
Dependency theory was established in 1950s by Raul Prebisch
Raúl Prebisch
Raúl Prebisch was an Argentine economist known for his contributions to structuralist economics such as the Prebisch–Singer hypothesis, which formed the basis of economic dependency theory. He became the executive director of the Economic Commission for Latin America in 1950. In 1950, …
What are the basic tenets of dependency theory?
Basic tenets of dependency theory Dependency theory is based on the notion that there is a group of wealthy states (core) and a periphery of poor underdeveloped states (Third world). Resources are extracted by the core from the periphery to sustain their economic growth and wealth. This is an on going process.
What are the disadvantages of dependency theory?
Finally, dependency theory encourages the on confederation of periphery regions in order to have a strong voice and also control terms of trade. Below are some weaknesses of dependency theory. Firstly, theory paid little attention to internal disintegrations that hinders development in the periphery regions.
What are the criticisms of dependency theory?
While the dependency theories have provided a welcome critique from the South about the North, they were not without some shortcomings and critics. The principal criticism of dependency theories has been that the school does not provide any substantive empirical evidences to support its arguments.
How does dependency theory differ from modernization theory?
The main difference between dependency theory and modernization theory is that dependency theory mainly focuses on poor and underdeveloped countries, while modernization theory mainly focuses on rich and developed countries. Dependency theory and modernization theory are two opposing theories in sociology.
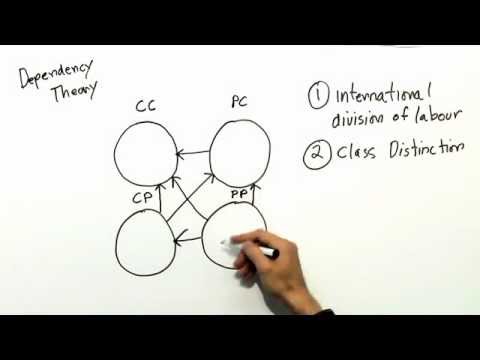
What is the main argument of dependency theory?
Dependency theory focused on individual nations, their role as suppliers of raw materials, cheap labor, and markets for expensive manufactured goods from industrialized countries. The unequal exchange relationship between developed and developing countries was viewed as contributing to poor economic growth.
When was dependency theory developed?
dependency theory, an approach to understanding economic underdevelopment that emphasizes the putative constraints imposed by the global political and economic order. First proposed in the late 1950s by the Argentine economist and statesman Raúl Prebisch, dependency theory gained prominence in the 1960s and '70s.
Why is dependency theory important?
The Dependency Theory analyses the internal dynamics of underdeveloped countries and relates their underdevelopment to their positions in the international economic system. It also examines the relation between the internal and external structures.
What conditions led to the emergence of dependency theory?
According to the author, what conditions led to the emergence of dependency theory? Latin American scholars observed that the global economy was structured to extract resources from less developed nations and transfer them to industrialized nations.
Where did dependency theory originated?
Background. Dependency Theory developed in the late 1950s under the guidance of the Director of the United Nations Economic Commission for Latin America, Raul Prebisch.
What are the strengths of dependency theory?
To start with, dependency theory has the following strengths. Firstly, the theory analyses the inequality existing between the poor and the rich countries. Moreover, the theory breaks some political bonds and explains reasons why the wealthy nations are taking advantage of the poor countries (Doukhan, 2003).
What is the criticism of dependency theory?
The principal criticism of dependency theories has been that the school does not provide any substantive empirical evidences to support its arguments.
Is dependency theory still valid?
In today's realm, dependency thoughts are still useful in analyzing the widening inequalities between the poor and rich countries, or in analysing the divisions within a developed or a developing country context.
How does dependency theory explain global inequality?
Dependency Theory It states that global inequality is primarily caused by core nations (or high-income nations) exploiting semi-peripheral and peripheral nations (or middle-income and low-income nations), creating a cycle of dependence (Hendricks 2010).
How does dependency theory explain poverty?
The structural explanation for global stratification is called dependency theoryThe view that global poverty results from colonialization and exploitation of the poorest nations by the richest nations and by multinational corporations., which may be considered a conflict explanation of global inequality.
