Enterobacteriaceae
The family Enterobacteriaceae is a very large family of Gram-negative bacteria that has been studied and characterized for almost a hundred years. It was first proposed by Rahn in 1936 and now included over 50 genera and over 200 species. Its classification above the level of famil…
Salmonella
Salmonella is a genus of rod-shaped gram-negative bacteria of the family Enterobacteriaceae. The two species of Salmonella are Salmonella enterica and Salmonella bongori. Salmonella enterica is the type species and is further divided into six subspecies that include over 2,500 serot…
Escherichia
Escherichia is a genus of Gram-negative, non-spore-forming, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacteria from the family Enterobacteriaceae. In those species which are inhabitants of the gastrointestinal tracts of warm-blooded animals, Escherichia species provide a portion of the micr…
Is Enterobacter the same as Enterobacteriaceae?
Is Enterobacter the same as Enterobacteriaceae? Enterobacter, (genus Enterobacter), any of a group of rod-shaped bacteria of the family Enterobacteriaceae. Enterobacter are gram-negative bacteria that are classified as facultative anaerobes, which means that they are able to thrive in both aerobic and anaerobic environments.
Is acenobacter and Acinetobacter the same organism?
Acinetobacter is a group of bacteria commonly found in soil and water and sometimes found on the skin of healthy people. There are many types or “species” of Acinetobacter that can cause human disease. The species Acinetobacter baumannii accounts for about 80% of reported infections. Outbreaks of Acinetobacter infection typically occur in hospital intensive care units (ICUs) and healthcare settings with very ill or disabled patients.
Are organisms that obtain energy from other organisms?
The organisms that obtain their energy from other organisms are called consumers. All animals are consumers, and they eat other organisms. What are the three ways organisms can get energy? Energy is the ability to do work. The form of energy that living things need for these processes is chemical energy, and it comes from food.
What does Enterobacteriaceae mean?
Enterobacteriaceae. Enterobacteriaceae is a large family of gram negative, non-spore forming rods, which are facultative anaerobes and capable of fermenting sugars to various end products. From: Food Chemistry, 2015.
See more
What are the organisms in Enterobacteriaceae?
What are the diseases that enterobacteriaceae cause?
What temperature does Enterobacteriaceae grow?
What bacteria cause pneumonia in the elderly?
Why are enterobacteriaceae important?
How many species are there in Enterobacteriaceae?
Which family of organisms ferment glucose?
See more
About this website
Is Enterobacter non pathogenic?
Many members of Class Enterobacteriaceae are nonpathogenic commensals, which live in the human intestines, becoming pathogenic under abnormal circumstances. Other enterobacteria are always pathogenic. The enterobacteriaceae are rod-shaped bacteria.
Is Enterobacteriaceae an opportunistic pathogen?
Relevance of Enterobacter to public health Enterobacter species are considered opportunistic pathogens, rarely causing disease in healthy individuals. The species E. cloacae and E.
What are 3 general characteristics of the Enterobacteriaceae?
The Enterobacteriaceae are facultative anaerobes or aerobes, ferment a wide range of carbohydrates, possess a complex antigenic structure, and produce a variety of toxins and other virulence factors.
What bacteria are considered Enterobacteriaceae?
