
Simple Polysaccharides
- Starch. Amylose: the inner part, formed of straight-chain of α-D-glucose units linked by α-1,4 glucosidic bonds, it gives a blue color with iodine.
- Glycogen. Glycogen is the storage form of carbohydrates in animals, it is stored mainly in the liver and muscles.
- Cellulose. It is a structural polysaccharide present in plants. ...
What foods contain polysaccharides?
The following is a list of common non-starchy vegetables:
- Amaranth or Chinese spinach.
- Artichoke.
- Artichoke hearts.
- Asparagus.
- Baby corn.
- Bamboo shoots.
- Beans (green, wax, Italian)
- Bean sprouts.
Why is polysaccharide often called a complex carbohydrate?
Why are polysaccharides referred to as complex carbohydrates? Polysaccharides are macromolecules formed from monosaccharides. Monosaccharides are sugar molecules in their simplest form, such as glucose. Polysaccharides are sometimes referred to as complex carbohydrates. If your blood sugar ever gets too low, glycogen will be broken down into glucose for more energy.
Are polysaccharides building blocks of carbs?
Polysaccharides. Polysaccharides or starches are other molecules that make up the building blocks of carbohydrates. Polysaccharides are also known as complex carbohydrates, due to the fact that they are comprised of lengthy binds of glucose. 1. Starches. Starches are made up of lengthy chains of the molecule glucose.
Why polysaccharides are tasteless and disaccharides are sweet?
These receptors are loosely categorised into sweet, sour, bitter and salty. Our sweet-receptors bind to specific types of molecules, namely monosaccharides and disaccharides Polysaccharides are not as sweet because they do not readily bind to the sweet-receptors on our tongue, as the other smaller molecules do!
Are simple carbohydrates monosaccharides or polysaccharides?
There are two major carbohydrate subgroups: simple and complex. Simple carbohydrates contain the monosaccharide and disaccharide groups. Monosaccharides are comprised of a single simple sugar unit, glucose, fructose, or galactose, and they cannot be broken down into simple sugar units.
Are polysaccharides a type of carbohydrate?
What are Polysaccharides? Polysaccharides are major classes of biomolecules. They are long chains of carbohydrate molecules, composed of several smaller monosaccharides.
Are polysaccharides simple?
A polysaccharide is a complex carbohydrate. Polysaccharides are polymers made up of many monosaccharides. They are very large, often branched, molecules.
Which carbohydrates are polysaccharides?
Polysaccharides are long chains of monosaccharides linked by glycosidic bonds. Three important polysaccharides, starch, glycogen, and cellulose, are composed of glucose. Starch and glycogen serve as short-term energy stores in plants and animals, respectively.
Is polysaccharide a complex carbohydrate?
Complex carbohydrates, also known as polysaccharides, are starches formed by longer saccharide chains, which means they take longer to break down. Chemically, they usually comprise of three or more linked sugars.
Are polysaccharides also called simple sugars?
Polysaccharides are highly branched compounds. They are made of many simple sugars linked together by glycosidic bonds. This is a type of bond that connects carbohydrates.
What is the classification of polysaccharide?
Polysaccharides can be broadly classified into two classes: Homo-polysaccharides – are made up of one type of monosaccharide units. ex: cellulose, starch, glycogen. Hetero-polysaccharides – are made up of two or more types of monosaccharide units.
How are polysaccharides different from monosaccharides?
The main difference between Monosaccharides Disaccharides and Polysaccharides is that monosaccharides are monomers of sugars and disaccharides are composed of two monomers whereas polysaccharides are composed of a large number of monomers.
Is polysaccharide a protein?
The main difference between proteins and polysaccharides is that proteins are composed of amino acids, while polysaccharides are composed of long chains of sugar molecules. On a smaller scale, proteins are synthesized from long chains of peptides to form their primary structure.
What is a simple carbohydrate?
Overview. Simple carbohydrates are broken down quickly by the body to be used as energy. Simple carbohydrates are found naturally in foods such as fruits, milk, and milk products. They are also found in processed and refined sugars such as candy, table sugar, syrups, and soft drinks.
Are disaccharides simple or complex?
Monosaccharides and disaccharides are considered simple carbohydrates, while oligosaccharides and polysaccharides are considered complex carbohydrates.
Are simple carbohydrates monosaccharides?
Based on the chemical structures, simple carbohydrates can be divided into two categories, namely monosaccharides (single sugar molecule) and disaccharides (two single sugar molecules joined together). Glucose, fructose and galactose are the three monosaccharides important in nutrition.
