Annelid
The annelids, also known as the ringed worms or segmented worms, are a large phylum, with over 22,000 extant species including ragworms, earthworms, and leeches. The species exist in and have adapted to various ecologies – some in marine environments as distinct as tidal zones a…
What is the feeding mechanism of annelids?
Annelids are heterotrophic. They are metamerically segmented invertebrates. They have a well developed complete digestive system. They feed on soil, small invertebrates or dead and decaying organic matter. According to their diverse habitat, their feeding mechanism differs. Earthworms live in the soil. They are soil-eaters.
How many types of annelids are there?
Jump to navigation Jump to search. The annelids (Annelida, from Latin anellus, "little ring"), also known as the ringed worms or segmented worms, are a large phylum, with over 22,000 extant species including ragworms, earthworms, and leeches.
What animals eat annelids?
They are a major part of the diet for many fish and for many land animals such as moles, hedgehogs and birds such as the black bird. How common are Annelids? Annelids are often almost invisible in a habitat as they tend to be burrowing animals when present in largest numbers.
Where do annelids live?
The species exist in and have adapted to various ecologies – some in marine environments as distinct as tidal zones and hydrothermal vents, others in fresh water, and yet others in moist terrestrial environments. The Annelids are bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic, coelomate, invertebrate organisms.
What type of feeders are annelids?
Annelids are heterotrophic. They are metamerically segmented invertebrates. They have a well developed complete digestive system. They feed on soil, small invertebrates or dead and decaying organic matter.
Are Annelida deposit feeders?
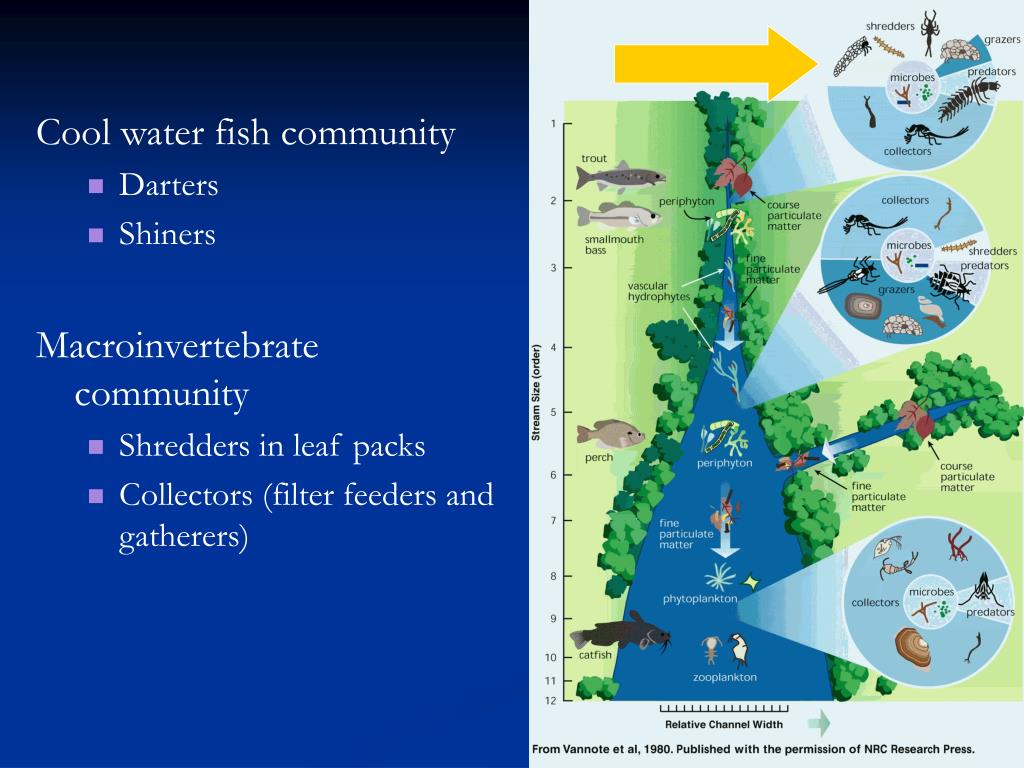
Ecology of Annelids Annelids live in a diversity of freshwater, marine, and terrestrial habitats. They vary in what they feed on and how they obtain their food. Earthworms are deposit feeders. They burrow through the ground, eating soil and extracting organic matter from it.
How do annelids transport nutrients?
