
What are T lymphocytes responsible for?
T lymphocytes eliminate nascent tumors and intracellular microorganisms such as viruses and some bacteria, and regulate the strength of adaptive immune responses. Functionally, T lymphocytes lyse malignant or infected cells, induce inflammatory responses, and synthesize and secrete soluble intercellular messengers called cytokines.
What are the main functions of T cells?
One of the main functions of T-cells is to initiate immune responses against invading pathogens.
Are antigens produced by T lymphocytes?
The T and B lymphocytes (T and B Cells) are involved in the acquired or antigen-specific immune response given that they are the only cells in the organism able to recognize and respond specifically to each antigenic epitope. The B Cells have the ability to transform into plasmocytes and are responsible for producing antibodies (Abs).
Are T cells white blood cells?
T cells are a type of white blood cell. The purpose of these blood cells is to help your body detect and fight off infection or illness. These blood cells form and begin to develop in your bone...
Is T cell and T lymphocyte the same?
T cell, also called T lymphocyte, type of leukocyte (white blood cell) that is an essential part of the immune system. T cells are one of two primary types of lymphocytes—B cells being the second type—that determine the specificity of immune response to antigens (foreign substances) in the body.
What are the two types of T lymphocytes?
There are several types of T cells; the most common and well-known are the CD4+ T cells (helper T cells) and CD8+ T Cells (cytotoxic T cells, or killer T cells). T cells cannot recognize soluble, free antigens. T cells can only recognize protein-based, receptor-bound antigens.
Are all T cells lymphocytes?
There are two main types lymphocytes: T cells and B cells. B cells produce antibody molecules that can latch on and destroy invading viruses or bacteria. T cells are direct fighters of foreign invaders and also produced cytokines, which are biological substances that help activate other parts of the immune system.
What are the 4 types of T cells?
T Cell ActivationEffector Cells. Depending on the APC a naïve cell comes across it can become an effector T cell. ... Cytotoxic T Cells. Cytotoxic T Cells, also known as CD8+ cells, have the primary job to kill toxic/target cells. ... Helper T Cells. ... Regulatory T Cells. ... Memory T Cells. ... Applications.
How do you increase your T cells?
Eat fruits and vegetables high in folic acid, vitamin B6, and thiamin. These vitamins and minerals can increase the number of t-cells in your body so try to include them in your daily diet. One of the best ways to get these nutrients is to eat a varied diet that includes fresh fruit and vegetables.
What is the main function of T lymphocyte?
T lymphocytes are part of the immune system and develop from stem cells in the bone marrow. They help protect the body from infection and may help fight cancer. Also called T cell and thymocyte.
What are the three types of T lymphocytes?
There are 3 main types of T cells: cytotoxic, helper, and regulatory. Each of them has a different role in the immune response.
Do T cells regenerate?
T cell production by the thymus naturally wanes with age, but stress, toxic chemotherapy, radiation or infection can also torpedo thymic output. “But the thymus actually has this remarkable capacity to regenerate itself,” Dudakov said.
How many T cells are in our body?
There are 25 million to a billion different T-cells in your body. Each cell has a unique T-cell receptor that can fit with only one kind of antigen, like a lock that can fit with only one shape of key. Antigens and receptors work a lot like a lock and key.
Which type of T cell is most effective against viruses?
Cytotoxic T lymphocytesCytotoxic T lymphocytes, natural killer (NK) cells and antiviral macrophages can recognize and kill virus-infected cells. Helper T cells can recognize virus-infected cells and produce a number of important cytokines.
What will happen if you lose all of your regulatory T cells?
LOSS OF REGULATORY T-CELL FUNCTION IN AUTOIMMUNE DISEASE. The loss of dominant peripheral tolerance, which is normally controlled by Tregs, can lead to spontaneous autoimmune disease, immunopathology, metabolic disease, allergy, and loss of fetal–maternal tolerance during pregnancy.
What causes T cell exhaustion?
T cell exhaustion is a progressive loss of effector function due to prolonged antigen stimulation, characteristic of chronic infections and cancer. In addition to continuous antigen stimulation, antigen presenting cells and cytokines present in the microenvironment can also contribute to this exhausted phenotype.