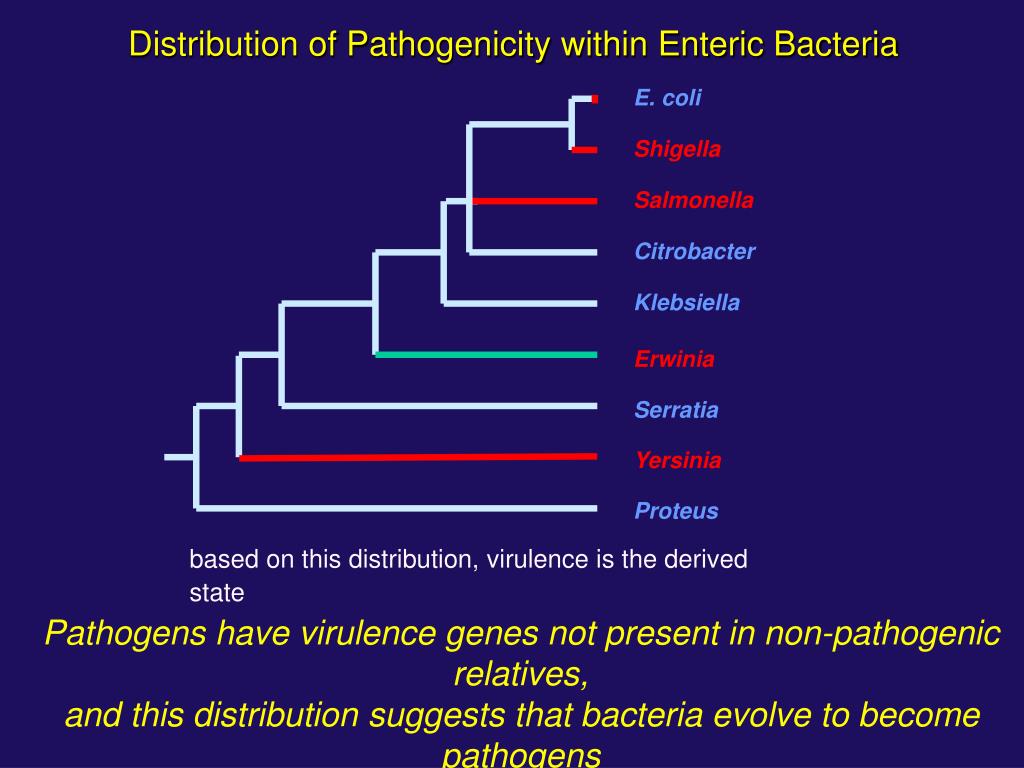
The Enterobacteriaceae are a large family of bacteria, including many of the more familiar pathogens, such as Salmonella, Shigella and Escherichia coli. Members of the Enterobacteriaceae are bacilli (rod-shaped), facultative anaerobes, fermenting sugars to produce lactic acid and various other end products.
Is Enterobacter aerogenes a known pathogen?
It is also a well-known nosocomial pathogen contributing to bacteremia, endocarditis, septic arthritis, osteomyelitis, and skin/soft tissue infections, and lower respiratory tract- urinary tract and intra-abdominal infections (Fata et al., 1996). E.
How are Enterobacteriaceae classified?
Enterobacter, (genus Enterobacter), any of a group of rod-shaped bacteria of the family Enterobacteriaceae. Enterobacter are gram-negative bacteria that are classified as facultative anaerobes, which means that they are able to thrive in both aerobic and anaerobic environments.
Which genus of the enteric group is considered a primary pathogen?
Escherichia coli (E coli) is the most commonly isolated organism in the clinical laboratory. Enteric Infections: E coli is a major enteric pathogen, particularly in developing countries.
Which are considered true enteric pathogens?
The enteric group includes two other important some other intestinal pathogens of humans: Salmonella and Shigella. Shigella dysenteriae causes bacillary dysentery: Salmonella enterica, causes food poisoning and gastroenteritis. Salmonella typhi, which infects via the intestinal route, causes typhoid fever.
What is the difference between Coliforms and Enterobacteriaceae?
The key difference between Coliforms and Enterobacteriaceae is that the Coliforms are a group of grams negative, rod-shaped and lactose fermenting bacteria while Enterobacteriaceae is a large family of grams negative bacteria.
What is non Enterobacteriaceae?
Many gram neg rods are considered enteric or "gut" bacteria (called enterobacteriaceae) and use aerobic respiration. The non-enterobacteriaceae aerobic gram neg rods (non-gut bugs) can be further categorized by their fermentation patterns.
Is Staphylococcus aureus an Enterobacteriaceae?
Staphylococcus aureus was present in five patients and Enterobacteriaceae species in only one individual. Candida albicans was not found in any samples from the palatal mucosa of the 25 individuals without dentures. Of 36 healthy denture wearers C. albicans was found in 9 (25%).
Which of the following are characteristics shared between all bacteria in the Enterobacteriaceae family?