What are the 4 types of carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates are divided into four types: monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides. Monosaccharides consist of a simple sugar; that is, they have the chemical formula C6H12O6.
What are 3 types of carbohydrates?
Food contains three types of carbohydrates: sugar, starches and fiber. Carbohydrates are either called simple or complex, depending on the food's chemical structure and how quickly the sugar is digested and absorbed.
What are the 5 carbohydrates?
They are normally broken down into five major classifications of carbohydrates:Monosaccharides.Disaccharides.Oligosaccharides.Polysaccharides.Nucleotides.
What are the types of carbohydrates?
There are three main types of carbohydrates:Sugars. They are also called simple carbohydrates because they are in the most basic form. ... Starches. They are complex carbohydrates, which are made of lots of simple sugars strung together. ... Fiber. It is also a complex carbohydrate.
What is a polysaccharide?
A polysaccharide is a large molecule made of many smaller monosaccharides. Monosaccharides are simple sugars, like glucose. Special enzymes bind these small monomers together creating large sugar polymers, or polysaccharides. A polysaccharide is also called a glycan. A polysaccharide can be a homopolysaccharide, ...
What determines the structure of a polysaccharide?
The structure of the molecules being combined determines the structures and properties of the resulting polysaccharide. The complex interaction between their hydroxyl groups (OH), other side groups, the configurations of the molecules, and the enzymes involved all affect the resulting polysaccharide produced.
What is the difference between chitin and glucose monosaccharides?
In chitin, the glucose monosaccharides have been modified with a group containing more carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen. The side chain creates a dipole, which increases hydrogen bonding.
How are monosaccharides formed?
All polysaccharides are formed by the same basic process: monosaccharides are connected via glycosidic bonds. When in a polysaccharide, individual monosaccharides are known as residues. Seen below are just some of the many monosaccharides created in nature. Depending on the polysaccharide, any combination of them can be combined in series.
What is the role of polysaccharides in plants?
Cellular Support. By far one of the largest roles of polysaccharides is that of support. All plants on Earth are supported, in part, by the polysaccharide cellulose. Other organisms, like insects and fungi, use chitin to support the extracellular matrix around their cells.
How do polysaccharides store energy?
While the enzymes that produce energy only work on the monosaccharides stored in a polysaccharide, polysaccharides typically fold together and can contain many monosaccharides in a dense area. Further, as the side chains of the monosaccharides form as many hydrogen bonds as possible with themselves, water cannot intrude the molecules, making them hydrophobic. This property allows the molecules to stay together and not dissolve into the cytosol. This lowers the sugar concentration in a cell, and more sugar can then be taken in. Not only do polysaccharides store the energy, but they allow for changes in the concentration gradient, which can influence cellular uptake of nutrients and water.
How do polysaccharides affect the concentration gradient?
Not only do polysaccharides store the energy, but they allow for changes in the concentration gradient, which can influence cellular uptake of nutrients and water.
What are homopolysaccharides?
Homopolysaccharides – Pentosans. Complex carbohydrates, polymerized anhydrides of simple sugars, i.e. chains of monosaccharide residues, each linkage formed by the elimination of a molecule of H 2 O (glycosidic linkages). High molecular weight compounds, usually insoluble in H 2 O. Hydrolysis by acids or enzymes produces intermediate smaller ...
Which compound is composed of only one sugar type, also referred to as homoglycans?
Quantitatively they are the most important carbohydrates. Homopolysaccharides – composed of only one sugar type, also referred to as homoglycans. 1.
What percentage of starch is amylose?
Amylose comprises twenty to thirty percent of the total starch in grains and roots, the amount is genetically controlled and increases with maturity. Back to top. Amylopectin: a branched glucose polymer shaped like the branches of a tree with chains of: a-1, 4 linked glucose residues (20-30) cross linked by.
What are the two types of sugars that are composed of only one sugar type?
Homopolysaccharides – composed of only one sugar type, also referred to as homoglycans. 1. Pentosans: Yield pentose sugars on hydrolysis. Xylans. Arabans. These polymers are B-linked and are not degradable by mammalian enzymes. Xylans are common in alfalfa and arabans are present in wood, nuts, and some vegetables.
What is animal starch?
Glycogen: Sometimes called animal starch because it is the only storage carbohydrate found in animals , and even then it only appears in small amounts in the muscle and liver. Like starch, it has a branched structure, but is more branched than starch and has shorter side chains.
What is the largest molecule in nature?
Molecular weight approaches 1,000,000 and is one of the largest molecules in nature. In plants, starch occurs in the form of distinct granules with characteristic structures. This offers a means of identifying raw starches under the electron microscope.
