Full Answer
Are protozoans unicellular or multicellular?
As we discussed, protozoans are unicellular and consist of a eukaryotic cell. The specialized internal structures are present in the cell which perform metabolic functions. They have generally one membrane-bound nucleus in the cell which has diffused appearance due to chromatin which is scattered everywhere.
What are the specialized structures of protozoal cells?
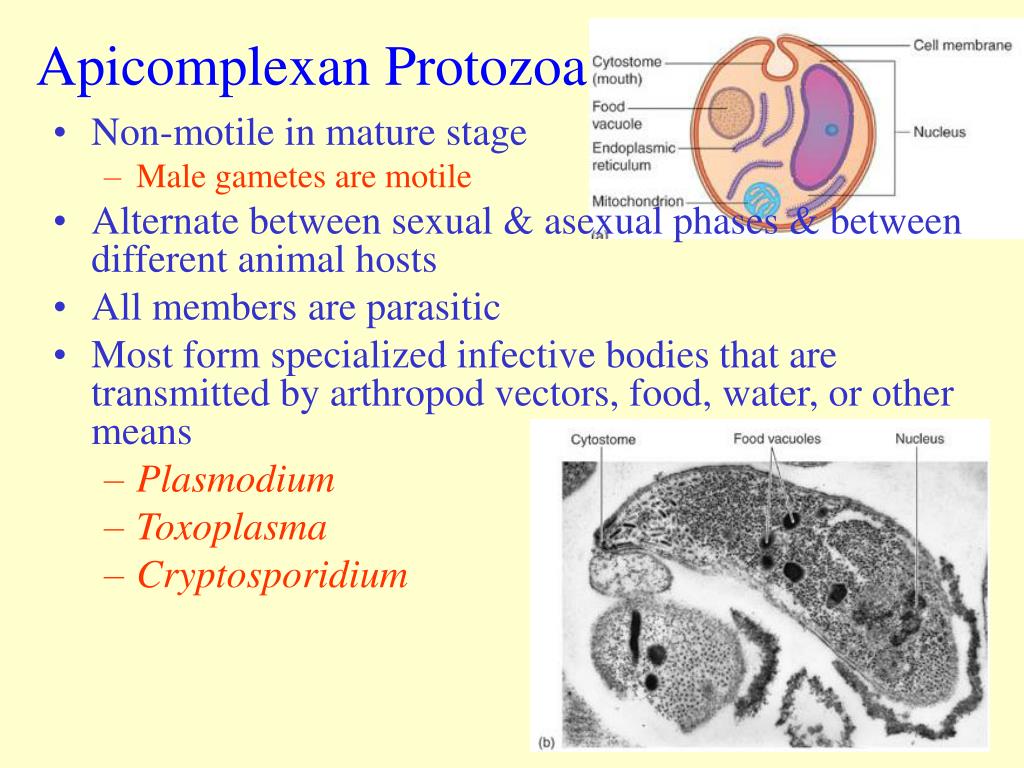
Some species have specialized structures called cytostomes, through which particles pass in phagocytosis. Many protozoal species move independently by one of three types of locomotor organelles: flagella, cilia, and pseudopodia.
What is the function of protozoa in humans?
The protozoa in the humans reside in the red blood cells. It eats up hemoglobin and converts it into a poisonous substance Haemozoin. When the RBC breaks down, the hemozoin is released into the bloodstream causing chills, headache and fever.
How are protozoa specialized?
They find an uninfected red blood cell, and use a special combination of organelles at the end of their cell to force the cell to draw the parasite in. This special group of organelles, known as the apical complex, allows the parasitic protozoa to hide within blood cells.
What type of cells do protozoa have?
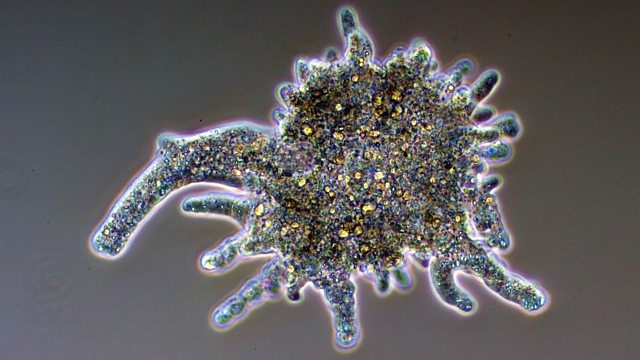
Protozoa, or protozoans, are single-celled, eukaryotic microorganisms. Some protozoa are oval or spherical, others elongated. Still others have different shapes at different stages of the life cycle. Cells can be as small as 1 μm in diameter and as large as 2,000 μm, or 2 mm (visible without magnification).