Common characteristics of the family Enterobacteriaceae are:They are gram-negative, short rods.They are non-sporulating, facultative anaerobes.More items...•
The enterobacteriaceae and their significance to the food industry
Request PDF | On Jan 1, 2011, C. Baylis and others published The enterobacteriaceae and their significance to the food industry | Find, read and cite all the research you need on ResearchGate
Enterobacteriaceae - Wikipedia
Enterobacteriaceae is a large family of Gram-negative bacteria.It was first proposed by Rahn in 1936, and now includes over 30 genera and more than 100 species. Its classification above the level of family is still a subject of debate, but one classification places it in the order Enterobacterales of the class Gammaproteobacteria in the phylum Pseudomonadota.
Enterobacteriaceae - Infectious Disease Advisor
OVERVIEW: What every clinician needs to know Pathogen name and classification. The family Enterobacteriaceae consists of a number of species that are gram-negative bacilli (GNB).
Enterobacteriaceae | definition of ... - Medical Dictionary
Enterobacteriaceae: [ en″ter-o-bak-tēr″e-a´se-e ] a family of gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacteria, usually motile, made up of saprophytes and plant and animal parasites of worldwide distribution, found in soil, water, and plants and in animals from insects to humans. In humans, disease is produced by both invasive ...
Enterobacteriaceae Family • Microbe Online
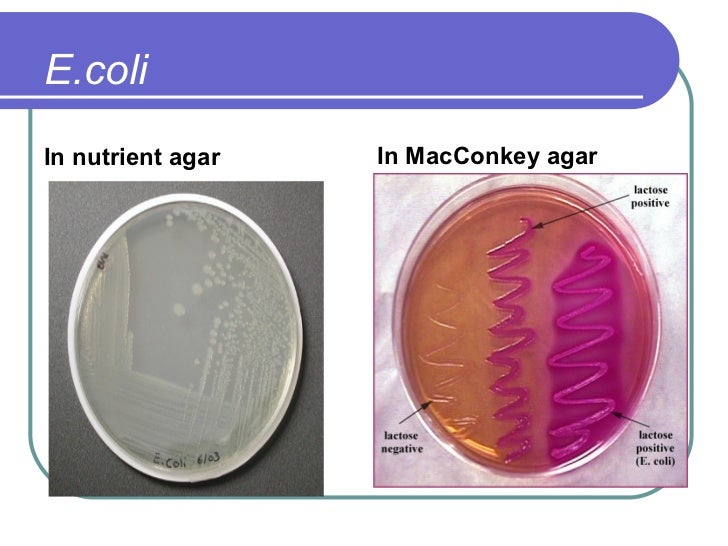
They are gram-negative, short rods ; They are non-sporulating, facultative anaerobes; These organisms have simple nutritional requirements and MacConkey agar is used to isolate and differentiate organisms of the Enterobacteriaceae family (pink-colored colonies of lactose fermenter-coliforms and pale-colored colonies of the non-lactose fermenter)
What are the organisms in Enterobacteriaceae?
Enterobacteriaceae is a large, heterogeneous group of Gram-negative rods that includes bacteria that naturally inhabit the mammalian gut but also can occur and multiply in other environments – for example, species of Escherichia, Citrobacter, Enterobacter, Proteus, Hafnia, Klebsiella, Providencia, and Serratia, and also some of the most important enteric pathogens, such as Salmonella spp., Shigella spp., Yersinia enterocolitica, and pathogenic E. coli. All members of the Enterobacteriaceae family ferment glucose with acid production and reduce nitrates. Certain physiological groups of organisms may be recognized within Enterobacteriaceae. Psychrotrophic members of this family are not uncommon, although the Enterobacteriaceae are regarded widely as being mesophilic. The psychrotrophic strains of Enterobacter, Hafnia, and Serratia may grow in temperatures as low as 0 °C.
What are the diseases that enterobacteriaceae cause?