Is potato starch a mammalian?
This structure also affects the rate at which starch is digested by enzymes – Amylases – such as bacterial a-amylase, bovine or porcine pancreatic amylase, diastase in malted grains. Raw potato starch is very resistant to mammalian hydrolysis so it should be cooked first.
What are the different types of polysaccharides?
These types of polysaccharide carbs include cellulose, hemicellulose, pectin, gum and mucilage. Cellulose cannot be digested by the human digestive system, so cellulose passes through the digestive tract without being absorbed.
What enzyme breaks down starch?
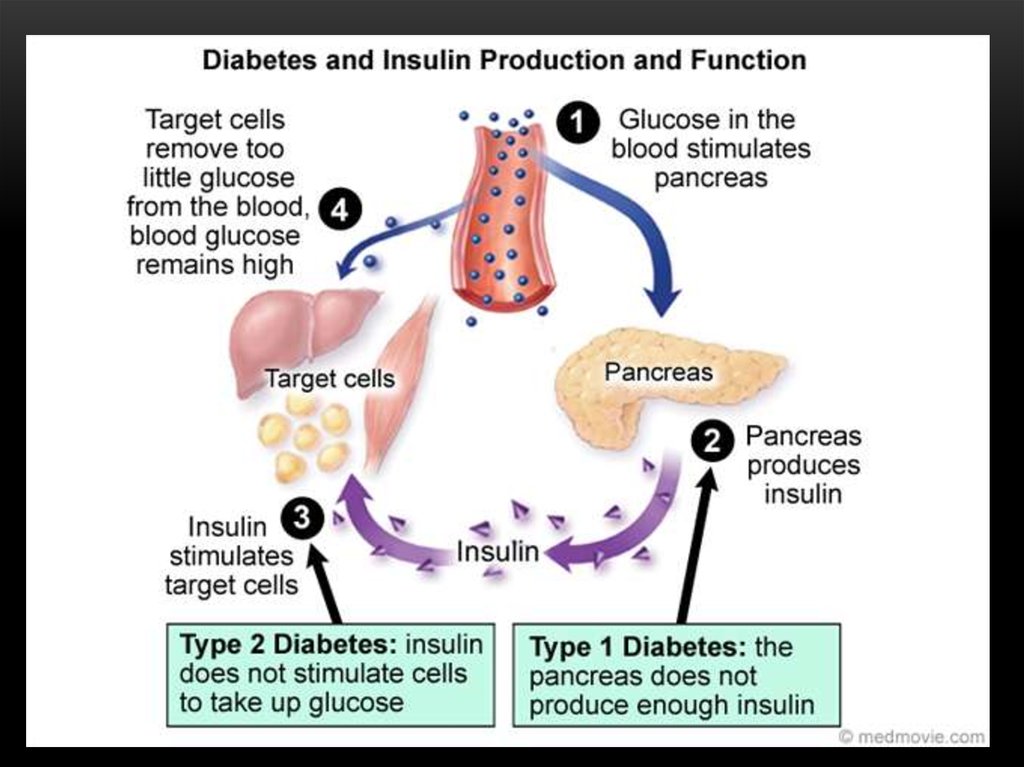
When humans eat starch, an enzyme called amylase - found in our saliva and intestines - breaks down the starch and allows the glucose to be absorbed into the bloodstream. Once absorbed into the bloodstream, the human body uses insulin to disperse and distribute the glucose to areas and cells where it is needed for energy or stores it as "liquid fuel" - glycogen.
Polysaccharides carbohydrates Definition
Polysaccharides are large molecules that are composed of more than 50 repeating units of fundamental monosaccharides or disaccharides.
Overview of Polysaccharides Carbohydrates
Polysaccharides are the most abundant carbohydrates found in nature. The structure comprises long-chainpolymericcarbohydrates. The structural unit is the monosaccharide carbohydrates together with the help of glycosidic linkages.
Homopolysachharides
Starch is a homopolysaccharide that is made up of only D-glucose units. It is a branched polymer. In plants, it acts as a stored form of glucose. To test the presence of starch in a sample, iodine test is performed. Amylose present in starch imparts a blue-black color upon reaction with iodine. As amylase is linear, it forms a helical structure.
Heteropolysachharides
Glycosaminoglycan is an unbranched and negatively-charged polymer, which is made up of disaccharide units of [acid sugar-amino sugar]ₙ. N-acetylglucosamine and N-galactosamine are the two kinds of amino sugars and uronic acid. Generally, the glucuronic acid is the acid sugar part. Hyaluronic acid is the simplest glycosaminoglycan.
