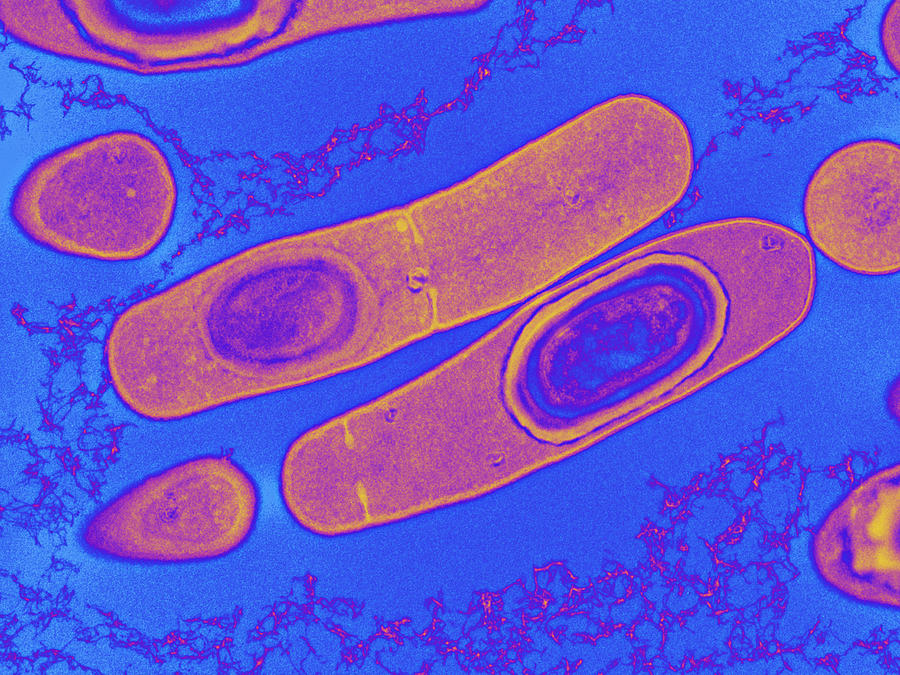
Clostridium difficile is an opportunistic, spore-forming, gram-positive, anaerobic bacillus. It is transmitted from one patient to another through direct or indirect contact, through the oral ingestion of its vegetative cells or endospores (i.e. the fecal-oral route) or from a contaminated environment or medical device.
Is there a cure for Clostridium difficile?
The CDC website states, ” Transplanting stool from a healthy person to the colon of a patient with repeat C. difficile infections has been shown to successfully treat C. difficile. These “fecal transplants” appear to be the most effective method for helping patients with repeat C. difficile infections. This procedure may not be widely available and its long-term safety has not been established.”
Where does Clostridium difficile really come from?
How does c diff make you ill? The actions of antibiotics taken for other conditions can change your gut bacteria and allow toxic c.difficile to attack your stomach cell linings. Where does it come from? C.Difficile is found in the soil, in animals and the food chain. It often enters our houses through the dust on our feet.
What is the advantage of endospore to Clostridium?
When vegetative cells of certain bacteria such as Bacillus spp and Clostridium spp are subjected to environmental stresses such as nutrient deprivation, they produce metabolically inactive or dormant form-endospore. Formation of endospores circumvent the problems associated with environmental stress and helps them to survive.
How long does Clostridium difficile live outside the body?
When C. diff germs are outside the body, they become spores. These spores are an inactive form of the germ and have a protective coating allowing them to live for months or sometimes years on surfaces and in the soil. The germs become active again when these spores are swallowed and reach the intestines.

Can Clostridium produce spores?
The ability of Clostridium perfringens to form spores plays a key role during the transmission of this Gram-positive bacterium to cause disease.
What causes C. diff to form spores?
diff produces spores when attacked by antibiotics. The spores can live in the open air or in dirt for up to two years. Normal disinfectants are not effective against the spores. This means that even if you kill the C.
What is the morphology of Clostridium difficile?
Morphology: C. difficile are Gram-positive rods, measuring 3–5 μm in length and 0.5 μm in width. They are capsulated, motile by peritrichous flagella and sporulating in nature. Some strains also contain S-layer.
How does Clostridium difficile grow?
difficile to thrive2. C. difficile is transmitted as a dormant spore via the fecal-oral route and subsequently germinates within the gastrointestinal tract, producing vegetative cells capable of generating several toxins and causing severe disease and colitis3.
Is C. diff a bacteria or spore?
C. diff is a spore-forming, Gram-positive anaerobic bacillus that produces two exotoxins: toxin A and toxin B. It is a common cause of antibiotic-associated diarrhea (AAD) and accounts for 15 to 25% of all episodes of AAD.
Does Bacillus produce endospores?
Examples of bacteria that can form endospores include Bacillus and Clostridium. The endospore consists of the bacterium's DNA and part of its cytoplasm, surrounded by a very tough outer coating. Endospores can survive without nutrients.
Does Clostridium botulinum produce endospores?
Clostridium botulinum is a highly dangerous pathogen that forms very resistant endospores that are ubiquitous in the environment, and which, under favorable conditions germinate to produce vegetative cells that multiply and form the exceptionally potent botulinum neurotoxin.
How do C. diff spores spread?
diff germs are carried from person to person in poop. If someone with C. diff (or caring for someone with C. diff) doesn't clean their hands with soap and water after using the bathroom, they can spread the germs to people and things they touch.