Enterobacteriaceae can cause a wide range of illnesses, which include wound infections, urinary tract infections, gastroenteritis, meningitis, pneumonia, septicemia, and hemolytic uremic syndrome. Not all are regarded as truly pathogenic – some are regarded as opportunistic. They are ubiquitous in the environment and have been detected in soil, water, plants, and the gastrointestinal tract of animals and humans. Due to its widespread distribution, it can easily contaminate the food chain. The family includes a number of important foodborne pathogens such as Salmonella; Yersinia enterocolitica; pathogenic Escherichia coli, including Escherichia coli O157:H7; Shigella spp.; and Cronobacter spp. Some members of the Enterobacteriaceae family also cause food spoilage such as Erwinia spp. and Pectobacterium spp. In the food industry, Enterobacteriaceae are commonly used as indicator organisms that can indicate poor hygiene practices or failure of a manufacturing process. The various members of the Enterobacteriaceae family are more thoroughly described throughout this book.
What temperature does Enterobacteriaceae grow?
The psychrotrophic strains of Enterobacter, Hafnia, and Serratia may grow in temperatures as low as 0 °C. Enterobacteriaceae is a useful indicator of hygiene and postprocessing contamination of heat-processed foods. This family has been used as indicators of food quality and also for food safety.
What bacteria cause pneumonia in the elderly?
Enterobacteriaceae may cause community-acquired pneumonia in the elderly and are implicated in ventilator-associated pneumonia.63 In particular, K. pneumoniae and E. cloacae are among the most frequent bacteria responsible for ventilator-associated pneumonia, after Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Klebsiella pneumoniae was originally described as the agent of Friedländer's pneumonia, a severe lobar pneumonia, and remains an important cause of hospital- and community-acquired pneumonia, even though the incidence of community-acquired pneumonia has decreased in North America and Europe 61 (see ‘ Other infections and rare or emerging Enterobacteriaceae pathogens ’ below and Chapter 28 ).
Why are enterobacteriaceae important?
Enterobacteriaceae is a useful indicator of hygiene and postprocessing contamination of heat-processed foods. This family has been used as indicators of food quality and also for food safety. Enterobacteriaceae counts are an effective method to assess environments, such as postprocess food contact surfaces and help to quickly determine potential sources of contamination. Enterobacteriaceae may be superior to the coliforms as indicators of sanitation because, collectively, they have greater resistance to the environment than the coliforms and can better assess glucose-positive, lactose-negative members of the food microflora.
How many species are there in Enterobacteriaceae?
There are over 30 genera and 120 species of Enterbacteriaceae but more than 95% of clinically significant strains fall into 10 genera and less than 25 species.
Which family of organisms ferment glucose?
All members of the Enterobacteriaceae family ferment glucose with acid production and reduce nitrates. Certain physiological groups of organisms may be recognized within Enterobacteriaceae. Psychrotrophic members of this family are not uncommon, although the Enterobacteriaceae are regarded widely as being mesophilic.
What is the original order of Enterobacteriaceae?
Enterobacteriaceae was originally the sole family under the order 'Enterobacteriales' . The family contained a large array of biochemically distinct species with different ecological niches, which made biochemical descriptions difficult. The original classification of species to this family and order was largely based on 16S rRNA genome sequence analyses, which is known to have low discriminatory power and the results of which changes depends on the algorithm and organism information used. Despite this, the analyses still exhibited polyphyletic branching, indicating the presence of distinct subgroups within the family.
Why are enterobacteria important?
Some enterobacteria are important pathogens, e.g. Salmonella, or Shigella e.g. because they produce endotoxins. Endotoxins reside in the cell wall and are released when the cell dies and the cell wall disintegrates. Some members of the Enterobacteriaceae produce endotoxins that, when released into the bloodstream following cell lysis, ...
What is the name of the family of bacteria that is Gram negative?
Enterobacteriaceae is a large family of Gram-negative bacteria. It was first proposed by Rahn in 1936, and now includes over 30 genera and more than 100 species. Its classification above the level of family is still a subject of debate, but one classification places it in the order Enterobacterales of the class Gammaproteobacteria in the phylum Proteobacteria. In 2016, the description and members of this family were emended based on comparative genomic analyses by Adeolu et al.
What genes are used in carbapenem resistant Enterobacteriaceae?
Various carbapenemases genes (blaOXA-48, blaKPC and blaNDM-1, blaVIM and blaIMP) have been identified in carb apenem resistant Enterobacteriaceae including Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae.