What is the relationship between dependency theory and colonialism?
Dependency theories propose that colonialism and neocolonialism —continuing economic dependence on and exploitation of former colonial countries—are the main causes global poverty.
What is the difference between world systems theory and dependency theory?
Dependency theorists tend to focus on the power of transnational classes and class structures in sustaining the global economy, whereas world systems analysts tended to focus on the role of powerful states and the interstate system.
What is dependency theory by Andre Gunder Frank?
According to dependency theory, the people of less-developed countries are not to blame for the failure of their societies to develop. Instead, he suggested that Western nations deliberately failed to develop these countries.
Who developed the world system theory?
Immanuel WallersteinWorld Systems Theory. The World Systems Theory was articulated in large part by Immanuel Wallerstein, who argued that in economics there are three types of economic nations - the core, the semi-periphery, and the periphery.
Is dependency theory still relevant today?
In today's realm, dependency thoughts are still useful in analyzing the widening inequalities between the poor and rich countries, or in analysing the divisions within a developed or a developing country context.
What is Marxist dependency theory?
The Marxist theory of dependency analyzed dependency as part of a monopolist, dynamic, and competitive world capitalist economy that transcended national states, creating relations of complementarity, subordination, commitment, and/or conflict among its various hegemonic internal bourgeoisies.
What is dependency theory?
Dependency theory is the notion that resources flow from a " periphery " of poor and underdeveloped states to a " core " of wealthy states, enriching the latter at the expense of the former. It is a central contention of dependency theory that poor states are impoverished and rich ones enriched by the way poor states are integrated into ...
Why is dependency theory so controversial?
Allen, dependency theory's claims are "debatable" due to fact that the protectionism that was implemented in Latin America as a solution ended up failing. The countries incurred too much debt and Latin America went into a recession. One of the problems was that the Latin American countries simply had too small national markets to be able to efficiently produce complex industrialized goods, such as automobiles.
How does aid dependency affect ownership?
Aid dependency also compromises ownership which is marked by the ability of a government to implement its own ideas and policies. In aid dependent countries, the interests and ideas of aid agencies start to become priority and therefore erode ownership.
How does political dependency affect the government?
Political dependency occurs when donors have too much influence in the governance of the receiving country. Many donors maintain a strong say in the government due to the country’s reliance on their money, causing a decrease in the effectiveness and democratic-quality of the government. This results in the receiving country’s government making policy that the donor agrees with and supports rather than what the people of the country desire. Government corruptibility increases as a result and inhibits reform of the government and political process in the country. These donors can include other countries or organizations with underlying intentions that may not be in favor of the people. Political dependency is an even stronger negative effect of aid dependency in countries where many of the problems stem from already corrupt politics and a lack of civil rights. For example, Zimbabwe and the Democratic Republic of the Congo both have extremely high aid dependency ratios and have experienced political turmoil. The politics of the Democratic Republic of the Congo have involved civil war and changing of regimes in the 21st century and have one of the highest aid dependency ratios in Africa.
What are the two main categories of dependency theorists?
Dependency theorists can typically be divided into two categories: liberal reformists and neo-Marxists. Liberal reformists typically advocate for targeted policy interventions, while the neo-Marxists believe in a command-centered economy.
How does dependency theory affect nations?
Dependency is perpetuated by using capitalism and finance . The dependent nations come to owe the developed nations so much money and capital that it is not possible to escape the debt, continuing the dependency for the foreseeable future.
What is the sine qua non of dependency?
The sine qua non of the dependency relationship is not the difference in technological sophistication , as traditional dependency theorists believe, but rather the difference in financial strength between core and peripheral countries –particularly the inability of peripheral countries to borrow in their own currency. He believes that the hegemonic position of the United States is very strong because of the importance of its financial markets and because it controls the international reserve currency – the US dollar. He believes that the end of the Bretton Woods international financial agreements in the early 1970s considerably strengthened the United States' position because it removed some constraints on their financial actions.
What is foreign dependency theory?
