What are the chances of a white dwarf becoming a black hole?
No chance of a black hole. A White Dwarf is a star whose mass was insufficient to collapse to form a black hole at the end of its life when fusion ceases. The electrons with the nucleus would collapse but not to the extent that electrons would combine with protons to form neutrons.
Can a white dwarf turn into a neutron star?
But is there any possibility that a white dwarf can turn into a neutron star (or possibly a black hole)? The answer is: to a neutron star - possibly; to a black hole, no.
Why can't we pass through black holes?
Because the gravity around black holes is so massive that it does some strange things. Well, assuming white holes exist, and that black holes connect to them, then yes someone could theoretically pass through the connecting Einstein-Rosen Bridge (also known as a wormhole).
Why don't white dwarfs go supernova?
If a white dwarf is siphoning off material from a stellar companion, when it reaches 1.4 solar masses (Chandrasekhar limit) it will become a Type 1a supernova. Since its mass was limited to 1.4 solar masses it can only become a neutron star, there is not enough mass to go BH.

Can a dwarf star become a black hole?
Some smaller stars are big enough to go supernova, but too small to become black holes — they'll collapse into super-dense structures called neutron stars after exploding as a supernova.
How does a white dwarf become a black dwarf?
Within this nebula, the hot core of the star remains—crushed to high density by gravity—as a white dwarf with temperatures over 180,000 degrees Fahrenheit (100,000 degrees Celsius). Eventually—over tens or even hundreds of billions of years—a white dwarf cools until it becomes a black dwarf, which emits no energy.
Is white dwarf the same as black hole?
A white dwarf is just an exposed stellar core, the remnant of a star like our Sun, which is not massive enough to collapse into a black hole after its last breaths, but it can still accrete material and eat like one.
Can a white dwarf become a supernova?
One of the stars, a carbon-oxygen white dwarf, steals matter from its companion star. Eventually, the white dwarf accumulates too much matter. Having too much matter causes the star to explode, resulting in a supernova.
Will our sun become a red giant?
In approximately five billion years, our own sun will transition to the red giant phase. When it expands, its outer layers will consume Mercury and Venus and also reach Earth. Scientists are still debating whether or not our planet will be engulfed, or whether it will orbit dangerously close to the red giant sun.
How long can a white dwarf last?
NASA estimates that the sun will stay a white dwarf for around 10 billion years. However, other estimates suggest stars can stay in this phase for 1015, or a quadrillion, years.
Can a white dwarf support life?
Researchers believe there may be a planet that could sustain life, in the vicinity of a dying sun. If confirmed, this would be the first time that a potentially life-supporting planet has been found orbiting such a star, called a "white dwarf".
What if our sun was a white dwarf?
The sun as a white dwarf When the sun is a white dwarf, most of the solar system will still be around. Mercury, Venus and Earth will be gone, but Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune will survive and continue to go around the sun. So will the asteroid belt, Kuiper belt and dwarf planets like Pluto.
Why are white dwarfs so hot?
The temperatures are extremely high in the core (15 million degrees Kelvin for main sequence stars burning hydrogen, and 100 million degrees for stars burning helium). As a result, when a low mass star dies by shedding its envelope leaving behind the core as a white dwarf, it is very hot at around 100 million degrees.
How hot is a nova?
Runaway fusion occurs when the temperature of this atmospheric layer reaches ~20 million K, initiating nuclear burning, via the CNO cycle.
Can a white dwarf explode?
White dwarfs are extremely dense stars that have consumed the majority of their gas. In some cases, excess hydrogen collects on the surface of a white dwarf, usually due to the white dwarf "stealing" material from a nearby star — that accretion can explode in a violent, energetic release called a nova.
Is a white dwarf hotter than the sun?
A typical white dwarf has a carbon and oxygen mass similar to the Sun, but is much smaller in size (similar to the Earth). It is much hotter (25,000 K), but because of its small size its luminosity is low. How then can we find them?