What are the other bacteria that cause disease?
Other disease-causing bacteria in this family include Enterobacter and Citrobacter. Members of the Enterobacteriaceae can be trivially referred to as enterobacteria or "enteric bacteria", as several members live in the intestines of animals.
How many clades are there in the Enterobacteriaceae family?
In 2017, a subsequent study using comparative phylogenomic analyses identified the presence of 6 subfamily level clades within the family Enterobacteriaceae, namely the “Escherichia clade”, “Klebsiella clade”, “Enterobacter clade”, “Kosakonia clade”, “Cronobacter clade”, “Cedecea clade” and a “Enterobacteriaceae incertae sedis clade” containing species whose taxonomic placement within the family is unclear. However, this division was not officially proposed as the subfamily rank is generally not used.
Which type of fimbriae are most involved in the adhesion of bacterial cells to their hosts?
Most have many flagella used to move about, but a few genera are nonmotile. Most members of Enterobacteriaceae have peritrichous, type I fimbriae involved in the adhesion of the bacterial cells to their hosts.
What is the family of Enterobacteriaceae?
The family Enterobacteriaceae consists of a number of species that are gram-negative bacilli (GNB). Salmonella, Shigella, and Yersinia are not discussed here. Most of the other Enterobacteriaceae cause a wide variety of extra-intestinal infections. Edwardsiella tardi can cause both extra-intestinal and intestinal infection.
Which is the most virulent bacterial infection?
ExPEC and Klebsiella are the most virulent, being able to cause infection in healthy hosts and cause the majority of infections.
Can Enterobacteriaceae cause extra intestinal infection?
The Enterobacteriaceae discussed here cause extra-intestinal infection (except Edwardsiella, which can cause extra- and intra-intestinal infection, and perhaps a toxin-producing variant of Klebsiella).
Can ExPEC cause septic shock?
Since nearly everyone is colonized with ExPEC, entry, not acquisition is generally the limiting step for infection. This is the most common cause of severe sepsis and septic shock. Bacteremia can arise from any site of infection.
Is antimicrobial use a global pathogen?
Antimicrobial use, co-morbidities, and extended length of hospital stay are associated with increased colonization with these GNB. As a result of these epidemiologic features, they are global pathogens. Generally, there are no seasonal differences in the incidence of infection.
Is Klebsiella oxytoca a hemorrhagic colitis?
Klebsiella causes extra-intestinal infection, but a hemorrhagic colitis has been associated with Klebsiella oxytoca. Members of this group are becoming highly resistant to antimicrobials, and some members are professional pathogens capable of infecting both healthy and compromised hosts.
Can enterobacteriaceae cause sepsis?
Infection due to all of the Enterobacteriaceae discussed here has the potential to be complicated by sepsis, severe sepsis (sepsis plus organ failure distant from the site of infection), and septic shock.
What is the family of Enterobacteriaceae?
Enterobacteriaceae are a large family of Gram-negative bacteria that includes a number of pathogens such as Klebsiella, Enterobacter, Citrobacter, Salmonella, Escherichia coli, Shigella, Proteus, Serratia and other species.
Which group of antibiotics are resistant to Enterobacteriaceae?
Enterobacteriaceae, like all bacteria, can develop resistance to antibiotics, including the carbapenem group of antibiotics, which are sometimes referred to as the last line of antibiotic treatment against resistant organisms.
What are the organisms in Enterobacteriaceae?
Enterobacteriaceae is a large, heterogeneous group of Gram-negative rods that includes bacteria that naturally inhabit the mammalian gut but also can occur and multiply in other environments – for example, species of Escherichia, Citrobacter, Enterobacter, Proteus, Hafnia, Klebsiella, Providencia, and Serratia, and also some of the most important enteric pathogens, such as Salmonella spp., Shigella spp., Yersinia enterocolitica, and pathogenic E. coli. All members of the Enterobacteriaceae family ferment glucose with acid production and reduce nitrates. Certain physiological groups of organisms may be recognized within Enterobacteriaceae. Psychrotrophic members of this family are not uncommon, although the Enterobacteriaceae are regarded widely as being mesophilic. The psychrotrophic strains of Enterobacter, Hafnia, and Serratia may grow in temperatures as low as 0 °C.
