian League quizlet?
It was originally the Hellenic League, but after the headquarters was moved to Delos, it became known as the Delian League. Its goal was to liberate Ionia from Persian rule and keep the Persians out of Greece.
Who founded the Delian League?
Aristides of AthensThe spectacular defeat of the Persians at Salamis in 480 led to the formation of a more permanent alliance. Three years later negotiations, led by Aristides of Athens, began on the Greek island of Delos. The result was the Delian League, a sort of ancient equivalent to NATO.
What was the Delian League and why did it fail?
It was created as a protection against Spartan aggression. It was a maritime self-defense league led by Athens. The Delian League was finally broken up by the capture of Athens by Sparta in 404 BC.
Why did the Delian League transform into the Athenian empire?
It sent Athenian colonists to settle other city-states, collected taxes, and used the shared navy for itself. In 454 BC, Pericles moved the treasury from Delos to Athens, allegedly to protect it from Persia. Effectively, it turned the Delian League into the Athenian Empire.
How was the Delian League successful?
The Athenian-dominated Delian League enjoyed success after success against the Persians in the 470s and 460s. Within twenty years after the rout of the Persian fleet in the battle of Salamis in 479, almost all Persian garrisons had been expelled from the Greek world and the Persian fleet driven from the Aegean.
Why did other city-states in the Delian League resent Athens?
Many of the city-states who had been giving money to the Delian League resented the fact that Athens was misusing the money it had been given. Sparta became angry with the Athenians and began to unite with allies who were also angry with Athens for taking their money. There were many city-states who sided with Athens.
What is a Delian?
/ (ˈdiːlɪən) / noun. a native or inhabitant of Delos. adjective. of or relating to Delos.
What was the initial goal of the Athenian led Delian League?
What was the initial goal of the Athenian-led Delian League? The alliance aimed at protecting the Aegean Islands, defending Ionia, and keeping the Persians out of Greece.
How did the Delian League make Athens stronger?
The Athenian Empire Its power in the League grew, especially after the famous statesman Pericles rose to power in Athens around 460 BC. Pericles began using the Delian League's resources, including its navy and taxes, for Athens. It was this money that let him build the massive temple in Athens called the Parthenon.
How was the Delian League successful?
The Athenian-dominated Delian League enjoyed success after success against the Persians in the 470s and 460s. Within twenty years after the rout of the Persian fleet in the battle of Salamis in 479, almost all Persian garrisons had been expelled from the Greek world and the Persian fleet driven from the Aegean.
How did Athens benefit from forming the Delian League?
The Delian League formed on the bases of defending Greek allied states against the threat of Persian Invasion and soon became a platform for Athenian dominance and empire. Yet the original League itself was based upon an alliance of which Athens was to be the leading member.
Why did the Ionian cities join the Delian League?
Following Hellenic victory at the Battle of Salamis, during the Persian Wars, Ionian cities joined together in the Delian League for mutual protection. The league was meant to be offensive as well as defensive: "to have the same friends and enemies" (typical terms for an alliance formed for this dual purpose [Larsen]), with secession forbidden. The member poleis placed Athens at the head ( hegemon) because of her naval supremacy. Many of the Greek cities were annoyed with the tyrannical behavior of the Spartan commander Pausanias, who had been leader of the Greeks during the Persian War.
What war did the Hellenic Poleis fight?
After the Persian Wars, which included Xerxes' invasion by land at the Battle of Thermopylae (the setting for the graphic novel-based movie ), the various Hellenic poleis (city-states) divided into opposing sides ranged around Athens and Sparta, and fought the Peloponnesian War .
What is the Greek word for the Peloponnesian League?
Hellenic = Greek. Hellenotamiai = treasurers, Athenian financial officers. Peloponnesian League = modern term for the military alliance of the Lacedaemonians and their allies. symmachia = a treaty where the signers agree to fight for one another.
How many members were there in the Delian League?
In The Outbreak of the Peloponnesian War (1989), author-historian Donald Kagan says the members included about 20 members from the Greek islands, 36 Ionian city-states, 35 from the Hellespont, 24 from around Caria, and 33 from around Thrace, making it primarily an organization of the Aegean islands and coast.
What was the purpose of the Peace of Callias?
The Peace of Callias, in 449, between Athens and Persia, put an end to the rationale for the Delian League, since there should have been peace, but Athens by then had a taste for power and the Persians started supporting the Spartans to Athens' detriment [Flower].
How long did the Delian League fight?
For 10 years, the Delian League fought to rid Thrace and the Aegean of Persian strongholds and piracy. Athens, which continued to demand financial contributions or ships from its allies, even when fighting was no longer necessary, became more and more powerful as her allies became poorer and weaker.
What was Thucydides' book on the formation of the Delian League?
Thucydides Book 1.96 on the formation of the Delian League. "96. When the Athenians had thus gotten the command by the confederates' own accord for the hatred they bare to Pausanias, they then set down an order which cities should contribute money for this war against the barbarians, and which galleys.
How did the Athenian Empire start its reign?
Instead, the Athenian Empire (454-404 BC) started its reign by moving the treasury of the Delian League from Delos to Athens. For the Second Athenian Confederacy (378-7 BC), a revival of the Delian League, the enemy was Sparta. It was created as a protection against Spartan aggression.
What was the name of the Greek confederation under the leadership of Athens?