How many types of T cells are there?
There are two major types of T cells: the helper T cell and the cytotoxic T cell. As the names suggest helper T cells 'help' other cells of the immune system, whilst cytotoxic T cells kill virally infected cells and tumours.
Why T lymphocytes are so called?
T cells derive their name from the thymus. After migration to the thymus, the precursor cells mature into several distinct types of T cells. T cell differentiation also continues after they have left the thymus.
How many T cells do we have?
There are 25 million to a billion different T-cells in your body. Each cell has a unique T-cell receptor that can fit with only one kind of antigen, like a lock that can fit with only one shape of key. Antigens and receptors work a lot like a lock and key.
What are the two main categories of the immune system?
There are 2 main parts of the immune system:The innate immune system. You are born with this.The adaptive immune system. You develop this when your body is exposed to microbes or chemicals released by microbes.
What is cytotoxic T cell?
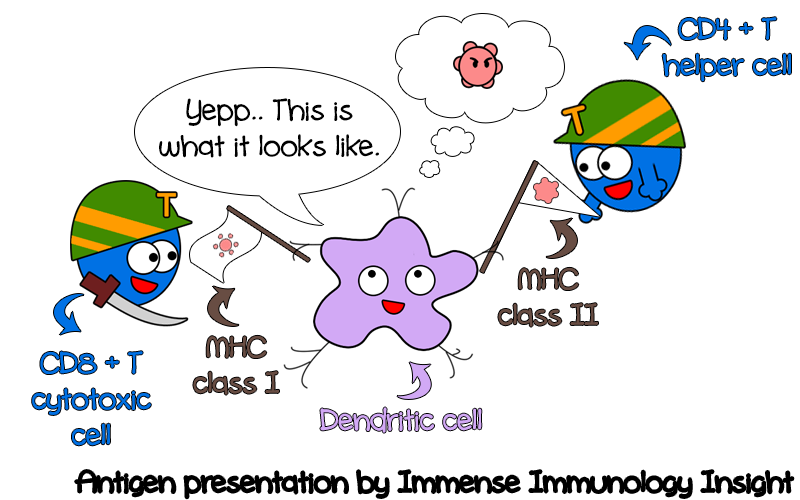
Cytotoxic T cells (CD8+ T cells) Cytotoxic T cells or CD8+ T cells are the T cells activated by the class I MHC molecules on the antigen-presenting cells. These are named CD8+ T cells as these contain the CD8 receptors on the surface. The receptor is present in about 40% of the total T cells.
How are T cells different from other lymphocytes?
T cells are different from other lymphocytes as these have a T-cell receptor on the surface, which is absent in other lymphocytes. T cells are one of the crucial factors in the adaptive immune response as the receptors interact with MHC complexes on antigen-presenting cells exposed to antigens. The range of antigens that can activate ...
Where are regulatory T cells formed?
The group of regulatory T cells can be formed either during the normal process of T cell development in the thymus or be induced peripherally. The regulatory cells formed in the thymus are called thymic Treg cells, and the induced cells are called peripherally derived Treg cells.
How many compartments are there in the thymus?
The thymus consists of four major compartments, where each of them performs a distinct function and regulates different stages of T cell development.
Which cells express self-antigens?
The thymic cortal epithelial cells express self-antigens on MHC molecules where the T cells interact with the molecules. The cells that do not interact with the molecules strongly enough due whereas others with high affinity to MHC cells survive.
What percentage of T cells are Helper T cells?
Helper T cells account for about 50-60% of total T cells, which then further activate other immune cells to protect the body from attacks by foreign particles. The activation of CD4+ T cells results in the differentiation of the cells and secretion of cytokines to regulate the overall immune response.
What are the different types of T cells?
The following are different types of T cells; 1. Helper T cells (CD4+ T cells) Helper CD4+ T cells or T helper cell s are lymphocytes that assist the maturation of other lymphocytes like B cells to differentiate into plasma cells and memory B cells.
What Are B Cell Lymphocytes?
