
What are type 2 muscle fibers?
Type 2 muscle fibers are the second major type of muscle fibers in the skeletal muscle. They are also known as fast-twitch fibers. There are two types namely type 2a and type 2b.
What are the differences between muscle fiber types?
Differences between muscle fiber types: Characteristic Type I Type IIa Type IIb Mitochondrial density High Medium Low Capillary density High Medium Low Myoglobin High Medium Low Metabolic Type Primarily aerobic/oxidative Primarily aerobic/ oxidative Primarily anaerobic/glycolytic 6 more rows ...
How do you build muscle type II fibers?
“To develop Type II fibers, one should focus on training with heavier weights, explosive exercises, and power movements regularly,” advises Breanne Celiberti, MS in Sport & Exercise Science, adjunct instructor in the Human Performance department at the University of Tampa.
What is the difference between Type 1 and Type 2 fibers?
Type 1 and type 2 muscle fibers are the main two types of muscle fibers of the skeletal muscle. Type 1 fibers are slow contracting and generate ATP using aerobic metabolism. They contain more mitochondria and high content of myoglobin.
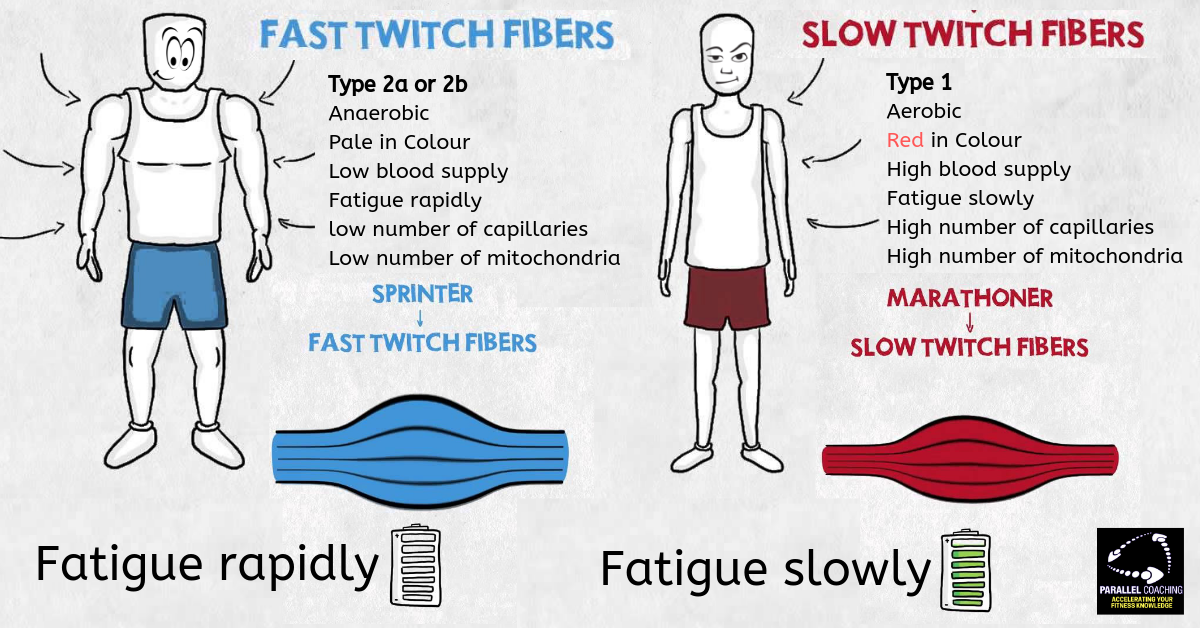
Are type II muscle fibers anaerobic?
Type II-b fibers are anaerobic with a high glycogen content and fast twitch rate. They have few capillaries and low endurance but a high power output. Your muscles need glycogen, ATP, and innervation to become active.
Do type 2 muscle fibers need oxygen?
Muscle fiber type 2a It's also called an intermediate muscle fiber or type 2a. This muscle fiber can use its own energy and be powered by oxygen from blood.
What is type 2 muscle fiber?
Type II fibers are the fast twitch muscle fiber. They are called fast twitch due to their ability to quickly generate force compared with type I fibers (3-5x faster), however they will fatigue at a much quicker rate (McArdle et al., 2015).
What muscle fibers are aerobic?
6 Things to Know About Slow-twitch, or Type I, Muscle Fibers: Slow-twitch fibers contain mitochondria, the organelles that use oxygen to help create adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is the chemical that actually fuels muscle contractions, and are considered aerobic.
Is smooth muscle aerobic or anaerobic?
anaerobic metabolismThey have a rapid onset of contractions. They primarily use anaerobic metabolism. They are resistant to fatigue.
Which muscle tissue uses aerobic respiration?
Type I muscle cells, or red muscle cells, use aerobic respiration, whereas type II muscle cells, or white muscle cells, use anaerobic respiration. Aerobic respiration requires oxygen; therefore, myoglobin must be present to carry oxygen within type I muscle cells. Aerobic respiration occurs in mitochondria.
What is the difference between Type 2A and 2B muscle Fibres?
Intermediate-twitch type-2A: used when moving a semi-heavy object. Fast-twitch type-2B: the largest fibres, called into action when all-out effort is required (fight or flight). They contract many times faster than slow-twitch fibres and with much greater force, but they fatigue quickly.
Which muscle fibers are best suited for anaerobic exercise?
Fast-twitch muscle fibers provide bigger and more powerful forces, but for shorter durations and fatigue quickly. They are more anaerobic with less blood supply, hence they are sometimes referred to as white fibers or type II.
Which type of muscle fibers adapt the most to aerobic training?