What are simple carbohydrates?
Simple carbohydrates are single-unit and two-unit sugars called monosacchar ides and disaccharides. They appear in all sorts of everyday foods including fruit, fruit juice, sweet potatoes, and beets. Simple carbs are the most basic form of macronutrients known as carbohydrates.
What are the types of carbohydrates that are broken down into simple carbs?
These types of carbohydrates can be broken down into simple carbs for energy use. Complex carbohydrates are important nutrients and can be found in starchy vegetables, legumes, and seeds, as well as whole grains such as bulgur, brown rice, and whole-wheat bread.
Why are carbohydrates important for health?
Simple carbohydrates are a readily available source of energy and a part of a healthy diet, but too many can spike blood sugar levels.
What is the most complex form of macronutrients?
Complex carbohydrates, or polysaccharides, are the most complicated form of the macronutrient group known as carbohydrates. On a molecular level they are made from chains of simple carbohydrates. Complex carbs take the form of starch and cellulose (in plants) or glycogen (in animals).
What is the difference between sucrose and maltose?
Sucrose: Sucrose is a disaccharide made from one molecule of glucose and one molecule of fructose. Maltose: Maltose is a disaccharide made from two molecules of glucose. Lactose: Lactose is a disaccharide found in dairy products. It contains one molecule of glucose and one molecule of galactose.
Which monosaccharide is most commonly found in plants?
Glucose: Glucose is the most commonly available monosaccharide and is frequently produced by plants as a product of photosynthesis. Some forms of glucose are called dextrose. Galactose: A monosaccharide with similar properties as glucose, galactose is not as abundant in nature. Fructose: Fructose is a simple carbohydrate produced by fruit.
Do processed foods contain sugar?
Many processed foods contain simple carbohydrates in the form of added sugars, often high fructose corn syrup or table sugar. These added sugars are, on a molecular level, the same simple sugars that naturally occur in foods, but dietitians warn against eating them in large quantities.
Which protein has a oligosaccharide chain?
Glycoproteins are proteins that have oligosaccharide chain (one or several) attached covalently to the polypeptide backbone, the carbohydrate moieties are smaller and more structurally diverse than the glycosaminoglycans of proteoglycans.
What is the function of carbohydrates in the body?
The liver contains approximately 100 grams of glycogen. These stored glucose molecules can be released into the blood to provide energy throughout the body and help maintain normal blood sugar levels between meals.
How do carbohydrates get into the body?
Carbohydrates are broken down into smaller units of sugar. These small units get absorbed out of your digestive tract and into your bloodstream. This blood sugar, or blood glucose, is transported through your bloodstream to supply energy to your muscles and other tissues. Carbohydrates supply energy to the body and prevent the breakdown of proteins for energy.
What are simple carbohydrates?
Simple carbohydrates are called simple sugars. Sugars are found in a variety of natural food sources including fruit, vegetables and milk, and give food a sweet taste. But they also raise blood glucose levels quickly.
What are the two main types of carbohydrates?
Foods for diabetes. Carbohydrates are sugars that come in 2 main forms – simple and complex. This is also referred to as simple sugars and starches. The difference between a simple and complex carb is in how quickly it is digested and absorbed – as well as it’s chemical structure. Most carbohydrates can be broken down by digestion into glucose ...
How are carbohydrates broken down?
Most carbohydrates can be broken down by digestion into glucose and these are the carbohydrates we shall look at in this article. For examples of carbohydrates that do not get fully broken down into glucose, see insoluble fibre and sugar alcohols.
What are complex carbs?
Strictly speaking, the term complex carbohydrate refers to any starches, including the highly refined starches found in: 1 White bread 2 Cakes 3 Most pastries and 4 Many other food sources
What is the best starch to eat?
Whole grain foods. Whole grain starches include the wheat grain and kernel which provide the majority of fibre and nutrients to be found in starchy foods. When it comes to picking starchy foods, such as rice, bread and any other products made from flour, it’s best to opt for whole grain versions of these products.
Does whole grain food raise blood sugar?
Whilst whole grain foods impact upon blood glucose levels more slowly than other forms of carbohydrate, higher levels of carbohydrate can still raise blood sugar levels substantially. Blood glucose testing before and meals is a good way to assess how much carbohydrate your body can adequately cope with.
Is sugar a monosaccharide?
Sugars can be categorised as single sugars (monosaccharides), which include glucose, fructose and galactose, or double sugars (disaccharides), which include sucrose (table sugar), lactose and maltose. Many processed foods contain added sugars but currently there is no UK law that requires manufacturers to state how much sugar has been added in ...