B cell lymphocytes don't attack and kill cells, viruses or bacteria themselves. Instead, they manufacture proteins called antibodies that actually stick to the surface of invaders, disabling those invaders and spotlighting them for clean up by other parts of your immune system. 5
How do lymphocytes kill?
Lymphocytes also kill cells in your body that are infected with a pathogen, and release chemicals to warn other cells of the danger. This process enables you to fight off infections and other dangers. Lymphocytes move around your body through the lymphatic system, which is part of the circulatory system.
What is the difference between autoimmune disease and Celiac disease?
In autoimmune disease , for example, T cell lymphocytes mistakenly attack your own tissues, mistaking your cells for foreign invaders. Celiac disease, for example, involves an autoimmune attack on the lining of your small intestine. 7 Scientists aren't certain what propels T cells to do this. You also can develop cancer ...
What happens when a lymphocyte spots a cell that's been infected with bacteria or a virus?
When a lymphocyte spots a cell that's been infected with bacteria or a virus, the lymphocyte will proceed to kill the cell. 2 It also will actually remember the infectious agent, so it can act faster the next time it encounters the same infectious problem. This enables your immune system to identify and fight repeat infections more quickly. 3
What is the function of T cells?
T cell lymphocytes' job is to continually scan and monitor your cells for infection and the risk of infection. This goes on without you realizing it's happening inside your body. The "T" in T cell stands for thymus, the small gland in your chest where T cells go to mature after they're manufactured by your bone marrow, ...
What is the role of lymphocytes in the immune system?
Lymphocytes' role in this is to fight infections by producing antibodies, which are chemicals that help your body stop and then remove foreign invaders such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, parasites, and toxic chemicals.
Where are B cells made?
Like T cell lymphocytes, B cell lymphocytes also are made in your bone marrow. They mature in your spleen. 6 .
What is a cytotoxic T cell?
A cytotoxic T cell (left) recognizes antigens on the surface of a cell infected with a virus (right), enabling the T cell to bind to and kill the infected cell. © C. Edelmann/Petit Format. Read More on This Topic. immune system: T cells.
What is a T lymphocyte?
Alternative Titles: T lymphocyte, thymus-derived cell, thymus-derived lymphocyte. T cell, also called T lymphocyte, type of leukocyte (white blood cell) that is an essential part of the immune system. T cells are one of two primary types of lymphocytes — B cells being the second type—that determine the specificity of immune response to antigens ...
What are regulatory T cells?
Regulatory T cells act to control immune reactions, hence their name. Cytotoxic T cells, which are activated by various cytokines, bind to and kill infected cells and cancer cells. Because the body contains millions of T and B cells, many of which carry unique receptors, it can respond to virtually any antigen.
What are the chemical messengers that helper T cells secrete?
Once stimulated by the appropriate antigen, helper T cells secrete chemical messengers called cytokines, which stimulate the differentiation of B cells into plasma cells ( antibody -producing cells).
Why does the body respond to antigens?
Because the body contains millions of T and B cells, many of which carry unique receptors, it can respond to virtually any antigen.
What is an encyclopedia editor?
Encyclopaedia Britannica's editors oversee subject areas in which they have extensive knowledge, whether from years of experience gained by working on that content or via study for an advanced degree. ...
Where do T cells mature?
When T-cell precursors leave the bone marrow on their way to mature in the thymus, they do not yet express receptors for antigens and thus... T cells originate in the bone marrow and mature in the thymus.
What Are T-Lymphocytes?
Like all blood cells, T-lymphocytes come from haematopoietic stem cells, which are stem cells in our bone marrow. They work to fight infections and various types of cancer cells in an adaptive immune system, also referred to as an acquired immune system. Our adaptive immunity uses T-cells and B-cells (B-lymphocytes, also derived from bone marrow) to battle organisms and intracellular pathogens that slip through the frontlines of our bodies' defenses.
What is a low lymphocyte count?