Figure 3. Influence of exercise bout intensity on training-induced adaptations in muscle mitochondrial content. As the training bouts become more intense, more of the low oxidative (type IIb) fibers are recruited and become adapted to the training.
How many types of muscle fibers are there in the human body?
Type Ic, IIc, Iac, IIab fibers have all been identified, consequently meaning that there is a total of 7 different types of muscle fiber found in human skeletal muscle. If this sounds interesting, then you can learn more about this in the recommended further reading.
What are the fibers of skeletal muscle?
Each muscle is wrapped in a thick connective tissue called the epimysium. Within this is a number of muscle fibers which are bundled together to form a fascicle, which are held in place by the perimysium.
Why do muscle fibers change shape?
This is because muscle fibers are plastic, meaning they are capable of changing their size and shape. Even more interesting is the fact that they can also convert from one type to another! These changes to muscle fibers are due to a number of factors, these include your age but also your activity level.
What is the skeletal muscle made of?
Skeletal muscle is therefore made up of hundreds, if not thousands of muscle fibers. These fibers are singular protein dense cells which contain many nuclei, mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum. Each fiber is surrounded by a plasma membrane called the sarcolemma, and inside this sits the sarcoplasm, a gelatin-like substance which separates ...
What is the smallest connective tissue?
Within each muscle fiber we have a number of myofibrils which are aligned in parallel, each individual fiber is surrounded by endomysium – the smallest of the connective tissue.
Which muscle fibers produce the most force?
Type IIb muscle fibers are without doubt the most powerful, they produce the most force and are faster at getting to their peak force. However, they are easily fatiguable, meaning this high-level of force cannot be sustained for as long as type I fibers.
How many fibers are in a human muscle?
Muscles are rarely just one fiber type. Instead, what we see is that human muscles contain both type I and II fibers, however the mixture between these fiber types are often different between muscles. For example, approximately 80% of the soleus in humans is made up of type I fibers, however, this varies between individuals.
What are the two criteria to consider when classifying the types of muscle fibers?
Two criteria to consider when classifying the types of muscle fibers are how fast some fibers contract relative to others, and how fibers produce ATP. Using these criteria, there are three main types of skeletal muscle fibers. Slow oxidative (SO) fibers contract relatively slowly and use aerobic respiration (oxygen and glucose) to produce ATP.
Which fibers produce ATP?
Slow oxidative (SO) fibers contract relatively slowly and use aerobic respiration (oxygen and glucose) to produce ATP. Fast oxidative (FO) fibers have fast contractions and primarily use aerobic respiration, but because they may switch to anaerobic respiration (glycolysis), can fatigue more quickly than SO fibers.
What is the function of myoglobin in muscle fibers?
The myoglobin stores some of the needed O 2 within the fibers themselves (and gives SO fibers their red color). All of these features allow SO fibers to produce large quantities of ATP, which can sustain muscle activity without fatiguing for long periods of time.
What is FG fiber?
FG fibers are used to produce rapid, forceful contractions to make quick, powerful movements. These fibers fatigue quickly, permitting them to only be used for short periods. Most muscles possess a mixture of each fiber type. The predominant fiber type in a muscle is determined by the primary function of the muscle.
What is the purpose of SO fibers?
SO fibers are extensively supplied with blood capillaries to supply O 2 from the red blood cells in the bloodstream. The SO fibers also possess myoglobin, an O 2 -carrying molecule similar to O 2 -carrying hemoglobin in the red blood cells. The myoglobin stores some of the needed O 2 within the fibers themselves ...
Why are FO fibers oxidative?
They are oxidative because they produce ATP aerobically, possess high amounts of mitochondria, and do not fatigue quickly. However, FO fibers do not possess significant myoglobin, giving them a lighter color than the red SO fibers.
What is a type 1 muscle fiber?
Type 1 muscle fibers are one type of muscle fibers in the skeletal muscle. Moreover, they are also known as slow-twitch fibers due to their slow contraction. They are rich in mitochondria and also contain more myoglobin.
What type of fibers are used in aerobic and anaerobic respiration?
On the other hand, type 2a fibers use both aerobic and anaerobic metabolisms.
Which type of muscle fiber is more resistant to fatigue?
Both types contain myoglobin, capillaries, and mitochondria. Type 1 muscle fibers are more resistant to fatigue and produce energy continuously for a long time using aerobic metabolism. They are slow acting hence helpful for distance running etc. Type 2 muscle fibers are of two types; type 2a and type 2b.
What type of muscle fibers are attached to the skeleton?
There are three major types of muscles. Among them, skeletal muscle is one type, which is attached to the skeleton. The individual muscle fibers make up the skeletal muscle. There are two main types of muscle fibers namely type 1 ...
What are the three main types of skeletal muscle fibers?
Using these criteria, there are three main types of skeletal muscle fibers recognized (Table 1). Slow oxidative (SO) fibers contract relatively slowly and use aero bic respiration (oxygen and glucose) to produce ATP. Fast oxidative (FO) fibers have relatively fast contractions and primarily use aerobic respiration to generate ATP.
What is the primary metabolic pathway used by muscle fibers?
The primary metabolic pathway used by a muscle fiber determines whether the fiber is classified as oxidative or glycolytic. If a fiber primarily produces ATP through aerobic pathways, then it is classified as oxidative. More ATP can be produced during each metabolic cycle, making the fiber more resistant to fatigue.
Which type of muscle has a fast contraction?
Lastly, fast glycolytic (FG) fibers have relatively fast contractions and primarily use anaerobic glycolysis. Most skeletal muscles in a human body contain all three types, although in varying proportions. The speed of contraction is dependent on how quickly myosin’s ATPase hydrolyzes ATP to produce cross-bridge action.
