How serious is invasive ductal carcinoma?
Invasive ductal carcinoma describes the type of tumor in about 80 percent of people with breast cancer. The five-year survival rate is quite high -- almost 100 percent when the tumor is caught and treated early. Once the cancer has metastasized to distant organs like the bones or liver, the five-year survival rate drops by almost three fourths.
Is it really duct carcinoma in situ?
It is the cells lining the duct that can go “bad” in DCIS. If these abnormal cells, which are uncontrollably growing, stay inside the duct, they are referred to as Ductal Carcinoma In-Situ (DCIS). They are ductal cells that have become malignant, but they have remained in their original place (in-situ) and are thus a noninvasive cancer.
How do you pronounce cancer in situ?
Ductal carcinoma in situ pronunciation with meanings, synonyms, antonyms, translations, sentences and more Correct way to pronounce mirlo in Spanish is? mear-lowe
How long does DCIS take to become invasive?
It assumes that all breast carcinomas begin as DCIS and take 9 years to go from a single cell to an invasive lesion for the slowest growing lesions, 6 years for intermediate growing DCIS lesions, and 3 years for fast-growing DCIS lesions.

How long does DCIS take to become invasive?
It assumes that all breast carcinomas begin as DCIS and take 9 years to go from a single cell to an invasive lesion for the slowest growing lesions, 6 years for intermediate growing DCIS lesions, and 3 years for fast-growing DCIS lesions.
What percentage of DCIS becomes invasive?
“DCIS is non-invasive so women do not die of it. Their real concern arises if they develop invasive cancer and the cancer spreads. '' According to the study, the group of patients with the lowest risk has only a 2 percent chance of developing invasive cancer at 5 years and a 4 percent chance at 8 years.
Can DCIS turn into invasive cancer?
In some cases, DCIS may become invasive cancer and spread to other tissues. At this time, because of concerns that a small proportion of the lesions could become invasive, nearly all women diagnosed with DCIS currently receive some form of treatment.
How does carcinoma in situ become invasive?
Carcinoma in situ is the earliest stage of a cancer, and is, at this stage, considered "non-invasive." With regard to staging, carcinoma in situ is considered stage 0 cancer. Stage 1 to stage 4 are all considered "invasive" cancers, as they have spread beyond something called the "basement" membrane in tissues.
How do you know if DCIS has spread?
The doctor will remove a bit of tissue to look at under a microscope. They can make a diagnosis from the biopsy results. If the biopsy confirms you have cancer, you'll likely have more tests to see how large the tumor is and if it has spread: CT scan.
Can DCIS spread after biopsy?
Will DCIS return or spread? Since DCIS is a noninvasive form of cancer, it does not spread throughout the body (metastasize). For patients having a lumpectomy with radiation, the risk of local recurrence ranges from 5% to 15%. For those having mastectomy, the risk of local recurrence is less than 2%.
How serious is ductal carcinoma in situ?
DCIS is non-invasive because it hasn't spread beyond the milk ducts into other healthy tissue. DCIS isn't life-threatening, but if you're diagnosed with DCIS, you have a higher-than-average risk of developing invasive breast cancer later in life.
What is the best treatment for ductal carcinoma in situ?
Radiation therapy Treatment of DCIS has a high likelihood of success, in most instances removing the tumor and preventing any recurrence. In most people, treatment options for DCIS include: Breast-conserving surgery (lumpectomy) and radiation therapy. Breast-removing surgery (mastectomy)
Should I get a double mastectomy for DCIS?
“The findings suggest that patients and their doctors should focus on risk factors and appropriate therapy for the diseased breast, not the opposite breast, and that ipsilateral DCIS should not prompt a bilateral mastectomy.”
What is the evidence to suggest that DCIS is a precursor of invasive carcinoma?
Clinical observational studies have further corroborated the hypothesis that DCIS is a precursor of IBC. Perhaps the most persuasive evidence to suggest that DCIS and IBC are progressive stages of an evolutionary continuum is that they affect the same anatomical site.