How long does it take for a white dwarf star to become a black dwarf star?
But there's no need to start searching for the elusive black dwarfs yet. At the moment, they're strictly theoretical. Scientists have calculated that a white dwarf will take at least a hundred million billion years to cool down and become a black dwarf, according to astronomer Ethan Siegel.
What happens to a white dwarf at the end of its life?
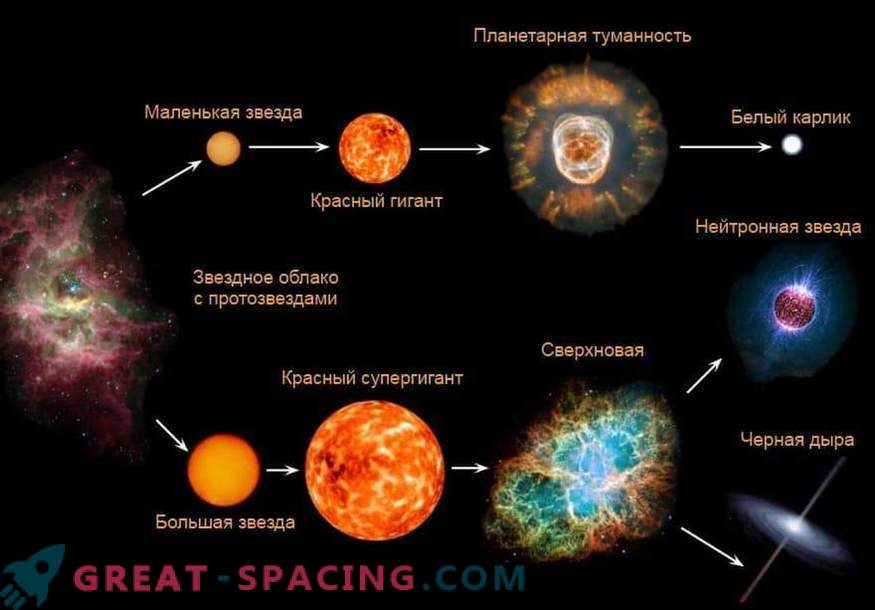
White dwarf formation The most massive stars, with eight times the mass of the sun or more, will never become white dwarfs. Instead, at the end of their lives, white dwarfs will explode in a violent supernova (opens in new tab), leaving behind a neutron star (opens in new tab) or black hole (opens in new tab).
What would a black dwarf be made of?
Since the theoretical black dwarf is just a white dwarf that has cooled completely, then it should be the same composition as a white dwarf. The final end product of fusion is iron, therefore a black dwarf would be made of iron.
What happens at the black dwarf stage?
A Black dwarf is Hypothesized as the final stage of the life cycle of a Sun-like Star. When Sun burns all of its hydrogen to helium, its core will shrink and it will rearrange itself, expanding its outer layers o form a Redgiant Star.
How does a white dwarf collapse?
On the other hand, the white dwarf is supported by electron degeneracy. If neutronisation begins to occur in the core, then protons (in nuclei) capture electrons to form neutrons. This destabilises the star causing it to collapse. The collapse would proceed (quickly) in a similar way to a core collapse supernova. The nuclei would dissociate, neutronisation would run to near-completion and the collapse would be halted by the formation of a neutron star.
Can a black hole be formed by a neutron star?
There is little possibility that a black hole could be formed by such a collapse. The collapsing object would be of order 1.4 solar masses and comfortably smaller than the maximum mass of observed neutron stars (at least 2 solar masses). Therefore the collapse will be halted at the neutron star phase.
Is a neutron star a black hole?
The answer is: to a neutron star - possibly; to a black hole, no.
Can a white dwarf survive a supernova?
But some white dwarfs have iron cores, for example, https://arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/9911371, and it might be expected that the iron core would survive the supernova. Whether it could gain enough material to collapse into a neutron star I couldn't say, it doesn't sound easy but never say never.