What are the two types of carbohydrates that plants produce?
Plants and animals produce complex carbohydrates to store energy. These complex carbs take several common forms. Glycogen: Glycogen is made of long chains of glucose. It is the primary polysaccharide in animals, and it is also commonly found in fungi and bacteria. Starch: Starch is the plant equivalent of glycogen.
What are the most common carbohydrates?
6 Common Simple Carbohydrates 1 Glucose: Glucose is the most commonly available monosaccharide and is frequently produced by plants as a product of photosynthesis. Some forms of glucose are called dextrose. 2 Galactose: A monosaccharide with similar properties as glucose, galactose is not as abundant in nature. 3 Fructose: Fructose is a simple carbohydrate produced by fruit. It is sometimes called levulose. 4 Sucrose: Sucrose is a disaccharide made from one molecule of glucose and one molecule of fructose. 5 Maltose: Maltose is a disaccharide made from two molecules of glucose. 6 Lactose: Lactose is a disaccharide found in dairy products. It contains one molecule of glucose and one molecule of galactose.
Why do plants and animals need complex carbohydrates?
Both plants and animals use complex carbs to store energy. When it comes time to burn the energy, the complex carbohydrates are converted to simple sugars for easy access. Complex carbohydrates play a key role in healthy diets.
What are simple carbs?
Simple carbs appear in fruit, fruit juice, sweet potatoes, and veggies like beets. They provide a readily available source of energy. Many processed foods contain simple carbohydrates in the form of added sugars, often high fructose corn syrup or table sugar. These added sugars are, on a molecular level, the same simple sugars ...
What is the cellulose in a plant?
Wood trunks and plant stalks are primarily made of cellulose. Many vegetables contain ample cellulose, which gives them their signature crunch. Chitin: Chitin is a polysaccharide produced by insects, crustaceans, and fungi that gives them their structure.
What is the most complex form of macronutrients?
Complex carbohydrates, or polysaccharides, are the most complicated form of the macronutrient group known as carbohydrates. On a molecular level they are made from chains of sugar molecules called monosaccharides and disaccharides. Both plants and animals use complex carbs to store energy. When it comes time to burn the energy, ...
What is the plant equivalent of glycogen?
Starch: Starch is the plant equivalent of glycogen. It also consists of long chains of glucose. Many types of plants produce starch, but it is especially prevalent in green, leafy plants. Cellulose: Cellulose is a type of complex carbohydrate that gives plants their structure via their cell walls.

Terminology
Functions
Formation
Mechanism
- The structure of the molecules being combined determines the structures and properties of the resulting polysaccharide. The complex interaction between their hydroxyl groups (OH), other side groups, the configurations of the molecules, and the enzymes involved all affect the resulting polysaccharide produced. A polysaccharide used for energy storage will give easy access to the …
Chemistry
- The glycosidic bonds between monosaccharides consist of an oxygen molecule bridging two carbon rings. The bond is formed when a Hydroxyl group is lost from the carbon of one molecule, while the hydrogen is lost by the hydroxyl group of another monosaccharide. The carbon on the first molecule will substitute the oxygen from the second molecule as its own, and glycosidic bo…
Structure
- Cellulose and chitin are both structural polysaccharides that consist of many thousand glucose monomers combined in long fibers. The only difference between the two polysaccharides are the side-chains attached to the carbon rings of the monosaccharides. In chitin, the glucose monosaccharides have been modified with a group containing more carbon, nitrogen, and oxyge…
Causes
- When a glycogen or starch molecule is broken down, the enzymes responsible start at the ends furthest from the center. This is important, as you will notice that because of the extensive branching there are only 2 starting points, but many ends. This means the monosaccharides can be quickly extracted from the polysaccharide and be utilized for energy. The only difference bet…
Examples
- 2. Plants produce both the starch amylose, and the structural polymer cellulose, from units of glucose. Most animals cannot digest cellulose. Even ruminants such as cattle cannot digest cellulose and rely on symbiotic internal organisms to break the bonds of cellulose. However, all mammals produce amylase, an enzyme which can break down amylose. Why can amylase not b…
Properties
- B. The glycosidic bonds of cellulose are stronger. C. The extracellular matrix created by cellulose cannot be broken down.
Types
- 3. Hyaluronan is a molecule found in the joints of vertebrates that provides support by creating a jelly-like matrix to cushion the bones. Hyaluronan is created from several different monosaccharides bonded together in long chains. Which of the following describe hyaluronan? 1. Homopolysaccharide 2. Heteropolysaccharide 3. Polymer 4. Monomer