What are the diseases that enterobacteriaceae cause?
Enterobacteriaceae can cause a wide range of illnesses, which include wound infections, urinary tract infections, gastroenteritis, meningitis, pneumonia, septicemia, and hemolytic uremic syndrome. Not all are regarded as truly pathogenic – some are regarded as opportunistic. They are ubiquitous in the environment and have been detected in soil, water, plants, and the gastrointestinal tract of animals and humans. Due to its widespread distribution, it can easily contaminate the food chain. The family includes a number of important foodborne pathogens such as Salmonella; Yersinia enterocolitica; pathogenic Escherichia coli, including Escherichia coli O157:H7; Shigella spp.; and Cronobacter spp. Some members of the Enterobacteriaceae family also cause food spoilage such as Erwinia spp. and Pectobacterium spp. In the food industry, Enterobacteriaceae are commonly used as indicator organisms that can indicate poor hygiene practices or failure of a manufacturing process. The various members of the Enterobacteriaceae family are more thoroughly described throughout this book.
Why are enterobacteriaceae important?
Enterobacteriaceae is a useful indicator of hygiene and postprocessing contamination of heat-processed foods. This family has been used as indicators of food quality and also for food safety. Enterobacteriaceae counts are an effective method to assess environments, such as postprocess food contact surfaces and help to quickly determine potential sources of contamination. Enterobacteriaceae may be superior to the coliforms as indicators of sanitation because, collectively, they have greater resistance to the environment than the coliforms and can better assess glucose-positive, lactose-negative members of the food microflora.
How are Enterobacteriaceae isolates identified?
All Enterobacteriaceae isolates are identified biochemically using systems like API 20E manufactured by bioMérieux. Important serotypes can also be differentiated by their O (lipopolysaccharide), H (flagellar), and K (capsular) antigens.
What is the role of Enterobacteriaceae in the human body?
The Enterobacteriaceae includes organisms with a wide range of disease-causing potential, encompassing beneficial commensal microbiota, opportunistic pathogens that can inflict considerable morbidity and mortality on compromised hosts, and principal pathogens capable of initiating illness in individuals in perfect health.
What bacteria cause pneumonia in the elderly?
Enterobacteriaceae may cause community-acquired pneumonia in the elderly and are implicated in ventilator-associated pneumonia.63 In particular, K. pneumoniae and E. cloacae are among the most frequent bacteria responsible for ventilator-associated pneumonia, after Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Klebsiella pneumoniae was originally described as the agent of Friedländer's pneumonia, a severe lobar pneumonia, and remains an important cause of hospital- and community-acquired pneumonia, even though the incidence of community-acquired pneumonia has decreased in North America and Europe 61 (see ‘ Other infections and rare or emerging Enterobacteriaceae pathogens ’ below and Chapter 28 ).
How many species are there in Enterobacteriaceae?
There are over 30 genera and 120 species of Enterbacteriaceae but more than 95% of clinically significant strains fall into 10 genera and less than 25 species.
How are members of the Enterobacteriaceae family identified?
Members of the Enterobacteriaceae family are identified based on their biochemical properties. Commonly used biochemical tests to identify them are (Please click on the test name to know more about that particular test);
What are the characteristics of Enterobacteriaceae?
Enterobacteriaceae family contains a large number of genera that are biochemically and genetically related to one another. Many of the traditional or familiar bacteria are found in this family e.g. Escherichia, Shigella, Salmonella, Enterobacter, Proteus, Yersinia etc.
Which bacteria reduce nitrate to nitrogen?
Usually reduces Nitrate to Nitrite ( distinguishes enteric bacteria from bacteria that reduce nitrate to Nitrogen gas, such as Pseudomonas and many other oxidase-positive bacteria). Produces acid from glucose; ability to ferment lactose- distinguishes enteric from obligately aerobic bacteria.
Is Shigella lateral or peritrichous?
Motility if present is by means of peritrichous ( lateral) flagella, except Shigella and Klebsiella which are non-motile.