What does Clostridium look like under microscope?
Under the microscope, they appear as long, irregular (often drumstick- or spindle-shaped) cells with a bulge at their terminal ends (forms subterminal spores). Under Gram staining, C. difficile cells are Gram-positive and show optimum growth on blood agar at human body temperatures in the absence of oxygen.
What are C. diff spores highly resistant to?
Spores of C. difficile are resistant to high temperatures, ultraviolet light, harsh chemicals, and antibiotics. Furthermore, because spores are resistant to antibiotics, they can remain in the gastrointestinal tract and potentially contribute to recurrent disease following treatment and eradication of vegetative C.
Are Clostridium difficile spores killed by alcohol?
Background. Alcohol-based hand rubs (ABHRs) are an effective means of decreasing the transmission of bacterial pathogens. Alcohol is not effective against Clostridium difficile spores.
What temperature kills C. diff spores?
Unsurprisingly, temperatures greater than 85°C are required to completely eliminate all C. difficile spores when in an aqueous environment.
How long are C. diff spores active?
C. difficile spores can be shed to the environment by both asymptomatic and symptomatic patients and may survive for up to 5 months on inanimate surfaces (17).
What temperature kills C. diff spores?
Unsurprisingly, temperatures greater than 85°C are required to completely eliminate all C. difficile spores when in an aqueous environment.
Are Clostridium difficile spores killed by alcohol?
Background. Alcohol-based hand rubs (ABHRs) are an effective means of decreasing the transmission of bacterial pathogens. Alcohol is not effective against Clostridium difficile spores.
What are C. diff spores highly resistant to?
Spores of C. difficile are resistant to high temperatures, ultraviolet light, harsh chemicals, and antibiotics. Furthermore, because spores are resistant to antibiotics, they can remain in the gastrointestinal tract and potentially contribute to recurrent disease following treatment and eradication of vegetative C.
What are the characteristics of Clostridium difficile?
General Characteristics of Clostridium difficile. Clostridium difficile is a species of Gram-positive, rod-shaped, spore-forming bacteria. C. difficile are anaerobic—lives in the absence of oxygen.
How long does Clostridium difficile live on an inanimate surface?
In the presence of oxygen, the vegetative form of C. difficile can survive up to 24 hours on an inanimate surface; whereas, C. difficile spores can survive up to 2 years on inanimate surfaces that are exposed to oxygen. HABITAT—Where does Clostridium difficile live?
What is the vegetative state of C. difficile?
In the vegetative state, the bacterium is able to use nutrients to grow and divide. However, when conditions become unfavorable, C. difficile is able to enter a dormant state and form a highly resistant spore.
How does C. difficile get its energy?
Since C. difficile is anaerobic, it obtains its energy, ATP, by fermentation of carbon and nitrogen substrates. C. difficile requires six amino acids for fermentative metabolism and growth—leucine, isoleucine, proline, tryptophan, valine, and glycine.
How does C difficile reproduce?
C. difficile reproduces by binary fission. As seen in the picture on the right, the circular strand of DNA begins replicating. Then, the cell begins elongating as the new copies of DNA start to move to opposite ends of the cell.
Where does C. difficile live?
C. difficile inhabits the microflora of intestines of humans . Around 3% of healthy adults and up to 70% of babies have a number of C. difficile bacteria living in their gut. However, the number of C. difficile bacteria is kept very low and in control by the millions of harmless bacteria in the intestines that aid in digestion.
What are the unfavorable conditions for a fungus?
Unfavorable conditions include a deprivation of nutrients, an exposure to a very acidic environment, or an exposure to high temperatures. These spores are very resistant to heat, radiation, drying, chemicals, and even oxygen (for up to two years).
Where is Clostridium difficile found?
Clostridium difficile (Figure 1) is a part of the normal bacteria living in the intestine (colonic flora). It is also present in the environment in places such as soil, water, and animal feces. Their spores survive well in hospital environments and are resistant to environmental factors and many disinfectants.
What is the treatment for Clostridium difficile?
Treatment for Clostridium difficile will consist of a different type of antibiotic, typically oral metronidazole (flagyl) or oral vancomycin. Probiotics such as bacteria and yeast that help restore the normal balance of the bacterial flora are beneficial. In some cases a fecal transplant may be necessary.
How is C difficile transmitted?
C. Difficle is transmitted by fecal-oral route. Ingested bacterial spores survive gastric acidity. In the intestine, spores germinate into vegetative form. In severe cases, Clostridium difficile toxins can cause pseudomembranous colitis, which is a severe inflammation of the colon.
What causes watery diarrhea?
Clostridium difficile causes antibiotic associated diarrhea. In mild to moderate cases, there is a watery diarrhea, mild abdominal tenderness and distension. In severe cases it causes pseudomembranous colitis, which is the formation of whitish yellow plaques (Figure 3). This causes severe watery diarrhea and may progress to a life-threatening toxic ...
What is the name of the organism that forms endospores?
Clostridium form endospores under adverse environmental conditions. Spores are a survival mechanism for the bacteria. The main species of clostridium causing disease in humans are: · Clostridium difficile: a condition associated with antibiotics causing diarrhea.
Do antibiotics kill C difficules?
Antibiotics will kill the bacteria in the intestines that are competing with the C. difficle, but the antibiotics do not kill the C. Difficle, making it easier for the C. Difficle to overgrow and secrete its toxins causing pseudomembranous colitis (Figure 2). Download.