Dependency theory, sometimes called foreign dependency, is used to explain the failure of non-industrialized countries to develop economically despite investments made into them from industrialized nations.
How did Neocolonialism take over?
Rather, neocolonialism took over, suppressing developing nations through capitalism and finance. Many developing nations became so indebted to developed nations they had no reasonable chance of escaping that debt and moving forward.
What is the term for the domination of more advanced countries over those that are less developed?
Neocolonialism refers to the overall domination of more advanced countries over those that are less developed, including their own colonies, through economic pressure, and through oppressive political regimes. Colonialism effectively ceased to exist after World War II, but this didn't abolish dependency.
Who developed the Dependency Theory?
In the development of the Dependency Theory a pioneering contribution was made by Andre Gunder Frank and Wallerstein. Both of them strongly advocated that the underdevelopment of the Third World (Periphery) was conditioned by the development and expansion of a developed economy upon which the former was dependent.
What is dependency theory?
The Dependency Theory analyses the internal dynamics of underdeveloped countries and relates their underdevelopment to their positions in the international economic system. It also examines the relation between the internal and external structures.
What is underdevelopment in the capitalist system?
Underdevelopment is explained by it as a product of capitalist expansion which is accompanied by unequal exchanges and in which the Centre/Core/Metropolis exploits the resources and labour of the periphery for its advantage . The periphery lives in a state of dependency and is characterised by underdevelopment.
What is the central point of Dependency Theory?
The central point in the Dependency Theory is that the nature of social phenomena in the Third World countries is determined by the process of underdevelopment which characterizes these countries and which is the result of the expansion of World Capitalism. Further, this process of underdevelopment is intimately and inseparably related ...
What is the periphery of the economy?
The periphery lives in a state of dependency and is characterised by underdevelopment. “Dependency is a situation in which the economy of certain countries is conditioned by the development and expansion of another economy to which the former is subjected.
How did the underdeveloped countries become developed?
The only way open for the underdeveloped countries, believe the dependency theorists, to become developed was to overthrow the existing system.
Which group rejects the dependency theorists?
Even the Marxists, the revolutionary socialists, and the communists reject most of the ideas of the dependency theorists, particularly their conceptualisation of capitalism not as mode of production but as a social system characterised by a particular sort of exchange relationship.
What is dependency theory?
Dependency theory is a popular theory within the social sciences to explain economic. development of states. The theory developed during the late 1950s and over the following two. decades, principally under liberal reformer Raúl Prebisch, director of the United Nations.
What are the characteristics of dependency theory?
Three main characteristics of dependency theory are salient. First, the international system is. seen as the sum of two sets of states: dominant and dependent. Second, dependency theory. holds that external forces are critical in terms of economic activity of dependent states.
What theory holds expected underdevelopment?
resulted in deep problems in terms of underdevelopment. Dependency theory holds expected
What is modernization theory?
international organizations. By contrast, modernization theory considers nature, economic situations, world market. integration, and technological development or transfers of technology between developed. countries and underdeveloped countries. The deficiency in this theory derives from its internal.
What is the relationship between dominant and dependent states?
capitalism ), between dominant and dependent states are a vibrant process, with exchanges. taking place between the states playing a considerable role in the reinforcement of patterns of. inequality.
What is state development theory?
theory, an earlier theory of state development that ceded much of its explanatory ground. during the 1960s and even the 1970s following U.S. interventionist challenges overseas, as. well as problems associated with race relations, economic inflation, and the decline of the. U.S. dollar.
Is dependency theory without limitations?
The propositions of dependency theory are not without limitations. Although the theory has
Why is the dependency approach useful?
Following the dependency approach argumentation, it seems to be useful to lump countries that have a shared experience of colonization and economic dependence into one single category in order to explain global inequalities. But in an increasingly globalized world, challenging the question of global inequality based on arguments that rely on neocolonialism and economic dependency becomes difficult to sustain (Randall 2004, p. 42).
Which feature of dependency theory is common to all countries of the periphery?