A low lymphocyte count is known as lymphocytopenia, and can arise if your body isn't producing sufficient lymphocytes, if the lymphocytes you do produce are being destroyed, or if they are trapped in places like your spleen or lymph nodes. With a lower lymphocyte count you are more at risk of developing infections, and that low count is often associated with the following conditions:
What amino acid is involved in inflammatory T cells?
Glutamine is a nonessential hydrophilic amino acid that is coupled with naive T-cell activation and linked to the amino acid transporter ASCT2. Researchers have found that inflammatory T-cell responses rely on amino acid transporter ASCT2 and come with a rapid glutamine uptake. Though it's still not largely understood, it's nevertheless clear that glutamine plays a role in the immune response necessary to defeat deadly pathogens.
What organs do T cells move through?
Most of our lymphocytes, including T-cells, move through the lymph nodes and other lymphatic organs like the tonsils and spleen, but they can't do so unaided. There are amino acids necessary for this immune response.
What cells are stimulated by helper T cells?
As soon as a specific infection triggers them, helper T cells produce chemicals, of which, some chemicals stimulate B lymphocytes to develop into plasma cells, while others stimulate killer T lymphocytes to target and kill cells that may have either become infected by the infection or become cancerous.
What is the function of plasma cells?
The function of antibodies is to act as a cover on the infected cell so T lymphocytes recognize which cells to destroy. When infections become covered with antibody, they are more easily targeted by other proteins in ...
How do T lymphocytes help the immune system?
As soon as a specific infection triggers them, helper T cells produce chemicals, of which, some chemicals stimulate B lymphocytes to develop into plasma cells, while others stimulate killer T lymphocytes to target and kill cells that may have either become infected by the infection or become cancerous. Regulatory T lymphocytes help to control the immune system to prevent it getting out of hand. Natural killer T lymphocytes also produce chemicals to help regulate the immune response and protect against infections and cancerous tumors. Memory T lymphocytes stay around for a long time after the immune system has finished responding. In this way, they can react quickly if the same infection appears again and multiply to produce a large number of T lymphocytes to kill it.
How do B lymphocytes work?
The viruses and infections which enter the blood or lymph of the body, humoral immunity works against it. B lymphocytes initially produce proteins called antibodies that can capture the infections as they travel in the blood. When they come across infections, B lymphocytes are stimulated into action and produce plasma cells and memory B cells. Each plasma cell is specialized to make a particular antibody, a specialized protein to attack a specific infection. The function of antibodies is to act as a cover on the infected cell so T lymphocytes recognize which cells to destroy. When infections become covered with antibody, they are more easily targeted by other proteins in the immune system, as well as by the specialized cells known as phagocytes that are responsible for eating foreign substances and infected cells. While plasma cells disappear after an immune response is finished, memory B lymphocytes stay around for a long time. If the same infection appears again, antibodies are already available to help fight it off.
What are the functions of lymphocytes?
B Lymphocytes originate in the bone marrow and the lymph nodes while T Lymphocytes originate from the thymus. The function of both these lymphocytes is to protect the body against infection and are necessary components of our immune system. Without the B and T lymphocytes our body will lose its ability to fight and stop different infections and viruses that enter our body. These lymphocytes are also known as B cells and T cells. In simpler words the function of these two lymphocytes is after the T and B lymphocytes are developed they go to their respective site and when they encounter an infection from outside they come into action, the helper T cells send signals to the B cells which produce the plasma cells, these plasma cells acts instantly and produces the specialized antibody for that particular infection and coats or covers the cell which is infected in the specific organ. After that the B cells send signals again to the T cells which produce killer cells and kill or destroy the infection. Both these cannot work without each other. They work together to make the immune system strong.
Why do T lymphocytes produce chemicals?
Natural killer T lymphocytes also produce chemicals to help regulate the immune response and protect against infections and cancerous tumors. Memory T lymphocytes stay around for a long time after the immune system has finished responding.
What happens if you don't have B and T lymphocytes?
Without the B and T lymphocytes our body will lose its ability to fight and stop different infections and viruses that enter our body. These lymphocytes are also known as B cells and T cells. In simpler words the function of these two lymphocytes is after the T and B lymphocytes are developed they go to their respective site ...