What type is protozoa?
Protozoa are single celled organisms. They come in many different shapes and sizes ranging from an Amoeba which can change its shape to Paramecium with its fixed shape and complex structure. They live in a wide variety of moist habitats including fresh water, marine environments and the soil.
What are characteristics of protozoa?
Protozoa are unicellular eukaryotic microorganisms lacking a cell wall and belonging to the Kingdom Protista. Protozoa reproduce asexually by fission, schizogony, or budding. Some protozoa can also reproduce sexually. Relatively few protozoa cause disease.
Is protozoa multicellular or unicellular?
Protozoa are microscopic unicellular eukaryotes that have a relatively complex internal structure and carry out complex metabolic activities. Some protozoa have structures for propulsion or other types of movement.
Are protozoans multicellular?
Protozoans are also strictly non-multicellular and exist as either solitary cells or cell colonies.
Do protozoa have cell membranes?
The protozoan cell. The protozoan cell carries out all of the processes—including feeding, growth, reproduction, excretion, and movement—necessary to sustain and propagate life. The cell is enclosed in a membrane called the plasma membrane.
How are protozoans classified or grouped?
The classes of protozoa are categorized by a variety of factors: cell architecture, motility structure, even hosts. They do not photosynthesize, rather being chemoheterotrophic like animals. This means that they use chemicals for energy production and they get their carbon from the same compounds, e.g. sugar.
What do all protozoans have in common?
Due to the extreme diversity of the protozoa the only feature common to all protozoa is that they are unicellular eukaryotic micro-organisms. Protozoa possess typical eukaryotic organelles and in general exhibit the typical features of other eukaryotic cells.
What are the three main characteristics of protozoans?
Characteristics of Protozoa:They do not have cell wall; some however, possess a flexible layer, a pellicle, or a rigid shell of inorganic materials outside the cell membrane.They have the ability during their entire life cycle or part of it to move by locomotor organelles or by a gliding mechanism.More items...
How are protozoa different from other organisms?
Like all protists, protozoa are single-celled organisms with a cell nucleus. Some have more than one nucleus. Protozoa are heterotrophs, which means they can not make their own food, but instead must ingest other organisms for energy.
What are 2 general characteristics of protozoans?
General characteristics of protozoans are that they are heterotrophs, they lack a cell wall and reproduce asexually by fission.
Do protozoa have DNA or RNA?
As in other eukaryotes, protozoa contain repetitive DNA elements within their genomic DNA, whose proportion can vary greatly between different species. Horizontal transfer of genes of bacterial origin has contributed to some of the unique metabolic features observed in protozoan parasites.
What are protozoa cell walls made of?
For example, cell walls of plant cells are composed primarily of cellulose and fungal cell walls and cyst walls in many protozoa are composed primarily of chitin.
Do protozoa have cell membrane?
The protozoan cell. The protozoan cell carries out all of the processes—including feeding, growth, reproduction, excretion, and movement—necessary to sustain and propagate life. The cell is enclosed in a membrane called the plasma membrane.
Which cell organelles is found exclusively in protozoans?
Plastid is the collective name given to a series of organelles found exclusively in plant (and some protozoan) cells.
Why are the different phyla of the kingdom Protista not closely related?
Although the different phyla of the kingdom Protista are not closely related, they are nonetheless classified together because of their large differences from the other kingdoms of plants, animals and fungi. The name “protozoa” has a dynamic history, at one time including only the “animal-like” unicellular forms of life.
What organelle allows parasites to hide in blood cells?
This special group of organelles, known as the apical complex, allows the parasitic protozoa to hide within blood cells. This makes Plasmodium and other parasitic Apicomplexans very hard to kill, as the blood cells would have to be destroyed as well.