How often does DCIS come back?
Researchers compared the rate of recurrence five years and ten years after diagnosis, as well as survival rates. Overall, they found that patients had a 3.4% risk of a recurrence after five years and a 7.6% risk after ten years.
What stage is ductal carcinoma in situ?
Stage 0 breast cancer, ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is a non-invasive cancer where abnormal cells have been found in the lining of the breast milk duct. In Stage 0 breast cancer, the atypical cells have not spread outside of the ducts or lobules into the surrounding breast tissue.
How often is DCIS upgraded?
Indeed, in a number of published series of DCIS lesions diagnosed using needle biopsy, upgrading occurs in 2-49% of cases (Table I). The main consequence of upgrading from DCIS to an invasive breast carcinoma is a change in the treatment strategy during its course.
What percentage of DCIS is grade 3?
There was no significant difference in the distribution of grades between the DCIS detected by mass screening and the DCIS not detected by mass screening (from the interval group); 16.4–18.8 % were low grade, 27.2–31.6 % were intermediate grade, and 52.0–54.0 % were high grade (Table 3).
What is the recurrence rate of DCIS?
Patients with DCIS have a 15% chance of invasive local recurrence, Dr. Narod noted, but “preventing the invasive local recurrence has nothing to do with preventing death.
What is the survival rate for DCIS?
Generally, patients diagnosed with DCIS have an excellent long-term breast-cancer-specific survival of around 98% after 10 years of follow-up24–27 and a normal life expectancy.
What is ductal carcinoma in situ?
Ductal Carcinoma In Situ (DCIS) About 1 in 5 new breast cancers will be ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS). Nearly all women with this early stage of breast cancer can be cured. DCIS is also called intraductal carcinoma or stage 0 breast cancer. DCIS is a non-invasive or pre-invasive breast cancer.
Can a DCIS patient have a mastectomy?
In most cases, a woman with DCIS can choose between breast-conserving surgery (BCS) and simple mastectomy.
Is DCIS invasive or noninvasive?
DCIS is a non-invasive or pre-invasive breast cancer. This means the cells that line the ducts have changed to cancer cells but they have not spread through the walls of the ducts into the nearby breast tissue.
Can DCIS be invasive?
However, DCIS can sometimes become an invasive cancer. At that time, the cancer has spread out of the duct into nearby tissue, and from there, it could metastasize to other parts of the body.
What is ductal carcinoma in situ?
What is DCIS (ductal carcinoma in situ)? DCIS is an early form of breast cancer. Breast cancer starts when cells in the breast begin to divide and grow in an unusual and uncontrolled way. Breasts are made up of lobules (milk-producing glands) and ducts (tubes that carry milk to the nipple).
What is it called when cancer cells are in situ?
When cancer cells have developed within the ducts of the breast and remain within the ducts (‘in situ’), it is called DCIS. The cancer cells have not yet developed the ability to spread outside these ducts into the surrounding breast tissue or to other parts of the body. ...
How to remove DCIS?
In the x-ray department or breast clinic, a mammogram or ultrasound scan will be used as a guide to insert a fine wire into the breast under local anaesthetic. The wire is then carefully secured under a small dressing and left in place until the operation to remove the area of DCIS. The operation is usually done under a general anaesthetic on the same day, and the wire will be removed during the operation.
Why do we remove DCIS from breast?
The aim of treatment is to remove all the DCIS from within the breast to reduce the chance of it becoming an invasive cancer.
How is DCIS graded?
DCIS is graded based on what the cells look like under the microscope. They will be given a grade according to how different they are to normal breast cells and how quickly they are growing.
What are the different grades of DCIS?
DCIS is graded as: 1 Low grade – the cancer cells look most like normal breast cells and are usually slow growing 2 Intermediate grade – the cancer cells look less like normal breast cells and are growing faster 3 High grade – the cancer cells look different to normal breast cells and may be fast growing
Can a breast x-ray show a DCIS?
