See more

What is PCC oxidation?
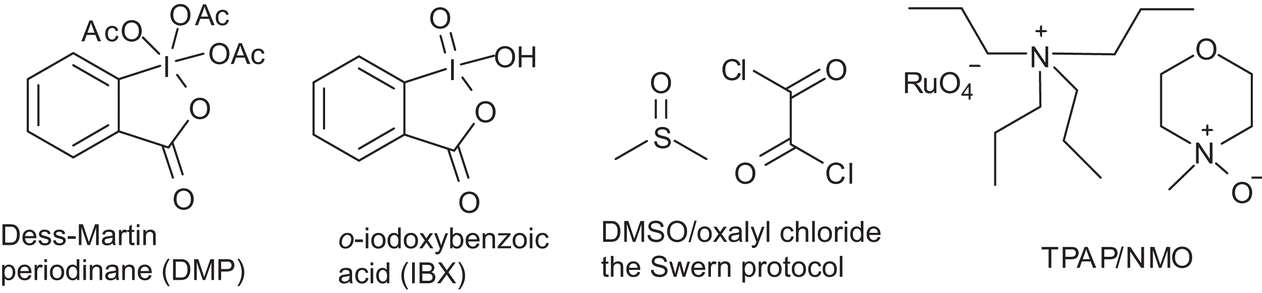
Pyridinium Chlorochromate (PCC) Oxidation. PCC oxidation is one of the selective methods for oxidizing primary alcohols to aldehydes. Like other mild oxidizing agents such as the Swern and Dess-Martin (DMP) oxidation, it stops the oxidation of the alcohol once a carbonyl group is formed.
How does the acid-base reaction start?
The reaction starts by converting the alcohol to its corresponding chromate ester, which then undergoes a deprotonation by a base to form a C=O double bond: In the acid-base step, either the chloride ion or the alcohol can serve as a base to remove the hydrogen.
Is PCC a chromium oxidizer?
For now, let’s focus on the PCC oxidation. It belongs to the family of chromium-based oxidizing agents most of which are CrO 3, Na 2 Cr 2 O 7, and chromic acid but unlike those, it is a mild oxidizing agent.
Is PCC a salt?
PCC is a Cr 6+ salt formed between py ridine (C 6 H 5 N), HCl, and CrO 3. It is soluble in halogenated organic solvents such as dichloromethane which allows carrying out the reaction in the absence of water.
Is alcohol a ketone or aldehyde?
If it is a primary alcohol, the product is an aldehyde while the oxidation of secondary alcohols results in a ketone: This is the advantage of mild oxidizing agents since, remember, strong oxidizing agents oxidize primary alcohols all the way to carboxylic acids.
Why is PCC preferred over Swern oxidation?
In this reaction, PCC is preferred over Swern oxidation because it does not require low temperature, it is easy to manipulate and it does not generate bad odour. 2.75 eq. PCC, NaOAc o CH2Cl2, 2 h, r.t. ' ". Ref. 240. The starting alcohol is very unstable and must be oxidized immediately after its preparation.
What is PCC reacting with?
PCC reacts with tertiary allylic alcohols, forming an intermediate chromate ester that evolves giving a conjugated enone or enal. Sometimes, the isomeric chromate ester produces the epoxidation of the alkene, giving an epoxy alcohol that can be further oxidized to an epoxy ketone.
How does PCC transform tetrahydrofurans?
PCC transforms 5,6-dihydroxyalkenes into tetrahydrofurans in a highly stereoselective manner284 (see Equation below). This transformation can be explained by the initial formation of a cyclic chromate ester by reaction with the diol moiety, followed by an intramolecular oxidative addition of the chromate ester on the alkene.
Why does uneventful oxidation occur?
An uneventful oxidation of both alcohols occurs, because geometrical constrains prevent the formation of the intermediate lactol. Very often, uneventful oxidations with no formation of lactone are found, even in cases in which the formation of an intermediate stable lactol looks likely.299.
How does PCC evolve?
As in other chromium-based reagents (see pages 12 and 38), sometimes intermediate chromate esters, resulting from a primary reaction between alcohols—including tertiary alcohols—and PCC, evolve by breakage of a carbon-carbon bond when it results in the generation of a stable cation. Stable cations generated in this way include cations located at allylic236 positions and at tertiary carbons,312 as well as cations stabilized by nitro-
What is PCC deposited over?
Normally, PCC is deposited over the alumina.g. Occasionally, ca. 10-20 equivalents of acetic acidh are added in order to accelerate the reaction. Sometimes, the reaction flask is sonicated with ultrasound in order to fragment the surface of the PCC particles and, therefore, accelerate the reaction.
When does the PCC-induced formation of tetrahydrofurans fail?
Of course, the PCC-induced formation of tetrahydrofurans from 5, 6-dihydroxyalkenes fails when structural constrains prevent the approach of the intermediate cyclic chromate ester to the alkene.286