Annelids have a closed circulatory system in which blood is pumped along by muscles in blood vessels (Fig. 3.48). Blood flows through the microscopic capillaries, picking up food molecules from the digestive tract and oxygen from the skin and transporting them to the cells of the body.
How do annelids reproduce and feed?
They generally reproduce sexually by cross-fertilization and are often hermaphroditic, but many reproduce asexually by budding. The freshwater annelids include the oligocheates, the leeches, and several other less diverse classes.
What is annelids function?
In addition to improving soil fertility, annelids serve humans as food and as bait. Scientists observe annelids to monitor the quality of marine and fresh water.
Are annelids parasitic?
The name of the phylum is derived from the Latin word annellus, which means a small ring. Animals in this phylum show parasitic and commensal symbioses with other species in their habitat. Approximately 16,500 species have been described in phylum Annelida.
What are some ways that annelids are beneficial?
Burrowing annelids, like the earthworm, play an important role in helping organic matter decompose. Earthworms eat dead plants and animals. When they eat, they also take in soil and tiny pebbles. Earthworms take in nutrients from microorganisms in the material they ingest.
How do annelids get rid of waste?
d) Waste disposal i) In each segment worms have a specialized structure called a nephridia that filters metabolic waste out of the blood (like a human kidney) ii) Once the waste are out they go into a bladder and finally out a tube to be excreted.
What are the general characteristics of Annelida?
Characteristics of Phylum Annelida They have a long and segmented body. Annelids are bilaterally symmetrical. They are triploblastic. Also, they exhibit organ system grade of organisation, showing organ differentiation.
How do earthworms eat?
How do worms eat? worms or nightcrawlers often surface at night to pull fallen leaves down into their burrow. When the leaf softens a little they pull off small bits to munch on. Worms also "swallow" soil as they burrow.
Can annelids self fertilize?
These worms typically will find a partner to reproduce via cross fertilization. In cross fertilization, annelids align their bodies so that they can fertilize each other. Although many worms are hermaphrodites, they do not reproduce asexually, nor do they self-fertilize.
Why annelids are called segmented worms?
Annelids are often called “segmented worms” because they possess true segmentation of their bodies, with both internal and external morphological features repeated in each body segment.
Are snails deposit feeders?
For sediment particles <40 μm diameter, the snails deposit-feed (i.e., swallow all particles), although they may be capable of some selection according to size or the presence or absence of an organic film on the sediment surface.
Are molluscs deposit feeders?
Molluscs inhabit a range of environments from marine, freshwater, to terrestrial and have a variety of feeding modes including deposit feeders, filter feeders, herbivores, detritivores, and predators.
What do deposit feeders eat?
sedimentsDeposit feeders ingest particles associated with sediments or, in many cases, they ingest the sediment particles themselves and strip off nutrition in the form of detritus associated with the sediment grains and also associated microbes.
Are sea urchins deposit feeders?
As a matter of fact, the irregular sea urchins are major deposit-feeders, feeding on detritus particles by the ingestion of surface sediment (De Ridder et al., 1987).
1. Why is Filter-Feeding important?
When small prey densities are high, filter-feeding allows individuals to capture and process huge amounts of prey in a single mouthful, allowing th...
2. How do filter feeders clean water?
Shellfish such as oysters, clams, and other shellfish are effective filter feeders, absorbing extra nitrogen into their shells and tissue as they g...
3. What is the difference between suspension feeders and filter feeders?
Suspension feeders, on the other hand, eat items that are suspended in water, whereas filter feeders eat items that are so big that they aren't pro...
4. What is the Filter-Feeding mechanism?
Filter feeding is a type of aquatic feeding in which the animal consumes a large number of small prey pieces at once. Filter feeding, in contrast t...
5. How is suction feeding different from filter-feeding?
In Suction feeding, the prey particles in the fluid are ingested into the mouth of predators by sucking it. The throat cavity’s capacity is expande...
6. What is the significance of the filter-feeding method?
The filter-feeding is important not only for the organism but for the overall environment. It helps in cleaning the water body. Filter feeder organ...
7. What do the filter feeders feed upon?
There are a number of filter feeders like clams, sponges, krill, whales, fishes, etc. These organisms feed upon the phytoplankton which is their ma...
8. What is ram feeding?
Ram is also an important feeding method along with the other five methods. It is also called lunge feeding. In this type of feeding method, the hun...
9. Why is the word filter used in the filter-feeding method?
The word filter signifies that the organism has the adaptation technique of filtering out the unnecessary particles from the water to solely consum...
What do annelids eat?