DCIS usually has no symptoms. Most cases of DCIS are found during routine breast screening or if a mammogram (breast x-ray) is done for some other reason. Occasionally DCIS is found when someone has a breast change such as a lump or discharge (liquid) from the nipple.
How much risk of breast cancer after DCIS?
Six factors in particular emerged as the most significant indicators, with risk for invasive breast cancer after DCIS diagnosis ranging from 36% to 84%. They were…. Feeling a lump (84% risk). DCIS does not cause symptoms and 80% of the time is found only by mammography.
Where is the study titled "Predictors of an Invasive Breast Cancer Recurrence after DCIS?
Study titled “Predictors of an Invasive Breast Cancer Recurrence after DCIS: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses” by researchers at the Netherlands Cancer Institute , Amsterdam, published in Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention.
Why is DCIS so common?
DCIS has become increasingly common—possibly because women are living longer, more women are getting screening mammograms, and mammograms have become better at finding these small breast cancers. About 20% of all breast cancers are DCIS. Most women with DCIS have a lumpectomy, and some also have radiation. The risk for DCIS recurrence ...
What is DCIS in milk?
DCIS is cancer that starts in a milk duct and has not spread outside the duct. Often called “stage 0,” it’s such an early stage of cancer that some experts believe it’s actually a precancerous condition rather than actual cancer.
Can DCIS be treated with radiation?
However, as there hasn’t been a way to reliably predict which women with DCIS will develop invasive breast cancer, guidelines call for all women with the condition to be treated with either surgery alone or surgery and radiation…and frequently hormonal therapy as well. Doctors are coming to believe that this is overtreatment for the majority of women.
Does p16 cause breast cancer?
Overexpression of p16, a protein involved in regulating tumor-cell growth that is detected during biopsy, has been linked to more aggressive tumor growth. Being African-American (43% risk). For reasons that are not clearly understood, African-American women have higher rates of all types of breast cancer recurrence.
Is ductal carcinoma in situ life threatening?
Published Date: June 13, 2019. Most ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) breast cancer will never become life-threatening, even if left untreated. However, there hasn’t been a good way to tell when DCIS should be treated and when treatment can be safely skipped—until now. A new study has identified six factors that determine when DCIS is most likely ...
What does DCIS mean in mammograms?
Ductal Carcinoma in Situ (DCIS) As more women have gotten mammograms on a regular basis, DCIS has been found far more often. DCIS is a noninvasive precancer. It is not life threatening. If you have DCIS, it means that you have abnormal cells in the lining of a duct. While virtually all invasive cancer begins as DCIS, ...
How is DCIS treated?
The options for treating DCIS are: lumpectomy, lumpectomy and radiation, a combination of those with tamoxifen, or mastectomy. You don’t have to rush into any one treatment because your doctor or your friend or anyone else says you should. It’s your breast, and your life. Take the time to decide what’s best for you.
Why is DCIS not tested for HER2?
DCIS is not tested for HER2 for two reasons: one, DCIS is more likely than invasive cancer to be HER2+ (we don’t know why); two, DCIS is not treated with HER2-targeted therapies, so testing DCIS for HER2 would not influence treatment choices. I was diagnosed with DCIS.
What happens when a DCIS is high grade?
When DCIS is high-grade, there are many dead cells in the duct, and the cells that are alive are very aberrant. In this situation there is a higher chance that microinvasion—a spot where the DCIS has crossed the line to invasion—has occurred. It can be tricky to diagnose micrometastases in the sentinel node.
How to tell if you have DCIS?
When these microcalcifications are seen, it is recommended that a woman have a core biopsy or a wire localization biopsy. This will determine whether you actually have DCIS. If you do, the next step should always be to have another mammogram to see if the biopsy has gotten rid of all the microcalcifications, as no matter how thorough your surgeon has been, there still may be a few remaining. If the diagnosis is DCIS, make sure your pathology report includes information about the grade, presence of necrosis, margin, and estrogen receptor. This information is needed to determine how to treat the DCIS.
How many cancers are in the opposite breast?
