
Who had the worst trenches in WWI?
the english and french had worst trenches cause the western front was on the downhill side of europe and french/english built temporary trenches. the germans were on higher ground and built trenches to last. 57 views
What was life like in a World War One trench?
While the design of the trenches and the network of trenches seemed like a great tactic, the reality of the life in the trenches was a different story. Life in the trenches took its toll on the soldiers involved in the war. The soldiers in the front line trenches often stayed there for at least 10 days at a time, usually with very little sleep.
What were the living conditions like in the trenches?
Living conditions in the trenches were very, very poor. The trenches were very unsanitary; muddy and smelly. There were dead bodies piled up everywhere. The toilets would sometimes overflow. There were also many pests, mostly rats and lice, infested in the trenches. Trench Foot: Bad weather and rain flooded the trenches, making them very wet ...
Where was trench warfare first used in WW1?
Trenches were common throughout the Western Front. Trench warfare in World War I was employed primarily on the Western Front, an area of northern France and Belgium that saw combat between German...
When and why did they build trenches?
World War I was a war of trenches. After the early war of movement in the late summer of 1914, artillery and machine guns forced the armies on the Western Front to dig trenches to protect themselves.
What was the main reason for having trenches in the war?
Trenches provided a very efficient way for soldiers to protect themselves against heavy firepower and within four months, soldiers on all fronts had begun digging trenches. This photograph shows French infantry manning a forward line of trenches in Lorraine during January 1915.
When were the trenches built in ww1?
WWI started on 28 June 1914, and by the end of 1914, both sides had built trenches that went from the North Sea and through Belgium and France. Neither side made much ground for nearly three and a half years – from October 1914 to March of 1918.
How did trenches get built in ww1?
The trenches were dug by soldiers. Sometimes the soldiers just dug the trenches straight into the ground. This method was called entrenching. It was fast, but left the soldiers open to enemy fire while they were digging.
What are the advantages of trenches?
Trenches provided protection from bullets and shells, but they did carry their own risks. Trench foot, trench fever, dysentery, and cholera could inflict casualties as readily as any enemy.
Who had better trenches in ww1?
Differences Between German and British Trenches: Main difference between the two trenches was that the Germans dug their trenches first, which meant they got the better soil conditions because they dug their trenches on higher ground compared to the British trenches.
Do ww1 trenches still exist?
A few of these places are private or public sites with original or reconstructed trenches preserved as a museum or memorial. Nevertheless, there are still remains of trenches to be found in remote parts of the battlefields such as the woods of the Argonne, Verdun and the mountains of the Vosges.
Who started trench warfare?
Sébastien Le Prestre de Vaubantrench warfare, Warfare in which the opposing sides attack, counterattack, and defend from sets of trenches dug into the ground. It was developed by Sébastien Le Prestre de Vauban in the 17th century for laying siege to fortresses. Its defensive use was first institutionalized as a tactic during the American Civil War.
What is the full meaning of trenches?
a long, narrow excavation in the ground, the earth from which is thrown up in front to serve as a shelter from enemy fire or attack. trenches, a system of such excavations, with their embankments, etc. a deep furrow, ditch, or cut. Oceanography. a long, steep-sided, narrow depression in the ocean floor.
What are 3 interesting facts about trench warfare?
Well you've come to the right place....Trench warfare was started by the Germans in The First World War. ... There was 2,490 kilometres of trench lines dug during the First World War. ... Most trenches were between 1-2 metres wide and 3 metres deep. ... Trenches weren't dug in straight lines.More items...•
Why weren't trenches dug in straight lines?
All the trenches were dug in a zig-zag pattern so the enemy couldn't shoot straight down the line and kill many soldiers. If a mortar, grenade or artillery shell would land in the trench, it would only get the soldiers in that section, not further down the line.
Why did ww2 not have trenches?
In summary: The ability of radio-coordinated mechanized forces to maneuver in concert was what made trench-warfare untenable for most World War II fronts. These mechanized forces existed at the end of a long supply line, capable of operating at far greater distances and far greater speeds than previously possible.
What did trench warfare cause quizlet?
What did trench warfare cause? economies and resources within their own countries. No-man's land. A war of ____ is based on wearing the other side down with constant attacks and heavy losses.
When were trenches first used?