As outlined by Theotonio Dos Santos, one of the founders of dependency theory, the feature that the countries of the periphery have in common is dependency on the core countries:
How did free trade affect the ACP countries?
The promotion of free trade agreements should have benefited not only the EU but also ACP countries to fully integrate with the global economy and eliminate the inequality gap between the developed and the developing world. However, ACP-EU trade agreements had rather a negative impact on regional food-processing industries since they negatively affected the market conditions for ACP producers of competing products. ACP-EU trade agreements often led to the undermining of local prices in ACP countries and in turn negatively affected the income of its population at various stages, in particular of those involved in agricultural production and processing (Ulmer 2004, p. 56).
What is the problem with modernization theory?
The problem of an overall encompassing theory in explaining global inequalities is that it may lead to generalizations without considering the specific histories and developments of individual countries. This was a problem of modernization theory, which has been harshly criticized by dependency theorists, and certainly one could view modernization and dependency theory as acting in opposition and opposing each other, yet by providing categorizations such as “Core-Periphery” or “North-South”, dependency theory did not substantially differ from other ethnocentric theories. The problem of these categorizations is that they are inherently ethnocentric because the “Periphery” or the “South” is characterized by socioeconomic and political backwardness, measured against Western values and standards and this simply should not be ignored. Therefore, one has to question whether distinguishing the world by providing such categorizations is useful for analyzing global inequalities.
What is the definition of dependence?
Theotonio Dos Santos, one of the founders of dependency theory, describes dependence as “a situation in which the economy of certain countries is conditioned by the development and expansion of another economy to which the former is subjected” (Dos Santos 1970, p. 231).
When does dependency theory expire?
The relevance of dependency theory for understanding North-South and regional integration processes and their relation to global inequality becomes visible when examining the Cotonou Partnership Agreement (CPA), which was signed in June 2000 and expires in 2020, between the European Union (EU) and the African, Caribbean and Pacific (ACP) countries. The aim of the Cotonou Partnership Agreement was initially to set up an entirely new framework for trade and investment relations between the EU and the ACP states.
Is dependency theory a useless approach?
The existence of shortcomings in the dependency theory should not automatically indicate that dependency theory is a useless approach which cannot be used at least as a conceptual orientation to the global division of wealth.
Why did developed countries fear the development of poorer countries?
According to Frank, developed nations actually fear the development of poorer countries because their development threatens the dominance and prosperity of the West.
Why did developing countries fail to develop?
Andre Gunder Frank (1971) argues that developing nations have failed to develop not because of ‘internal barriers to development’ as modernization theorists argue, but because the developed West has systematically underdeveloped them, keeping them in a state of dependency (hence ‘dependency theory’.)
Why did European countries not develop in the 1960s?
By the 1960s most colonies had achieved their independence, but European nations continued to see developing countries as sources of cheap raw materials and labour and, according to Dependency Theory, they had no interest in developing them because they continued to benefit from their poverty.
What was Frank's view on the world?
Frank argued that a world capitalist system emerged in the 16 th century which progressively locked Latin America, Asia and Africa into an unequal and exploitative relationship with the more powerful European nations.
Why is Frank highlighting the increasing dominance of transnational corporations in exploiting labour and resources in poor countries?
Second, Frank highlights the increasing dominance of Transnational Corporations in exploiting labour and resources in poor countries – because these companies are globally mobile, they are able to make poor countries compete in a ‘race to the bottom’ in which they offer lower and lower wages to attract the company, which does not promote development.
Is dependency a phase or a permanent position?
