Does a VLAN support a layer 2 switch?
The only physical requirement is that the end station and the port to which it is connected both belong to the same VLAN. Adding virtual LAN (VLAN) support to a Layer 2 switch offers some of the benefits of both bridging and routing. Like a bridge, a VLAN switch forwards traffic based on the Layer 2 header, which is fast.
What is the main function of a layer 2 switch?
Summary:
- Layer2 is the process of using devices and MAC addresses on a LAN to segment a network.
- A Layer 3 switch is a switch that performs routing functions in addition to switching.
- Layer 2 switches perform the switching function to re-arrange the data frames from the source to its destination network.
What is the difference between Layer 2 switch and router?
What is the difference between Router and Switch?
- A switch works in the data link layer while a router works in the network layer. ...
- A router is more advanced and intelligent than a switch.
- A router is more costly than a switch.
- A router needs more processing power to run complex algorithms than what a switch needs.
What is layer 2 Ethernet switch?
Layer 2 Switch is a form of Ethernet switch that switches packets by looking at their physical addresses (MAC addresses). These switches operate at the data-link layer (or layer 2) of the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) reference model.. They essentially perform a bridging function between LAN segments because they forward frames based on their destination address without any concern for ...
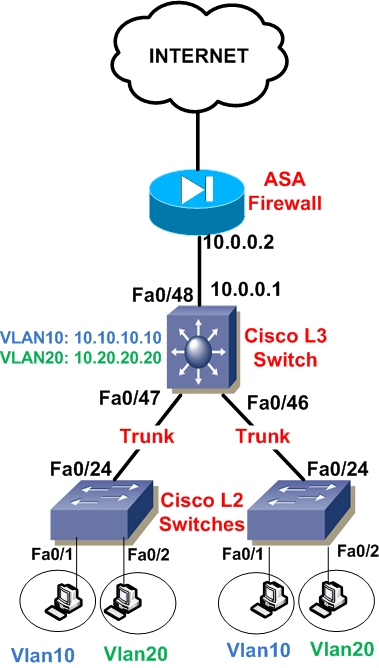
CAN layer 2 switch do routing?
The layer 2 and Layer 3 differs mainly in the routing function. A Layer 2 switch works with MAC addresses only and does not care about IP address or any items of higher layers. Layer 3 switch, or multilayer switch, can do all the job of a layer 2 switch and additional static routing and dynamic routing as well.
How does a layer 2 switch differ from a VLAN?
How does a layer-2 switch differ from a router? A layer-2 switch operates at the data link layer, and a router operates at the network layer. How does a layer-2 switch differ from a VLAN? When a VLAN switch receives a frame for another computer, it forwards the frame unchanged to the correct computer.
Is a VLAN Layer 2 or 3?
VLANs are data link layer (OSI layer 2) constructs, analogous to Internet Protocol (IP) subnets, which are network layer (OSI layer 3) constructs. In an environment employing VLANs, a one-to-one relationship often exists between VLANs and IP subnets, although it is possible to have multiple subnets on one VLAN.
How do I configure a VLAN on a Cisco layer 2 switch?
Layer 2 VLAN Configuration on a Cisco Switch (with Example)Accounting Department: IP Subnet 192.168. 2.0/24 –> VLAN 2.Management Department: IP Subnet 192.168. 3.0/24 –> VLAN 3.Engineering Department: IP Subnet 192.168. 4.0/24 –> VLAN 4.
Do you need a layer 3 switch for VLANs?
Since VLANs exist in their own layer 3 subnet, routing will need to occur for traffic to flow in between VLANs. This is where a layer 3 switch can be utilized. A Layer 3 switch is basically a switch that can perform routing functions in addition to switching.
Is there a layer 4 switch?
A layer 4 switch enables policy based switching mechanisms that limits different traffic types and prioritizes packets based on their base application importance. A layer 4 switch is among the types of multilayer switches, and is an enhancement to the layer 3 switch that uses hardware based switching techniques.
What layer do VLANs operate?
VLANs work at layer 2, or the data link layer of the OSI model.In simple networks, VLAN bridges can be created that group the ports on a switch into VLANs based on a mapping held within the bridge.
What is difference between l2 VLAN and L3 VLAN?
I answered them, Layer 2 VLAN is a single broadcast domain. It works on layer 2 (Datalink Layer). They can communicate only within it. And L3 VLAN is an Interface, that works on Network Layer.
What does a layer 2 switch do?
A layer 2 switch is primarily responsible for transporting data on a physical layer and in performing error checking on each transmitted and received frame. A layer 2 switch requires MAC address of NIC on each network node to transmit data.
How do I assign a VLAN to two switches?
Create the VLANs:Open a web browser.In the address bar of the web browser, type the IP address of the switch and press Enter.Type the admin password of the switch and click Login.Go to Switching - VLAN - Advanced - VLAN Configuration.In the VLAN ID field, type the ID of the VLAN you wish to create and click Add.More items...
