Can junctional escape rhythm be life-saving?
In case of sinus arrest (or any scenario in which atrial impulses do not reach the atrioventricular node), junctional escape rhythm may be life-saving. During complete heart block (third-degree AV-block) the block may be located anywhere between the atrioventricular node and the bifurcation of the bundle of His.
What causes a junctional or ventricular escape rhythm?
Conditions leading to the emergence of a junctional or ventricular escape rhythm include: Severe sinus bradycardia. Sinus arrest. Sino-atrial exit block. High-grade second degree AV block. Third degree AV block. Hyperkalaemia. Drugs: beta-blocker, calcium-channel blocker or digoxin poisoning.
What is the pathophysiology of a junctional escape complex?
A junctional escape complex is a normal response that may result from excessive vagal tone on the SA node (e.g. digoxin toxicity), a pathological slowing of the SA discharge, or a complete AV block. Rhythm: Irregular in single junctional escape complex; regular in junctional escape rhythm. P waves: Depends on the site of the ectopic focus.
What causes a junctional rhythm?
A Junctional rhythm can happen either due to the sinus node slowing down or the AV node speeding up. It is generally a benign arrhythmia and in the absence of structural heart disease and symptoms, generally no treatment is required.
Can you live with junctional rhythm?
AV nodal junctional rhythms generally are well tolerated; however, bradycardia for prolonged periods often causes symptoms such as dizziness and presyncope or, rarely, frank syncope in younger patients.
Is junctional escape rhythm a risk factor for heart failure?
Whenever there is a long enough pause before an impulse reaches the AV node, the junctional pacemaker can elicit a junctional beat. Sustained junctional escape rhythms may be seen with congestive heart failure, dioxin toxicity or myocarditis.
Can junctional rhythm cause strokes?
Junctional bradycardia is potentially associated with ischemic stroke, particularly in the absence of an identifiable retrograde P wave.
What symptoms might occur in a patient with junctional escape rhythm?
Junctional rhythm can cause symptoms due to bradycardia and/or loss of AV synchrony. These symptoms (which can be vague and easily missed) include lightheadedness, palpitations, effort intolerance, chest heaviness, neck tightness or pounding, shortness of breath, and weakness.
Why are junctional rhythms bad?
Even in the setting of acute MI, junctional rhythms are usually considered benign and require no treatment. However, in certain patients the loss of AV synchrony during a junctional rhythm will result in myocardial ischemia, heart failure, or hypotension.
How common is junctional rhythm?
How common is a junctional rhythm? A junctional rhythm is less common than other arrhythmias like atrial fibrillation. It is often found in children or adults who have: Had a recent heart transplant or heart surgery.
Which arrhythmia increases the risk of stroke?
Atrial fibrillation (A-fib) is an irregular and often very rapid heart rhythm (arrhythmia) that can lead to blood clots in the heart. A-fib increases the risk of stroke, heart failure and other heart-related complications.
Can skipped heart beats cause a stroke?
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is a heart condition that causes an irregular heartbeat and raises your risk of a serious stroke.
In which rhythm is decreased cardiac output most likely to be a concern?
Bradycardia. Bradycardia, whether of atrial or ventricular origin, decreases cardiac output and thereby decreases arterial pressure. The reduced pressure can result in syncope (i.e., fainting) and other symptoms related to hypotension.
What is the heart rate range for junctional escape rhythm?
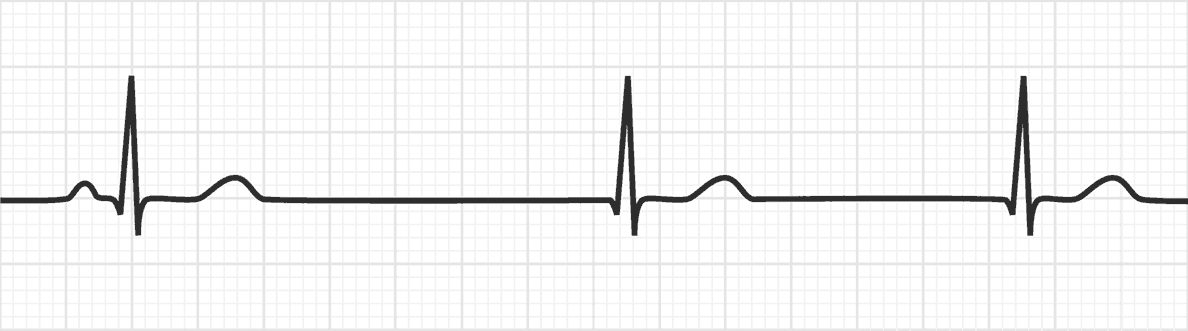
Junction escape rhythm: rate 40 to 60 beats per minute.