They have a well developed complete digestive system. They feed on soil, small invertebrates or dead and decaying organic matter. According to their diverse habitat, their feeding mechanism differs. Earthworms live in the soil.
Where does the digestion process take place in an annelid?
The digestion completes in the intestine followed by absorption of nutrients. The typhlosole region of the intestine increases the surface area of absorption. The undigested food is excreted out through the anus and known as worm castings. This was in brief about the feeding mechanism in Annelids.
What do earthworms eat?
Earthworms feed on soil with dead and decaying organic matter. Their body is segmented and the unsegmented alimentary canal runs throughout their body from mouth to anus. This type of digestive system is known as ‘tube within a tube’.
What animals are filter feeders?
Filter Feeding Animals. Clams, krill, sponges, baleen whales, and a variety of fish are among the filter feeding animals (including some sharks). Some birds, such as flamingos and certain duck species, are filter feeders as well.
What is filter feeding?
In zoology, filter feeding is a method of obtaining food in which food particles or microscopic creatures are randomly filtered from the water. Filter feeding is mostly found in small to medium-sized invertebrates, although it can also be seen in a few large vertebrates (e.g., flamingos, baleen whales). The gills of bivalves like the clam, which ...
How are food particles moved from the filter to the animal's mouth?
Food particles are moved from the filter to the animal's mouth via mechanisms. External Filter Feeders - All barnacles, both acorn and goose, as well as various types of polychaete worms, adopt this method. Barnacles are crustaceans that have been considerably changed, standing on their heads and sifting with their legs.
What is the phylum of annelida?
The phylum Annelida is divided into four main classes, one of which is the Polychaeta class. Filter feeders include several sedentary and tubicolous polychaetes (such as Sabella). Polychaetes have long bipinnate filaments or tentacles called radides on their heads, with a ciliated groove running along their oral surface. ...
What are the feeders for whales?
Filter feeders include blue and humpback whales, as well as other baleen whales. They take in large gulps of krill-infested saltwater, squeezing the water through their baleen, and swallowing their catch.
How many types of filter feeders are there?
There are Two Types of Filter Feeders: Internal Filter Feeders - Internal filter feeders have a basket-like filter inside a body cavity with two syphons that open to the outside. Water is brought in by one hole (the incurrent syphon), pumped through the filter to remove minute food particles, and then discharged via another opening ...
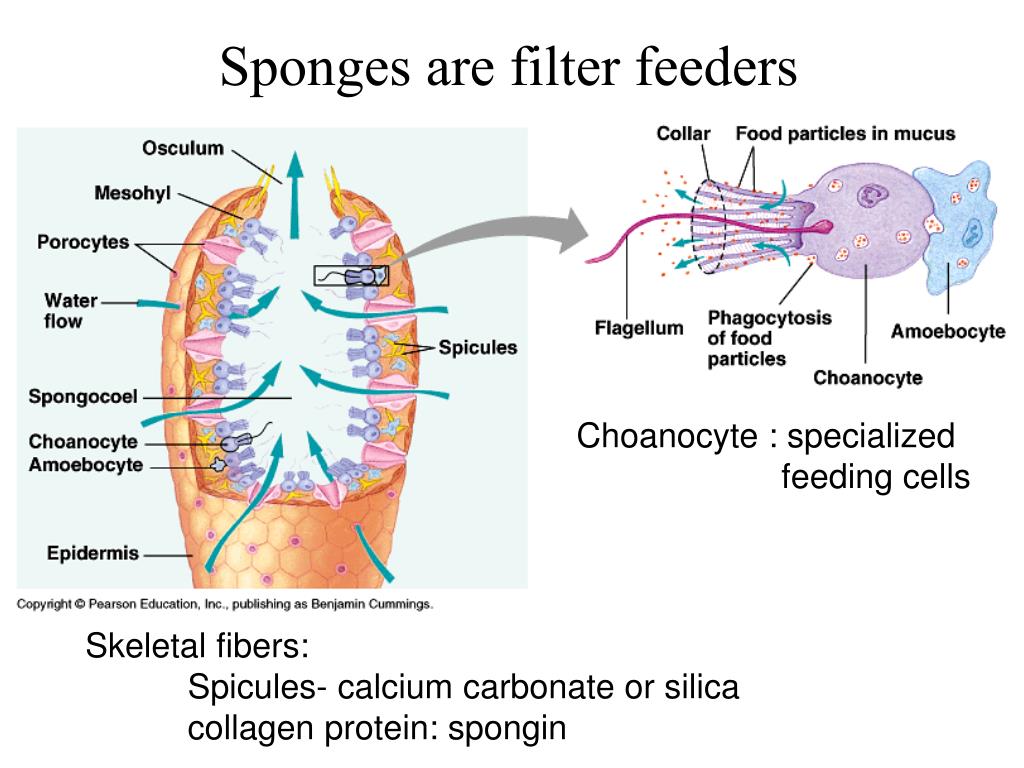
How do sponges feed?