What are the structures of the cilia?
Instead of flagella for locomotion, organisms in the phylum Ciliophora use much smaller structures called cilia. The cilia of these organisms cover their entire cell, and work together to propel the cell forward. Much like the individual paddles of a row boat, each cilia gives a forward moving power stoke, then whips back to the starting position in the recovery stroke. Organisms in the Ciliophora include a wide variety of body plans, including free-swimming organisms and sessile organisms that use their cilia to filter food from the water. Most ciliates exist on the bottom of marine environments, known as the benthic zone. However, these protozoa have also specialized as parasites in the digestive tracts of larger organisms.
What are the kinetoplastida made of?
Closely related to the Euglenida, the Kinetoplastida are also protected by a pellicle, although it is made exclusively of microtubules. Organisms in the Kinetoplastida share the unique characteristic of having a single, much enlarged and elongated, mitochondrion. Typically, cells have many small mitochondria, as opposed to one large one. The Kinetoplastida includes many parasitic organisms that cause disease in humans. Of these, leishmaniosis is the most notable, affecting over a million people a year. However, advances in medical treatments saves most of those infected, and only around 1000 people die annually from these protozoa.
Which phylum contains amoebas?
The phylum Rhizopoda contains the amoebas. The small, unicellular protozoa are some of the only protozoa that do not have any sort of hard covering. The amoebas move by extending their cytoplasm into the environment. These extensions are called pseudopodia.
Do parabasilids have fibers?
These organisms contain many flagella, up to thousands on a single cell, and have a special fiber that attached the Golgi apparatus to the base of the flagella. Many parabasilids exists as symbiotic protozoa in the digestive tracts of insects, particularly those that eat wood.
Is everything except fish a protozoa?
C. Everything except the fish! B is correct. Even on a microscopic level, there are many species that may look like protozoa, but are actually complex organisms with multiple cell layers. On the other side, many bacteria exist in a scoop of pond water, and are part of the domain Bacteria, not Protista.
What is a protozoan?
Protozoa (also protozoan, plural protozoans) is an informal term for a group of single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, that feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic tissues and debris. Historically, protozoans were regarded as "one-celled animals", because they often possess animal -like behaviours, ...
What are the pellicles of protozoa?
Pellicles of protozoan organisms vary from flexible and elastic to fairly rigid. In ciliates and Apicomplexa, the pellicle is supported by closely packed vesicles called alveoli. In euglenids, it is formed from protein strips arranged spirally along the length of the body.
What was Goldfuss's first class of organisms?
Goldfuss created Protozoa as a class containing what he believed to be the simplest animals. Originally, the group included not only single-celled microorganisms but also some "lower" multicellular animals, such as rotifers, corals, sponges, jellyfish, bryozoa and polychaete worms.
Which group of protozoa does not move at all?
The group includes flagellates (which move with the help of whip-like structures called flagella ), ciliates (which move by using hair-like structures called cilia) and amoebae (which move by the use of foot-like structures called pseudopodia ). Some protozoa are sessile, and do not move at all.
How many phases are there in protozoa?
Life cycle. Some protozoa have two-phase life cycles, alternating between proliferative stages (e.g., trophozoites) and dormant cysts. As cysts, protozoa can survive harsh conditions, such as exposure to extreme temperatures or harmful chemicals, or long periods without access to nutrients, water, or oxygen.
What is the term for a group of single-celled eukaryotes that feed on organic matter
Protozoa. This article is about the organism. For the infection, see Protozoan infection. Protozoa (also protozoan, plural protozoans) is an informal term for a group of single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, that feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic tissues and debris.
When was the protozoa first introduced?
In some systems of biological classification, Protozoa remains a high-level taxonomic group. When first introduced by Georg Goldfuss in 1818, Protozoa was erected as a class within the animals, and its etymology is literally "first animals".
Where are protozoa found?
These organisms are present in aquatic environments such as oceans or freshwater. These are free-living and many of these are parasitic in nature feeding on plants and animals. Most of the protozoa are aerobic, however, some of them are anaerobic and found in the rumen or human intestine. Their habitat also includes extreme atmospheres like hot springs and some form resting cyst and overcome dry environments.
What are protozoans made of?