In the wake of the Battle of the Marne—during which Allied troops halted the steady German push through Belgium and France that had proceeded over the first month of World War I—a conflict both sides had expected to be short and decisive turns longer and bloodier, as Allied and German forces begin digging the first ...
What are 3 interesting facts about trench warfare?
Well you've come to the right place....Trench warfare was started by the Germans in The First World War. ... There was 2,490 kilometres of trench lines dug during the First World War. ... Most trenches were between 1-2 metres wide and 3 metres deep. ... Trenches weren't dug in straight lines.More items...•
What is the full meaning of trenches?
a long, narrow excavation in the ground, the earth from which is thrown up in front to serve as a shelter from enemy fire or attack. trenches, a system of such excavations, with their embankments, etc. a deep furrow, ditch, or cut. Oceanography. a long, steep-sided, narrow depression in the ocean floor.
Why Trench Warfare in WWI?
Trench Lines
- Trenches were dug in a zigzag pattern so that if an enemy entered the trench, he could not fire straight down the line. A typical trench systemincluded a line of three or four trenches: the front line (also called the outpost or the fire line), the support trench, and the reserve trench, all built parallel to one another and anywhere from 100 to 400 yards apart. The main trench lines were c…
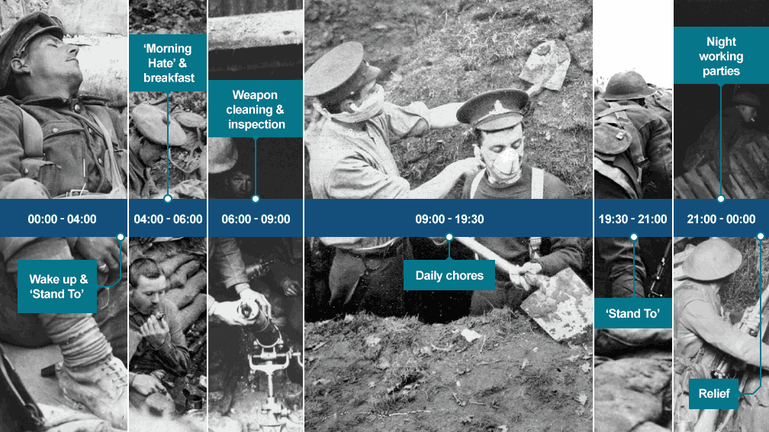
Daily Routine in The Trenches
- Routines varied among the different regions, nationalities, and individual platoons, but the groups shared many similarities. Soldiers were regularly rotated through a basic sequence: fighting in the front line, followed by a period in the reserve or support line, then later, a brief rest period. (Those in reserve might be called upon to help the front line if needed.) Once the cycle was completed, i…
Misery in The Mud
- Life in the trenches was nightmarish, aside from the usual rigors of combat. Forces of nature posed as great a threat as the opposing army. Heavy rainfall flooded trenches and created impassable, muddy conditions. The mud not only made it difficult to get from one place to another; it also had other, more dire consequences. Many times, soldiers became trapped in the …
Night Patrols and Raids
- Patrols and raids took place at night, under cover of darkness. For patrols, small groups of men crawled out of the trenches and inched their way into No Man's Land. Moving forward on elbows and knees toward the German trenches and cutting their way through the dense barbed wire on their way. Once the men reached the other side, their goal was to get close enough to gather inf…
Poison Gas Attacks
- In April 1915, the Germans unleashed an especially sinister new weapon at Ypresin northwestern Belgium: poison gas. Hundreds of French soldiers, overcome by deadly chlorine gas, fell to the ground, choking, convulsing, and gasping for air. Victims died a slow, horrible death as their lungs filled with fluid. The Allies began producing gas masks to protect their men from the deadly vap…
Shell Shock
- Given the overwhelming conditions imposed by trench warfare, it is not surprising that hundreds of thousands of men fell victim to "shell shock." Early in the war, the term referred to what was believed to be the result of an actual physical injury to the nervous system, brought about by exposure to constant shelling. Symptoms ranged from physical abnormalities (tics and tremors, …
The Legacy of Trench Warfare
- Due in part to the Allies' use of tanks in the last year of the war, the stalemate was finally broken. By the time the armistice was signed on November 11, 1918, an estimated 8.5 million men (on all fronts) had lost their lives in the so-called "war to end all wars." Yet many survivors who returned home would never be the same, whether their wounds were physical or emotional. By the end of …