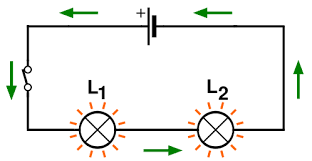
Why are the bulbs in a parallel circuit brighter?
Two bulbs in a simple parallel circuit each enjoy the full voltage of the battery. This is why the bulbs in the parallel circuit will be brighter than those in the series circuit. Another advantage to the parallel circuit is that if one loop is disconnected, then the other remains powered. Also, which bulb is brighter in a series circuit?
Do bulbs in parallel have the same brightness?
When in series, bulbs become dimmer as the potential difference is shared equally across the bulbs. In parallel, each branch shows the same potential difference, so the bulbs on one branch will have the same relative brightness. The current for each bulb will add up to the current near the battery.
Which bulb glows brighter when connected in series?
How to know if Bulbs are Connected in series or Parallel?
- In a series circuit, 80W bulb glows brighter due to high power dissipation instead of a 100W bulb.
- In a parallel circuit, 100W bulb glows brighter due to high power dissipation instead of an 80W bulb.
- The bulb which dissipates more power will glow brighter.
- In series, both bulbs have the same current flowing through them. ...
Are the lamps in buildings connected in parallel or series?
Various lamps and electrical appliances in our homes are connected in parallel so that each of the lamps or bobs and appliances can be operated independently. For us to have control over the individual lamps or loads, they have to be wired in parallel. Each connected electrical device and appliance are independent from others.

Why are incandescent bulbs brighter in parallel?
The reason being, in series, the applied voltage would be divided among the bulbs; but in parallel , the applied voltage would not be divided, and thus, each bulb would receive the total applied voltage.
Why does a 70W bulb grow brighter?
So, The one with more power will grow brightly because of low resistance as current will be higher. So, 70W bulb will grow more brightly.
Why do cold bulbs have a negative reflection?
Not much of one because cold bulbs have small resistances. When the jump gets to the second bulb though, it will pretty much look like a short circuit. This will cause a negative reflection, reducing the voltage to near zero.
How many volts does a light bulb need?
Light bulbs are designed to operate (in the US) at 120 volts (insert your local voltage there if applicable). Let’s work with 60 watt light bulbs.
What happens if the voltage in the series system is the same as the voltage in the parallel system?
If the voltage in the series system is still the same 120 VAC as the parallel system then the bulbs will be significantly dimmer.
How bright is an incandescent bulb?
If you look at the brightness of (for example) two 60 W bulbs connected in parallel, with 120 VAC applied and compare the brightness to two 60 W bulbs connected in series with 240 VAC applied, then the brightness will be exactly the same. This is because, in the series system each bulb will have 120 VAC across its terminals, same as the parallel system.
How to find current in a 60 watt light bulb?
There is a concept called Ohm’s law. First, let’s figure out the current used in a single 60 watt light bulb. Wattage=voltage x current. If we move things around according to mathematical principles, then current=wattage/voltage, or 60/120. That means that the current in a single 60 watt light bulb is 0.5 amps.
Which is brighter, a bulb arranged in series or a bulb arranged in parallel?
Therefore, we can see that if all other variables were kept constant, bulbs arranged in parallel are brighter than bulbs arranged in series.
What happens when one of the bulbs in a parallel arrangement fuses?
When one of the bulbs in a parallel arrangement fuses, the other bulbs in the circuit are still able to light up. On the other hand, when one of the bulbs in a series arrangement fuses, the other bulbs in the circuit will not light up. With the above analysis, let us now answer part (b).
What does it mean when a bulb is fused?
Let me do a quick introduction on what does it mean for a bulb to fuse. The filament is the part of the bulb that glows when electricity flows through, causing the bulb to light up. When too much electricity flows through the filament, the filament overheats and melts, resulting in a gap.
What happens when a circuit is arranged in series?
When the bulbs in a circuit are arranged in series, there is only one pathway that electricity can flow through.
Why do bulbs have fused filaments?
When bulbs have a melted filament, they have fused. Due to the gap in the filament, electricity is unable to flow through the filaments of fused bulbs, preventing them from lighting up. How will one fused bulb affect the other bulbs in the circuits? The outcome depends on how the bulbs are arranged in the circuit.
How many units of brightness are in a series circuit?
Recall that the number of batteries in a circuit determines the amount of electricity flowing through each pathway.] The bulbs in the series circuit have a brightness of 1 unit, while the bulbs in the parallel circuit have a brightness of 2 units.
What is the difference between two bulbs in a circuit?
The only difference (other than the number of switches) is the position of the bulbs in the circuit. When there are two bulbs in a circuit, they can either be arranged in series or in parallel.
Why are the bulbs in parallel?
The bulbs in parallel have lower total equivalent resistance, pulling more current and lowering terminal voltage. Depending on the power rating of the generator and the bulbs, it could be that the bulbs in parallel represent a load too large for the generator, lowering the voltage over the shunt too far, which reduces the magnetic field, which causes the induced voltage to go down, lowering the magnetic field further etc.. The bulbs in series have higher total resistance and won't pull the voltage down so much. So in this case, they could again be the ones burning brightest.
Why do we wire light bulbs in parallel?
2) As all answerers pointed it out, when we wire light bulbs in parallel instead of in series, we decrease the equivalent resistance of the circuit; and therefore increase the current passing through the filaments of the light bulbs. This leads to more power each light bulb is getting (due to Joule-Lenz law) and brighter light bulbs.
How many watts does a 120V light bulb have?
Lets start with two light bulbs, 120v AC, 60W each. If you connect them in parallel to the mains, each receives 120v, 0.5A (= 60W). If you now connect them in series, each light bulb now receives only 60v (due to voltage division), and assuming the same current (0.5A), it only receives 30W! Therefore, if the light bulbs light up at all, they each only has 30 watts of power, so they will be dimmer.
How to determine if a light bulb is in series?
Assume for a moment constant voltage source, and constant resistance for each bulb (not true for bulb but often used to simplify discussion at this level) then in series you have a total resistance of 2 R and power P = V I = V 2 2 R . This power is split by two bulbs so each sees V 2 / 4 R. When the bulbs are in parallel, each bulb sees the full voltage V so P = V 2 R. Since a bulb glows brighter when it gets more power the ones in parallel will glow brighter.
Why do generator bulbs go in parallel?
Depending on the power rating of the generator and the bulbs, it could be that the bulbs in parallel represent a load too large for the generator, lowering the voltage over the shunt too far, which reduces the magnetic field, which causes the induced voltage to go down, lowering the magnetic field further etc..
Why do light bulbs appear brighter?
The bulbs will only appear brighter if the available current to the system is not limited. In that case the series bulbs will have a lower voltage across each individual bulb and they will appear dimmer. If the power input to the circuit is a constant than the total wattage output from all bulbs is also constant and the bulbs will all appear the same (assuming the filaments for the bulbs are all identical resistance).
What is the brightness of a light bulb?
1) The brightness of a light bulb depends on various parameters, most of them being intrinsic properties of light bulbs. Essentially, the brightness depends upon the luminous flux of the light source. However, light sources which emit light with different wavelengths but same luminous flux can be perceived to have different brightness levels. Therefore, luminous flux is useful if we are comparing the brightness of light sources which emit light with same wavelength.