The rise and fall of the Delian League. The Delian League , or Confederacy of Delos, was the name used for the confederation of Greek states under the ‘leadership’ of Athens. According to some records, it lasted from the end of the Persian War, circa 478 BC, until the end of the Peloponnesian War in the year 404 BC.
How long did the Peloponnesian War last?
According to some records, it lasted from the end of the Persian War, circa 478 BC, until the end of the Peloponnesian War in the year 404 BC. As described in the statutes, power was originally distributed equally. Indeed, according to Thucydides, each state in the league had an equal vote . However from the beginning, the ‘unofficial’ leader ...
Where was the Delian League headquarters?
However from the beginning, the ‘unofficial’ leader of the Delian League was Athens. The original headquarters were at Delos, but they were later moved to Athens…a transition that meant more than just a change of location.
What city states joined the Alliance?
Around 200 city-states, including Eretria, Mykonos, Athos and Byzantium, joined the alliance by the mid-fifth century BC for the same reason. They wanted protection by the Athenians, who controlled the naval yards, thus turning them into the only ones who could fight against Persia.
Who built the Parthenon?
Indeed, this ‘income’ allowed Pericles, a Greek statesman, orator and general of Ath ens, to start building the Parthenon on the Acropolis… and other major ‘public’ works.
Why did Pericles move the Delian League to Athens?
In 454 BC, the Athenian general Pericles moved the Delian League's treasury from Delos to Athens, allegedly to keep it safe from Persia. However, Plutarch indicates that many of Pericles's rivals viewed the transfer to Athens as usurping monetary resources to fund elaborate building projects.
What happened to the Delian League during the siege of Thasos?
Additionally, their land, naval ships, and the mines of Thasos were confiscated by Athens. The siege of Thasos marks the transformation of the Delian league from an alliance into, in the words of Thucydides, a hegemony.
What was the Athenian Empire?
The Athenian Empire (454–404 BC) By 454 BC, the Delian League could be fairly characterised as an Athenian Empire; a key event of 454 BC was the moving of the treasury of the Delian League from Delos to Athens.
What was the Delian League?
The Delian League, founded in 478 BC, was an association of Greek city-states, with the number of members numbering between 150 and 330 under the leadership of Athens, whose purpose was to continue fighting the Persian Empire after the Greek victory in the Battle ...
What happened at the Battle of Coronea?
The Battle of Coronea, in 447 BC, led to the abandonment of Boeotia. Euboea and Megara revolted, and while the former was restored to its status as a tributary ally, the latter was a permanent loss. The Delian and Peloponnesian Leagues signed a peace treaty, which was set to endure for thirty years.
What was the cause of the Greco-Persian Wars?
The Greco-Persian Wars had their roots in the conquest of the Greek cities of Asia Minor, and particularly Ionia , by the Achaemenid Persian Empire of Cyrus the Great shortly after 550 BC. The Persians found the Ionians difficult to rule, eventually settling for sponsoring a tyrant in each Ionian city.
When did the Peloponnesian War start?
By 431 BC, the threat the League presented to Spartan hegemony combined with Athens's heavy-handed control of the Delian League prompted the outbreak of the Peloponnesian War; the League was dissolved upon the war's conclusion in 404 BC under the direction of Lysander, the Spartan commander.

History
Mutual Protection
- Following Hellenic victory at the Battle of Salamis, during the Persian Wars, Ionian cities joined together in the Delian League for mutual protection. The league was meant to be offensive as well as defensive: "to have the same friends and enemies" (typical terms for an alliance formed for this dual purpose [Larsen]), with secession forbidden. The member poleis placed Athens at the head …
Members of The Delian League
- In The Outbreak of the Peloponnesian War(1989), author-historian Donald Kagan says the members included about 20 members from the Greek islands, 36 Ionian city-states, 35 from the Hellespont, 24 from around Caria, and 33 from around Thrace, making it primarily an organization of the Aegean islands and coast. This free confederation (symmachia) of autonomous cities, co…
Athenian Supremacy
- For 10 years, the Delian League fought to rid Thrace and the Aegean of Persian strongholds and piracy. Athens, which continued to demand financial contributions or ships from its allies, even when fighting was no longer necessary, became more and more powerful as her allies became poorer and weaker. In 454, the treasury was moved to Athens. Animosity developed, but Athens …
End of The Delian League
- The Delian League was broken up when Sparta captured Athens in 404. This was a terrible time for many in Athens. The victors razed the great walls linking the city to her harbor city of Piraeus; Athens lose her colonies, and most of her navy, and then submitted to the reign of the Thirty Tyrants. An Athenian league was later revived in 378-7 to protect against Spartan aggression an…
Terms to Know
- hegemonia = leadership.
- Hellenic= Greek.
- Hellenotamiai = treasurers, Athenian financial officers.
- Peloponnesian League= modern term for the military alliance of the Lacedaemonians and their allies.
Sources
- Starr, Chester G. A History of the Ancient World. Oxford University Press, 1991.
- Kagan, Donald. The Outbreak of the Peloponnesian War. Cornell University Press, 2013.
- Holden, Hubert Ashton, "Plutarch's Life of Perciles," Bolchazy-Carducci Publishers, 1895.
- Lewis, David Malcolm. The Cambridge Ancient History Volume 5: The Fifth Century BC., Boardman, John, Davies, J.K., Ostwald, M., Cambridge University Press, 1992.