What is the difference between Layer 2 and Layer 3 switches?
Layer2 is the process of using devices and MAC addresses on a LAN to segment a network. A Layer 3 switch is a switch that performs routing functions in addition to switching. Layer 2 switches perform the switching function to re-arrange the data frames from the source to its destination network.
How many VLANs can be configured on a Cisco switch?
VLAN Ranges. The extended system ID is always automatically enabled in Cisco NX-OS devices. The device supports up to 4094 VLANs in accordance with the IEEE 802.1Q standard in each VDC. The software organizes these VLANs into ranges, and you use each range slightly differently.
How to route traffic between VLANs?
To route traffic between VLANs you need a layer 3 switch/router. However, if your router supports dot1q/isl encapsulation then you can setup a trunk between the switch and the router and make the router forward traffic between the VLANs. This feature is called router-on-a-stick. HTH. Sundar.
What is OSPF protocol?
OSPF Routing Protocol is the most used protocol in the world, especially in the world of service provider, through this hand-on-labs workbook, you will discover another aspect of OSPF which is the RFCs that stands for "Request For Comments", A Request for... view more. Create Content. Login to create content.
What is a VLAN switch?
With the advent of VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network), network managers can logically divide the physical LAN into different broadcast domains by spanning across multiple switches or even routers. The first series of VLAN switches on the market are Layer 2 switches which operate at Layer 2 of the ISO Reference Model.
How does a layer 2 switch work?
A Layer 2 switch is a type of network switch or device that works on the data link layer via OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model and utilize s MAC address to determine the path through which the frames are to be forwarded. It uses hardware based switching techniques to connect and transmit data in VLAN. By looking at the destination MAC address in the frame header, the Layer 2 switch interconnects multiple end nodes of VLAN and intelligently forwards traffic between them without unnecessary flooding of frames onto the network. Generally speaking, Layer 2 switches come with different types of interfaces like 10 Mbps, 100 Mbps, 1 Gbps, 10 Gbps, etc. They can support full-duplex communication on each of its port. They expand network by connecting to the rest of the devices in the fabric through high speed ports that can be connected to either another Layer 2 or Layer 3 switch.
What is the difference between a layer 2 and layer 3 switch?
The most significant difference between Layer 2 and Layer 3 switch is the routing method. Layer 3 switch is capable of inter-VLAN routing and does not need additional device connected ...
How to enable routing between two VLANs?
The simplest way to enable routing between the two VLANs to simply connect an additional port from each VLAN into a Router. The Router doesn’t know that it has two connections to the same switch — nor does it need to. The Router operates like normal when routing packets between two networks.
What is a layer 3 switch?
A Layer 3 Switch is different from a traditional Layer 2 Switch in that it has the functionality for routing between VLANs intrinsically. In fact, when considering how a L3 Switch operates, you can safely imagine that a Layer 3 Switch is a traditional switch with a built in Router.
What is SVI in VLAN?
An SVI serves as the L3 termination point for each VLAN – aka , the way in or out of each VLAN. Another way of looking at it is that the SVI serves as the interface on the built-in Router of the Multilayer switch, allowing traffic from one VLAN to reach the built-in Router and be routed to another VLAN as necessary.
What is a router?
A router will perform the routing function necessary for two hosts on different networks to speak to one another. In the same way, a Router is what we will need in order for hosts in different VLANs to communicate with one another. There are three options available in order to enable routing between the VLANs:
How does sub interface work?
The logical operation of the Sub-interface topology works exactly as the separate physical interface topology in the section before it. The only difference is with Sub-interfaces, only one Router interface is required to terminate all VLANs.
Is L3 enabled by default?
Some L3 switches come with it enabled by default. Applying the command while it is already enabled will not cause any harm, so if in doubt as to whether it is already enabled or not, simply applying it again is safe. To apply an IP address to the VLANs, configure the SVI as follows:
Do switchports need a VLAN?
Of course, before assigning the switchport to a VLAN, it is a good idea to create the VLAN in the VLAN Database. The Router interfaces also use a standard configuration — configuring an IP address and enabling the interface:
Which layer of the network does routing operate on?
Routing operates at layer 3, where packets are sent to a specific next-hop IP address, based on destination IP address. Devices in the same layer 2 segment do not need routing to reach local peers.
Why are VLANs important?
VLANs allow for greater flexibility by allowing different layer 3 networks to be sharing the same layer 2 infrastructure. The image below shows an example of a multi-VLAN environment on a layer 2 switch: Since VLANs exist in their own layer 3 subnet, routing will need to occur for traffic to flow in between VLANs.
What layer is broadcast traffic in?
Broadcasts are contained in the same layer 2 segment, as they do not traverse past a layer 3 boundary.