Abstract
Foodborne pathogens of Enterobacteriaceae including Escherichia coli, Salmonella, Shigella, Yersinia, etc., causes a great number of diseases and has a significant impact on human health. Here, we reviewed the prevalence, virulence, and antimicrobial susceptibility of Enterobacteriaceae belonging to 4 genera: E.
1. Introduction
Foodborne illness is the biggest health problem in the world. Due to unsanitary food processing methods, this situation is very serious in developing countries. Approximately 70% of diarrhea cases in developing countries are related to the consumption of contaminated food.
2. Transmission of pathogens in the food chain
Foodborne pathogens are transmitted through the food chain in many ways, such as insect transmission, fecal-oral transmission, food and water transmission, animals transmission, and so on. Some pathogens, such as E.
3. Antimicrobial resistance, genetic diversity and molecular epidemiology of the Enterobacteriaceae foodborne pathogens
E. coli is one of the most common food-borne pathogens and may spread a variety of diseases through the food chain in different ecosystems. There are pathogenic and non-pathogenic strains of E. coli. Of these, pathogenic strains can cause a variety of intestinal diseases.
4. Novel technologies for detecting the pathogens
In recent years, the rapid detection of foodborne pathogens has developed rapidly. Molecular biology, nucleic acid hybridization, and other technologies have been highly valued and widely used in laboratory or factory production.
5. Controlling of the Enterobacteriaceae foodborne pathogens
At present, food pollution and poisoning caused by foodborne pathogens have attracted extensive attention.
6. Conclusion
A plenty number of studies have been confirmed that foodborne pathogens of Enterobacteriaceae and their resistance genes can not only remain in animal husbandry and related environment but also transmitted to human beings through the food chain or other ways, causing a major threat to public health.
What are the organisms in Enterobacteriaceae?
Enterobacteriaceae is a large, heterogeneous group of Gram-negative rods that includes bacteria that naturally inhabit the mammalian gut but also can occur and multiply in other environments – for example, species of Escherichia, Citrobacter, Enterobacter, Proteus, Hafnia, Klebsiella, Providencia, and Serratia, and also some of the most important enteric pathogens, such as Salmonella spp., Shigella spp., Yersinia enterocolitica, and pathogenic E. coli. All members of the Enterobacteriaceae family ferment glucose with acid production and reduce nitrates. Certain physiological groups of organisms may be recognized within Enterobacteriaceae. Psychrotrophic members of this family are not uncommon, although the Enterobacteriaceae are regarded widely as being mesophilic. The psychrotrophic strains of Enterobacter, Hafnia, and Serratia may grow in temperatures as low as 0 °C.
What are the diseases that enterobacteriaceae cause?
Enterobacteriaceae can cause a wide range of illnesses, which include wound infections, urinary tract infections, gastroenteritis, meningitis, pneumonia, septicemia, and hemolytic uremic syndrome. Not all are regarded as truly pathogenic – some are regarded as opportunistic. They are ubiquitous in the environment and have been detected in soil, water, plants, and the gastrointestinal tract of animals and humans. Due to its widespread distribution, it can easily contaminate the food chain. The family includes a number of important foodborne pathogens such as Salmonella; Yersinia enterocolitica; pathogenic Escherichia coli, including Escherichia coli O157:H7; Shigella spp.; and Cronobacter spp. Some members of the Enterobacteriaceae family also cause food spoilage such as Erwinia spp. and Pectobacterium spp. In the food industry, Enterobacteriaceae are commonly used as indicator organisms that can indicate poor hygiene practices or failure of a manufacturing process. The various members of the Enterobacteriaceae family are more thoroughly described throughout this book.
What temperature does Enterobacteriaceae grow?
The psychrotrophic strains of Enterobacter, Hafnia, and Serratia may grow in temperatures as low as 0 °C. Enterobacteriaceae is a useful indicator of hygiene and postprocessing contamination of heat-processed foods. This family has been used as indicators of food quality and also for food safety.
What bacteria cause pneumonia in the elderly?