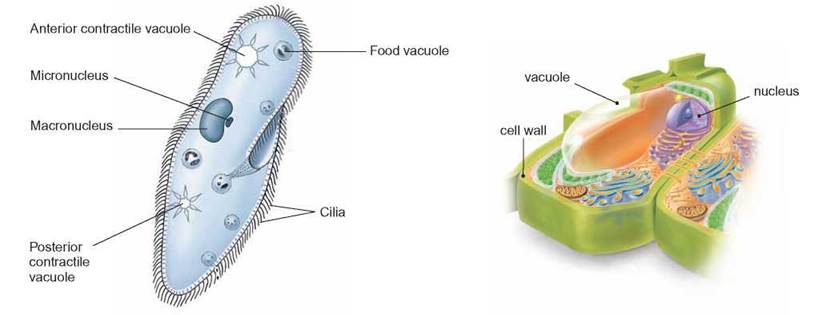
As we discussed, protozoans are unicellular and consist of a eukaryotic cell. The specialized internal structures are present in the cell which perform metabolic functions. They have generally one membrane-bound nucleus in the cell which has diffused appearance due to chromatin which is scattered everywhere. The vesicular nucleus of the cells contains an endosome or nucleoli which is a central body. The ciliates comprise macronucleus and micronucleus; the plasma membrane is also enclosed with locomotory projections such as cilia, flagella, and pseudopodia.
How big are protozoans?
The shell of one of the protozoa named foraminifera possesses a diameter of 20 cm. Their cells are enclosed within a thin plasma membrane and bear a hard shell on the outer surface. In ciliates, the cell is supported by Pellicle and its function is to provide the organisms with a definite shape and help in locomotion as it is flexible and rigid. These are flexible and available in varied shapes and their habitat is covered in the next point.
How do protozoa move?
Protozoa move from one place to another with the help of cilia, flagella or pseudopodia. Sporozoa are among the group which does not have any locomotory structure; instead, they possess subpellicular microtubules that help in the slow movement.
How do protozoans reproduce?
Protozoans follow the asexual method of reproduction and they also multiply with processes like binary fission, transverse fission, longitudinal fission, or budding. Some of the species also undergo sexual reproduction and it is done by conjugation, syngamy, or by the formation of gametocytes.
What is the life cycle of trophozoites?
They have an alternate life cycle between the dormant cyst stage and proliferating vegetative stage. An example where this kind of life cycle takes place is Trophozoites. The cyst stage is strong enough to survive harsh conditions in the absence of nutrients and water; this stage is usually dormant. It can remain without the host for a longer period of time and get transmitted. The other one, the trophozoite stage is known to be infectious as the organisms feed and multiply during this stage and also can cause diseases.
Do protozoans have a holozoic diet?
Protozoans have holozoic nutrition and belong to the heterotrophic category of organisms. They perform phagocytosis to ingest food and some of the groups have specialized structures known as cytostome for phagocytosis. In amoeba, their pseudopodia help in catching the prey and they have numerous cilia present in ciliates to help the food-laden water into the gullet.
Evolution
Others
Description
Clinical significance
Biology
Examples
Morphology
Characteristics
Ecology
- Several other phyla of protozoa exist, but cannot be covered here. Like all other protozoans, these organisms lack specialized tissues or layers of cells. Most are unicellular, although some exist in colonies or fibers. Due to their small size an adaptability, the protozoa have occupied nearly every environment on the planet.
Causes
Overview
Protozoa (singular protozoon or protozoan, plural protozoa or protozoans) is an informal term for a group of single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, that feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic tissues and debris. Historically, protozoans were regarded as "one-celled animals", because they often possess animal-like behaviours, such as motility and predation, and lack a cell wall, as found in plants and many algae.
History
Characteristics
Classification
Ecology
Bibliography
External links
Shape and Size
Habitat
Structure of Cell
- As we discussed, protozoans are unicellular and consist of a eukaryotic cell. The specialized internal structures are present in the cell which perform metabolic functions. They have generally one membrane-bound nucleus in the cell which has diffused appearance due to chromatin which is scattered everywhere. The vesicular nucleus of the cells conta...
Mode of Nutrition
Locomotion
Life Cycle of Protozoans
Reproduction