What is a characteristic of a junctional escape beat?
ECG features of Junctional Escape Rhythm Junctional rhythm with a rate of 40-60 bpm. QRS complexes are typically narrow (< 120 ms) No relationship between the QRS complexes and any preceding atrial activity (e.g. P-waves, flutter waves, fibrillatory waves)
Can anxiety cause junctional rhythm?
An issue with your heart's electrical wiring system can lead to junctional tachycardia. You may be born with it, or it might happen later. Drug use or anxiety could trigger the condition. In some cases, an injury during heart surgery may be the cause.
In which rhythm is decreased cardiac output most likely to be a concern?
Bradycardia. Bradycardia, whether of atrial or ventricular origin, decreases cardiac output and thereby decreases arterial pressure. The reduced pressure can result in syncope (i.e., fainting) and other symptoms related to hypotension.
What is the difference between junctional rhythm and junctional escape rhythm?
The terminology used to identify the type junctional rhythm depends on its rate and is as follows: Junctional bradycardia: rate below 40 beats per minute. Junction escape rhythm: rate 40 to 60 beats per minute. Accelerated junctional rhythm: rate of 60 to 100 beats per minute.
Which of the following is characteristic of a junctional escape beat?
What are the distinguishing characteristics of junctional escape rhythm? The rhythm is regular; the P wave may occur before, during, or after the QRS; and the P wave is inverted.
What is the distinguishing factor between junctional tachycardia and junctional escape rhythms?
What is the distinguishing factor between junctional tachycardia and junctional escape rhythms. The heart rate is faster in junctional tachycardia. In accelerated junctional rhythms, why is it unlikely that patients will show signs and symptoms of low cardiac output? The rate is the same as normal sinus rhythm.
What is the rhythm of a subsidiary pacemaker?
Under normal conditions, subsidiary pacemakers are suppressed by the more rapid impulses from above (i.e. sinus rhythm ). Junctional and ventricular escape rhythms arise when the rate of supraventricular impulses arriving at the AV node or ventricle is less than the intrinsic rate of the ectopic pacemaker.
Is atrial fibrillation a junctional escape rhythm?
The combination of atrial fibrillation with a regular rhythm (“regularised AF”) indicates that none of the atrial impulses are conducted to the ventricles, i.e. complete heart block is present. The narrow complex rhythm is therefore a junctional escape rhythm.
Where are pacemaker cells found?
Pacemaker cells are found at various sites throughout the conducting system, with each site capable of independently sustaining the heart rhythm. The rate of spontaneous depolarisation of pacemaker cells decreases down the conducting system:
What is junctional escape beat?
A junctional escape beat is a delayed heartbeat originating not from the atrium but from an ectopic focus somewhere in the atrioventricular junction. It occurs when the rate of depolarization of the sinoatrial node falls below the rate of the atrioventricular node. This dysrhythmia also may occur when the electrical impulses from the SA node fail to reach the AV node because of SA or AV block. It is a protective mechanism for the heart, to compensate for the SA node no longer handling the pacemaking activity, and is one of a series of backup sites that can take over pacemaker function when the SA node fails to do so. It can also occur following a premature ventricular contraction or blocked premature atrial contraction.
What is the interval of a P-R wave?
P-R interval: If the P wave occurs before the QRS complex, the interval will be less than 0.12 seconds.
How long is the P-R interval?
P-R interval: If the P wave occurs before the QRS complex, the interval will be less than 0.12 seconds. QRS Complex: Usually normal in duration and morphology, less than 0.12 seconds.
How many beats per minute is a junctional rhythm?
Junctional escape rhythm is a regular rhythm with a frequency of around 40–60 beats per minute.
What is the treatment for junctional rhythm?
Symptomatic junctional rhythm is treated with atropine. Doses and alternatives are similar to management of bradycardia in general.
What is the most common rhythm in the AV node?
The most common rhythm arising in the AV node is junctional rhythm , which may also be referred to as junctional escape rhythm. Junctional tachycardia is less common. Basic knowledge of arrhythmias and cardiac automaticity will facilitate understanding of this article.
Why is the P wave not visible?
In most cases, the P-wave is not visible because when impulses are discharged from the junctional area, atria and ventricles are depolarized simultaneously and ventricular depolarization (QRS) dominates the ECG. If the atria are activated prior to the ventricles, a retrograde P-wave will be visible in leads II, III and aVF prior to the QRS complex.
What is the vagal tone of a well trained athlete?
Well-trained athletes may have very high Vagal tone which lowers the automaticity in the sinoatrial node to the point where cells in the AV-junction establishes an escape rhythm. This is asymptomatic and benign.
What is the primary objective of junctional tachycardia?