This view argues that dependency is not just a phase, but rather a permanent position . The only way developing countries can escape dependency is to escape from the whole capitalist system. Under this category, there are different paths to development:

Overview
Dependency theory is of the notion that resources flow from a "periphery" of poor and underdeveloped states to a "core" of wealthy states, enriching the latter at the expense of the former. It is a central contention of dependency theory that poor states are impoverished and rich ones enriched by the way poor states are integrated into the "world system". This theory was officially developed in the late 1960s following World War II, as scholars searched for the root is…
History
In Imperialism, the Highest Stage of Capitalism (1916), Lenin proposed that wealth would extend to the advanced (industrial) capitalist countries from the underdeveloped countries. Later, dependency theory originates with two papers published in 1949, one by Hans Singer and one by Raúl Prebisch, in which the authors observe that the terms of trade for underdeveloped countries relative to the developed countries had deteriorated over time: the underdeveloped countries we…
Other theorists and related theories
Two other early writers relevant to dependency theory were François Perroux and Kurt Rothschild. Other leading dependency theorists include Herb Addo, Walden Bello, Ruy Mauro Marini, Enzo Faletto, Armando Cordova, Ernest Feder, Pablo González Casanova, Keith Griffin, Kunibert Raffer, Paul Israel Singer, and Osvaldo Sunkel. Many of these authors focused their attention on Latin America; dependency theory in the Islamic world was primarily refined by the Egyptian economist Samir …
Criticism
Economic policies based on dependency theory have been criticized by free-market economists such as Peter Bauer and Martin Wolf and others:
• Lack of competition: by subsidizing in-country industries and preventing outside imports, these companies may have less incentive to improve their products, to try to become more efficient in their processes, to please customers, or to research new innovations.
Examples of dependency theory
Many nations have been affected by both the positive and negative effects of the Dependency Theory. The idea of national dependency on another nation is not a relatively new concept even though the dependency theory itself is rather new. Dependency is perpetuated by using capitalism and finance. The dependent nations come to owe the developed nations so much money and capital that it is not possible to escape the debt, continuing the dependency for the foreseeable f…
Aid dependency
Aid dependency is an economic problem described as the reliance of less developed countries (LDCs) on more developed countries (MDCs) for financial aid and other resources. More specifically, aid dependency refers to the proportion of government spending that is given by foreign donors. Having an aid dependency ratio of about 15%-20% or higher will have negative effects on the country. What causes dependency is the inhibition of development and economic/…
See also
• Structuralist economics
• Chicago Boys
• The Shock Doctrine, by Naomi Klein, discussing economics shock therapy
• Western Hemisphere Institute for Security Cooperation, a.k.a. School of the Americas
Further reading
• Amin S. (1976), 'Unequal Development: An Essay on the Social Formations of Peripheral Capitalism' New York: Monthly Review Press.
• Amin S. (1994c), 'Re-reading the postwar period: an intellectual itinerary' Translated by Michael Wolfers. New York: Monthly Review Press.
• Amin S. (1997b), 'Die Zukunft des Weltsystems. Herausforderungen der Globalisierung. Herausgegeben und aus dem Franzoesischen uebersetzt von Joachim Wilke' Hamburg: …
• Amin S. (1976), 'Unequal Development: An Essay on the Social Formations of Peripheral Capitalism' New York: Monthly Review Press.
• Amin S. (1994c), 'Re-reading the postwar period: an intellectual itinerary' Translated by Michael Wolfers. New York: Monthly Review Press.
• Amin S. (1997b), 'Die Zukunft des Weltsystems. Herausforderungen der Globalisierung. Herausgegeben und aus dem Franzoesischen uebersetzt von Joachim Wilke' Hamburg: VSA.
Colonialism and Neocolonialism
An Example of Dependency Theory
- Africa received many billions of dollars in the form of loans from wealthy nations between the early 1970s and 2002. Those loans compounded interest. Although Africa has effectively paid off the initial investments into its land, it still owes billions of dollars in interest. Africa, therefore, has little or no resources to invest in itself, in its own economy or human development. It's unlikely th…
The Decline of Dependency Theory
- The concept of the dependency theory rose in popularity and acceptance in the mid to late 20th century as global marketing surged. Then, despite Africa's troubles, other countries thrived despite the influence of foreign dependency. India and Thailand are two examples of nations that should have remained depressed under the concept of the dependency theory, but, in fact, they …
The Solution
- A remedy for dependency theory or foreign dependency would likely require global coordination and agreement. Assuming such a prohibition could be achieved, poor, undeveloped nations would have to be banned from engaging in any sort of incoming economic exchanges with more powerful nations. In other words, they could sell their resources to develope...