Filter Feeding Mechanisms in the Sponges. Sponges are inanimate, yet they have a water current system composed of canals and chambers that allow them to pump in water, filter food, and consume a large amount of it. The sponge gets water through a pore called the ostra. The meal is subsequently captured by collar cells as it moves through the system.
What are annelids made of?
The annelids include earthworms, polychaete worms, and leeches. All members of the group are to some extent segmented, in other words, made up of segments that are formed by subdivisions that partially transect the body cavity. Segmentation is also called metamerism.
What is the body wall of an annelid?
Besides being segmented, the body wall of annelids is characterized by being made up of both circular and longitudinal muscle fibers surrounded by a moist, acellular cuticle that is secreted by an epidermal epithelium.
Is an annelid monoecious?
Annelids may be monoecious or dioecious. Larva may or may not be present; if present they are of the trochophore type. Some forms also reproduce asexually. They are protostomes, with spiral cleavage. Members of the Phylum Annelida can be found throughout the world, in marine, freshwater, and terrestrial environments.
Is an annelid a coelom?
Annelids are schi zocoelous and with a large and well-developed true coelom (i.e., one that is lined with mesoderm). Except in leeches, the coelom is partially subdivided by septa. Hydrostatic pressure is maintained across segments and helps maintain body rigidity, allowing muscle contractions to bend the body without collapsing it.
Who Belongs in Phylum Annelida?
If you are an avid gardener , you may often encounter a common member of the phylum Annelida. The earthworm, well-liked for creating healthy soil for our earth, is perhaps the most recognizable creature in this group. Known for their long, segmented bodies, annelids, such as earthworms, leeches, and many marine worms, certainly have their place in the world. In this lesson, we will learn more about phylum Annelida and gain an understanding of what makes them unique.
What are the three classes of Annelida?
There are three classes within phylum Annelida. First, we will take a look at Oligochaeta, the class containing the ever-popular earthworm (as well as many aquatic worms). Earthworms are often used in dissection labs to observe and analyze body parts of animals in this phylum. As previously mentioned, the segments are prominent on earthworms, giving them a ringed appearance. Each segment contains tiny bristles called setae, which help them grip the ground as they burrow.
Why are earthworms used in dissection labs?
Earthworms are often used in dissection labs to observe and analyze body parts of animals in this phylum. As previously mentioned, the segments are prominent on earthworms, giving them a ringed appearance. Each segment contains tiny bristles called setae, which help them grip the ground as they burrow.
What are annelids in birds?
Annelids are largish worms, easily visible to the naked eye, they are the worms we think of when considering the morning habits of the early bird. They often appear quite similar unless you are another worm, they may be free or tube living and have a range of feeding strategies. Earthworms help shape the very landscape and improve agricultural land.
What are the annelids that help to recycle dead leaves?
Earthworms are the best known Annelids, diligently going about their quiet business turning the soil over, helping to recycle dead leaves and other vegetation, improving the texture and nutrient content of the soil. There are many other types though including leeches and many aquatic and marine species that may be active hunters, filter feeders and may be surprisingly active swimmers. Their defining characteristic is their segmentation, they are made of a large number of repeated body sections each of which is more or less identical.
What are filter feeders?
There are many such as the feather-duster worms that are filter feeders, using radioles protruded from their burrows to capture small planktonic organisms in the water to bring to the mouth. Other filter feeders may live in tube and siphon water through one entrance and out again through a second in a similar manner to the rag worms above.
What did Charles Darwin think of annelids?
Charles Darwin thought they were one of the most important organisms on the earth, they are in no small part responsible for the gentle rolling landscape of England where he studied them. Locomotion in Annelids. The hydrostatic (contained water) skeleton of annelids is held within the segments as in A and B above.
Do annelids hunt?
Some annelids are hunters, the prey usually being other small invertebrates. Some are completely free living, other are tube dwellers and emerge from the tube to grab suitable prey with their jaws as they pass by. Many leeches catch their food in this manner too, often swallowing them whole, even if quite large.