Treatment of junctional tachycardia. The primary objective is to treat the underlying cause and/or eliminate provocative medications. Electrical cardioversion is ineffective and should be avoided (electrical cardioversion may be pro-arrhythmogenic in patients on digoxin).
What happens when cells in bundle of His are not reached by the atrial impulse?
In such scenarios, cells in the bundle of His (which possess automaticity) will not be reached by the atrial impulse and hence start discharging action potentials and an escape rhythm. This will also manifest as a junctional escape rhythm on the ECG.
What is the histopathology of a disease that can contribute to the AV node/His bundle?
Histopathology of a disease SA node that can contribute to the AV node/His bundle taking over as a pacemaker secondary to their intrinsic automaticity includes SA node fibrosis, atrophy, hypoplasia, or amyloidosis. A normal SA node histopathology does not rule out reduced SA node automaticity contributing to a junctional rhythm. [11][12]
What is the difference between atrioventricular and sinoatrial node?
The sinoatrial node (SA) is the default pacemaker and is located subepicardially and is crescent in shape. The atrioventricular node (AV) is a subendocardial structure situated in the inferior-posterior right atrium. It sits within an anatomic region bordered posteriorly by the coronary sinus ostium, superiorly by the tendon of Todaro, and anteriorly by the septal tricuspid valve annulus. This anatomic region is also commonly referred to as the triangle of Koch. The sinoatrial nodal artery supplies blood to the sinoatrial node, it branches off the right coronary artery in 60% of cases, whereas in 40% of cases, it comes from the left circumflex coronary artery. The blood supply to the AV node is from the AV nodal branch of the right coronary artery (90%) or the left circumflex artery (10%) depending on the right or left dominant blood supply to the heart. The first septal perforator of the left anterior descending artery also supplies blood to the AV node. A junctional rhythm is where the heartbeat originates from the AV node or His bundle, which lies within the tissue at the junction of the atria and the ventricle. Generally, in sinus rhythm, a heartbeat is originated at the SA node. This electrical activity then travels through the atria to the AV node from where it reaches the Bundle of His from where the electrical signals travel to the ventricles through the Purkinje fibers. [1][2][3][4][5][6]
What is junctional rhythm?
A junctional rhythm is an abnormal heart rhythm that originates from the AV node or His bundle. This activity reviews the evaluation and management of junctional rhythm and highlights the role of the interprofessional team in educating patients about their prognosis.
Where is the sinoatrial node?
The sinoatrial node is the natural cardiac pacemaker located in the upper right atrium. The atrioventricular node is a separate cardiac pacemaker located in the inferior-posterior right atrium. The His bundle is a separate cardiac pacemaker located at the inferior end of the atria and ventricle. A junctional rhythm is an abnormal heart rhythm ...
Where does the heartbeat originate?
A junctional rhythm is where the heartbeat originates from the AV node or His bundle , which lies within the tissue at the junction of the atria and the ventricle. Generally, in sinus rhythm, a heartbeat is originated at the SA node.
Where is the AV located?
The atrioventricular node (AV) is a subendocardial structure situated in the inferior-posterior right atrium. It sits within an anatomic region bordered posteriorly by the coronary sinus ostium, superiorly by the tendon of Todaro and anteriorly by septal tricuspid valve annulus.
What is the best way to manage a patient's rhythm?
Educating patients at risk for this rhythm and making a closed-loop communication between them and their providers can help further improve the management of these rhythms. An interprofessional team best manages this condition. Initial diagnosis is by primary care or emergency providers. Referral to a cardiologist may be indicated. Cardiology and emergency department nurses administer treatment, monitor responses, and report back to the physician or nurse practitioner. Pharmacists should review prescribed medications, check for drug-drug interactions, and educate patients about dosing and side effects. [Level 5]
How old is Alrashid?
You recently take over care of Ms. Alrashid, a 34 year old Egyptian woman admitted to your unit. Thirty (30) minutes ago she converts from Sinus Rhythm to atrial tachycardia. What symptoms are she likely to report when you go in to assess her, and why?
What is second degree AV block?
All second degree AV blocks are the result of failure of the impulse generated by the SA node to reach the AV node.
Why does my wife feel dizzy?
She feels weak and dizzy because her heart rate is so fast ventricular filling time is decreased. This is likely to be why she is hypotensive.
Where is the white electrode placed?
The white electrode (RA) is placed at the infraclavicular fossa, close to the right shoulder.
Can a sinus arrest be life threatening?
Sinus arrest may be life threatening if atrial activity is not restarted.
Can sinus arrhythmia cause symptoms?
A person with sinus arrhythmia commonly has no symptoms.
Is Junctional Escape a lethal arrhythmia?
Junctional escape rhythms are lethal arrhythmias and should be eradicated.