Thirty-six cancers (noninvasive and invasive combined) developed in the opposite breast in the placebo group while 18 developed in the tamoxifen group. Statistically, tamoxifen lowered the rate of developing cancer in the opposite breast from 3.45 percent to 2.0 percent.
Is DCIS an invasive cancer?
While virtually all invasive cancer begins as DCIS, not all DCIS will go on to become an invasive cancer. An invasive cancer is one that has the potential to metastasize (spread). Right now we have no way to determine which DCIS will go on to become invasive cancer and which will not.
What Medication Treat Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
Tamoxifen may be prescribed for woman of all ages who have been treated for DCIS. In those women past menopause, the doctor may prescribe an aromatase inhibitor. These medications help lower the risk of DCIS or another type of cancer developing in either breast.
Treatment For Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
No two patients are the same. Your doctor will tailor your treatment plan based upon your test outcomes and case history. To name a few things, your doctor will consider:.
If Someone Has Dcis What Should Be The First Step In Deciding On Treatment
A person diagnosed with DCIS usually meets with a breast surgeon first. The doctor will assess the tumors size, grade, and hormone-receptor status, as well as other risk factors that are important for treatment decisions.
How Is Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Diagnosed
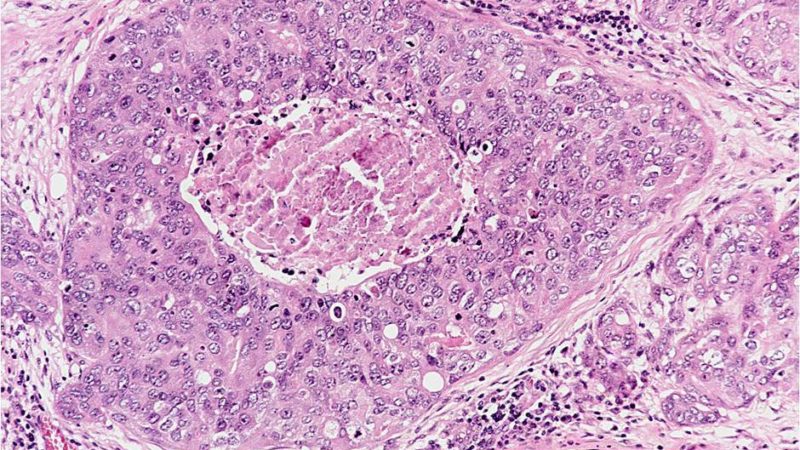
About 80% of cases are found by mammograms. On the mammogram, it appears as a shadowy area.
More About Invasive Breast Cancer With Central Necrosis
Sometimes medics refer to an infiltrative breast carcinoma with central necrosis as a centrally necrotizing breast carcinoma, . Historically, centrally necrotizing breast carcinomas have an aggressive course.
Health Literacy To Empower Patients
With the right information, patients can make the best decisions about their care. By partnering with patients, healthcare providers, and hospitals, we hope to provide all patients with the tools and knowledge to understand their pathology report.
Common Breast Cancer Types
After skin cancer, breast cancer is the most common type of cancer diagnosed in women. About 284,200 cases will be diagnosed in 2021, according to the American Cancer Society . Men also may develop breast cancer, though its much more rare.
Where do invasive breast cancer cells come from?
Most invasive breast cancers come from the mammary ducts. A few develop in the lobules.
What is DCIS in women?
DCIS is often called a pre - cancer (or stage zero cancer ): cancer cells appear in the mammary ducts but never move to invade other tissues. The disease, however, can evolve in some women to become malignant/invasive. Treatment for DCIS can involves surgery and radiotherapy.
Is it dangerous to have a breast tumor?
For this reason, they are not seen as dangerous, except when the tumor grows so much that it starts compressing and damaging nearby breast structures.
Is a cancer in situ real?
Carcinomas in situ are not real cancers. The tumor develops from the epithelial cells that line the ducts/lobules, but lack the ability to move ( in situ means, literally, in place ), so are never invasive (to be invasive is a defining characteristic for cancer).