Enterobacteriaceae may cause community-acquired pneumonia in the elderly and are implicated in ventilator-associated pneumonia.63 In particular, K. pneumoniae and E. cloacae are among the most frequent bacteria responsible for ventilator-associated pneumonia, after Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Klebsiella pneumoniae was originally described as the agent of Friedländer's pneumonia, a severe lobar pneumonia, and remains an important cause of hospital- and community-acquired pneumonia, even though the incidence of community-acquired pneumonia has decreased in North America and Europe 61 (see ‘ Other infections and rare or emerging Enterobacteriaceae pathogens ’ below and Chapter 28 ).
Why are enterobacteriaceae important?
Enterobacteriaceae is a useful indicator of hygiene and postprocessing contamination of heat-processed foods. This family has been used as indicators of food quality and also for food safety. Enterobacteriaceae counts are an effective method to assess environments, such as postprocess food contact surfaces and help to quickly determine potential sources of contamination. Enterobacteriaceae may be superior to the coliforms as indicators of sanitation because, collectively, they have greater resistance to the environment than the coliforms and can better assess glucose-positive, lactose-negative members of the food microflora.
How many species are there in Enterobacteriaceae?
There are over 30 genera and 120 species of Enterbacteriaceae but more than 95% of clinically significant strains fall into 10 genera and less than 25 species.
Which family of organisms ferment glucose?
All members of the Enterobacteriaceae family ferment glucose with acid production and reduce nitrates. Certain physiological groups of organisms may be recognized within Enterobacteriaceae. Psychrotrophic members of this family are not uncommon, although the Enterobacteriaceae are regarded widely as being mesophilic.

Overview
Enterobacteriaceae is a large family of Gram-negative bacteria. It was first proposed by Rahn in 1936, and now includes over 30 genera and more than 100 species. Its classification above the level of family is still a subject of debate, but one classification places it in the order Enterobacterales of the class Gammaproteobacteria in the phylum Pseudomonadota. In 2016, the descriptio…
Morphology
Members of the Enterobacteriaceae are bacilli (rod-shaped), and are typically 1–5 μm in length. They typically appear as medium to large-sized grey colonies on blood agar, although some can express pigments.
Most have many flagella used to move about, but a few genera are nonmotile. Most members of Enterobacteriaceae have peritrichous, type I fimbriae involved in the adhesion of the bacterial cell…
Metabolism
Like other Pseudomonadota, Enterobactericeae have Gram-negative stains, and they are facultative anaerobes, fermenting sugars to produce lactic acid and various other end products. Most also reduce nitrate to nitrite, although exceptions exist. Unlike most similar bacteria, Enterobacteriaceae generally lack cytochrome c oxidase, there are exceptions.
Catalase reactions vary among Enterobacteriaceae.
Ecology
Many members of this family are normal members of the gut microbiota in humans and other animals, while others are found in water or soil, or are parasites on a variety of different animals and plants.
Model organisms and medical relevance
Escherichia coli is one of the most important model organisms, and its genetics and biochemistry have been closely studied.
Some enterobacteria are important pathogens, e.g. Salmonella, or Shigella e.g. because they produce endotoxins. Endotoxins reside in the cell wall and are released when the cell dies and the cell wall disintegrates. Some members of the Enterobacteriaceae produce endotoxins that, whe…
Historical systematics and taxonomy
Enterobacteriaceae was originally the sole family under the order 'Enterobacteriales'. The family contained a large array of biochemically distinct species with different ecological niches, which made biochemical descriptions difficult. The original classification of species to this family and order was largely based on 16S rRNA genome sequence analyses, which is known to have low discriminatory power and the results of which changes depends on the algorithm and organism …
Molecular signatures
Analyses of genome sequences from Enterobacteriaceae species identified 21 conserved signature indels (CSIs) that are uniquely present in this family in the proteins NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (subunit M), twitching motility protein PilT, 2,3-dihydroxybenzoate-AMP ligase, ATP/GTP-binding protein, multifunctional fatty acid oxidation complex (subunit alpha), S-formylglutathione hydrolase, aspartate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase, epimerase, membrane prot…
Genera
The following genera have been validly published, thus they have "Standing in Nomenclature". The year the genus was proposed is listed in parentheses after the genus name.
• Biostraticola (2008)
• Buttiauxella (1982)
• Cedecea (1981)