Yes, any positively charged dye can be used such as safranin and basic fuchsin. Bacteria can be seen without staining. Also Know, what is direct staining? When a staining procedure colors the cells present in a preparation, but leaves the background colorless (appearing as white), it is called a direct stain.
Why is safranin used in Gram staining?
The safranin is also used as a counter-stain in Gram’s staining. In Gram’s staining, the safranin directly stains the bacteria that has been decolorized. With safranin staining, the gram-negative bacteria can be easily distinguished from gram-positive bacteria. Which type of cells would be stained by safranin?
What is safranin used for?
Safranin is used as a counterstain in some staining protocols, colouring all cell nuclei red. It can also be used for the detection of cartilage, mucin and mast cell granules.
What does the Safranin O stain of the removed flap show?
The Safranin O stain of the removed flap shows the green layer of fibrous connective tissue, the green periosteal membrane bone, and flecks of metaphyseal bone–central red cartilage core surrounded by green staining bone. Gerhard Krumschnabel, ... Erich Gnaiger, in Methods in Enzymology, 2014
What is the role of safranin in mitochondria?
Safranin is a lipophilic cationic dye which accumulates in mitochondria according to the inside negative potential in energized mitochondria.

What dyes can be used in direct staining?
In simple (or direct) staining only one dye is used, which is washed away after 30–60 seconds, before drying and examination. Gentian violet, crystal violet, safranin, methylene blue, basic fuchsin, and others are the dyes used in this method.
What stain uses safranin?
Safranin is used as a counterstain in some staining protocols, colouring cell nuclei red. This is the classic counterstain in both Gram stains and endospore staining. It can also be used for the detection of cartilage, mucin and mast cell granules.
What will happen if safranin is used as primary stain instead of crystal violet in Gram staining?
Since the safranin is lighter than crystal violet, it does not disrupt the purple coloration in Gram positive cells. However, the decolorized Gram negative cells are stained red.
Can safranin be used as a simple stain?
Simple Stain Basic stains, such as methylene blue, Gram safranin, or Gram crystal violet are useful for staining most bacteria. These stains will readily give up a hydroxide ion or accept a hydrogen ion, which leaves the stain positively charged.
What is the purpose of using safranin in Gram staining?
BioGnost's Gram Safranin solution is used for contrast staining of bacterial species that did not retain their primary dye, i. e. Gram-negative bacteria. That enables differentiating the blue and purple-colored Gram-positive bacteria from the red-colored Gram-negative bacteria.
What can be used instead of safranin?
The most common counterstain is safranin, which colors decolorized cells pink. An alternate counterstain is basic fuchsin, which gives the decolorized cells more of a bright pink or fuchsia coloration.
What happens if you leave safranin on too long?
The decolorizer should stay on the slide for no more than 15 seconds! If the decolorizer is left on too long, even gram positive cells will lose the crystal violet and will stain red.
What would happen if crystal violet and safranin stains were reversed?
What would happen if you made an error and reversed the crystal violet and safranin stain? Group of answer choices Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria would appear Gram-positive. No change would be observed, because the result depends on the cell wall structure, not on the order of the dyes.
Why is crystal violet used as a primary stain?
The gram stain utilizes crystal violet as the primary stain. This basic dye is positively charged and, therefore, adheres to the cell membranes of both gram negative and positive cells. After applying crystal violet and waiting 60 seconds the excess stain is rinsed off with water. Next, a mordant is used.
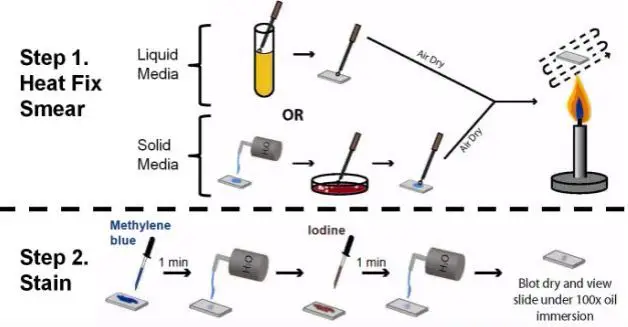
What is direct staining?
The cell wall of most bacteria has an overall net negative charge and thus can be stained directly with a single basic (positively charged) stain or dye. This type of stain allows us to observe the shape, size and arrangement of bacteria. Use the smear prepared in the previous procedure.
What is the difference between a basic direct stain and an acidic negative stain in terms of the charge of the chromophore?
Basic stains have a positively charged chromophore and because bacterial cells are normally negatively charged they dye the cell. Acidic stains have a negatively charged chromophore and they dye the background and leave the cells uncolored.
What dyes can be used for a simple stain?
True to its name, the simple stain is a very simple staining procedure involving a single solution of stain. Any basic dye such as methylene blue, safranin, or crystal violet can be used to color the bacterial cells.
What kind of stain is safranin and crystal violet?
In the Gram Stain technique, two positively charged dyes are used: crystal violet and safranin.
What color does safranin stain?
redSafranin O is a metachromatic, cationic dye. It is used as a counterstain in Gram staining. The stain colors Gram-negative bacteria pink to red and has no effect on Gram-positive bacteria.
What stains are used in Gram staining?
[1] Often the first test performed, gram staining involves the use of crystal violet or methylene blue as the primary color. [2] The term for organisms that retain the primary color and appear purple-brown under a microscope is Gram-positive organisms.
Why is safranin used for staining onion peel?
Safranin is used as a biological stain and it helps in the detection of cellulose, mucin, mast cells, etc. The cell wall of plants contains cellulose. Hence, safranin will stain the cellulose of cell walls making it appear pinkish red.
How does safranin stain work?
The safranin stain works by binding to acidic proteoglycans in cartilage tissues with a high affinity forming a reddish orange complex. The binding made cartilage tissues appear red when observed under the microscope.
How long to fix fast green stain?
Stain with fast green (FCF) solution for 5 minutes.
How long is Weigert's iron hematoxylin stable?
Weigert’s Iron Hematoxylin Working Solution: Mix equal parts of stock solution A and B. This working solution is stable for about 4 weeks.
