Can starch break down without amylase? Digestive Enzymes Without amylase, you would be unable to digest starches and sugars. Fiber is a form of carbohydrate as well, but amylase is unable to break it down and it passes through your body undigested.
Can amylase break down any substances other than starch?
The enzyme amylase does NOT break down cellulose because the enzyme does not recognize the sugar and cannot break it down. Amylase does break down starch into dissacharrides which are then further broken down by brush border enzymes of the intestine.
What happens to starch when amylase is added to it?
When amylase reacts with starch, it cuts off the disaccharide maltose (two glucose molecules linked together). As amylase breaks down starch, less and less starch will be present and the color of the solution (if iodine is added) will become lighter and lighter.
How does enzyme amylase affect starch?
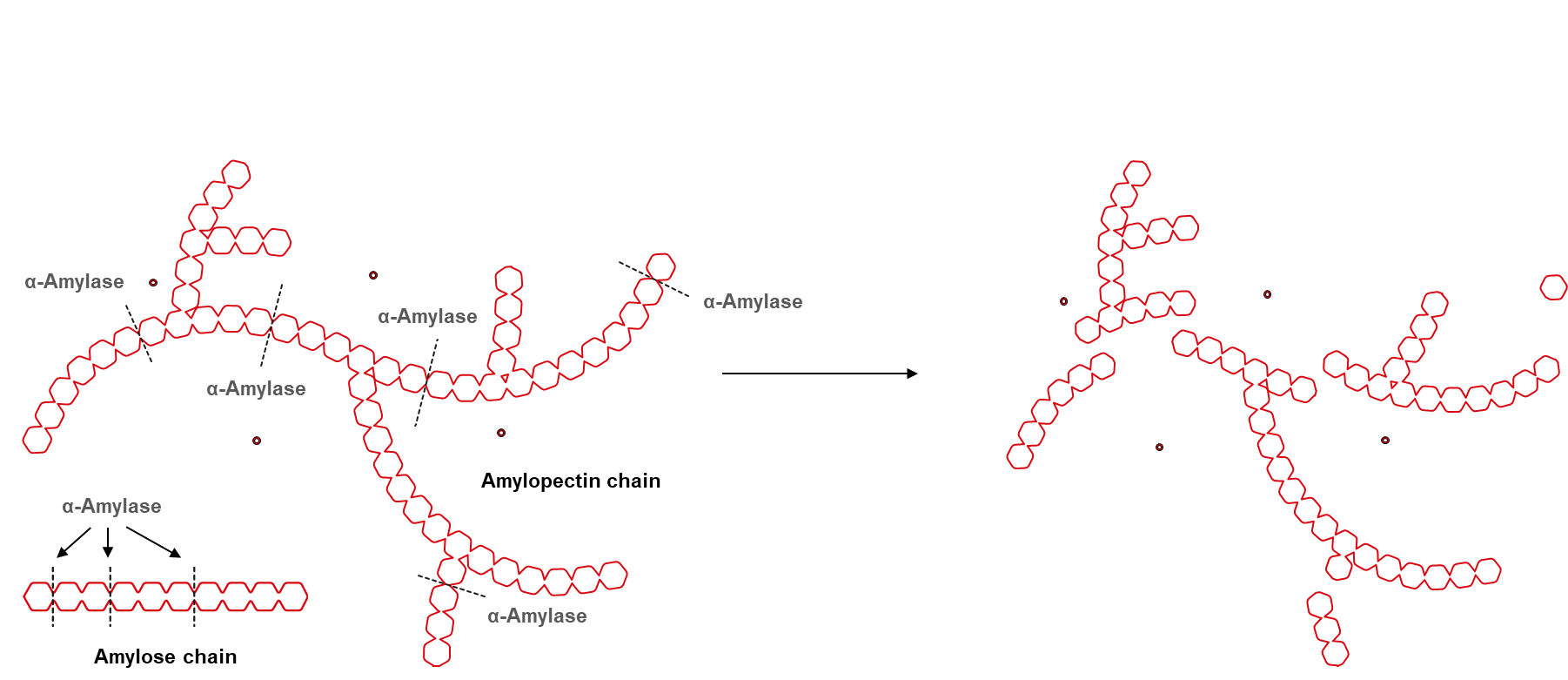
effect of enzyme concentration; The Effects Of Temperature. Amylase is an important metabolic enzyme. Its function is to catalyze the hydrolysis of starch into glucose. At high temperatures, Amylase becomes denatured, denatured amylase no longer catalyzes the hydrolysis of starch into glucose. EFFECT OF pH:
Does amylase break down food into a form of sugar?
The Role of the Amylase Enzyme The end goal of amylase is to break down carbohydrates into simple sugars that the body can use for energy, and this starts in the mouth. As food is chewed and mixed with saliva, amylase starts working to break down food into smaller molecules (1).
See more

What happens if you have no amylase?
Amylase. This enzyme helps break down starches into sugar, which your body can use for energy. If you don't have enough amylase, you may get diarrhea from undigested carbohydrates.
Why can amylase only break down starch?
Answer and Explanation: Amylase can breakdown starch but not cellulose, because the monosaccharide monomers in cellulose are bonded differently than in starch. This is because in cellulose, glucose monomers are bonded using beta glycosidic bonds while in starch the glycosidic bonds are alpha linkages.
Why do we need amylase enzyme?
Amylase enzymes are also made by the pancreas and salivary glands. They help break down carbs so that they are easily absorbed by the body. That's why it's often recommended to chew food thoroughly before swallowing, as amylase enzymes in saliva help break down carbs for easier digestion and absorption ( 10 ).
Which enzyme can break down starch?
AmylasesAmylases digest starch into smaller molecules, ultimately yielding maltose, which in turn is cleaved into two glucose molecules by maltase.
What happens when amylase is added to starch?
Amylase acts as a catalyst for digestion, and it breaks down large starch molecules into smaller sugar molecules (Figure 3). Starch is broken down into maltose, which then is converted into glucose which is used for energy (Figure 4).
What is amylase and what is its role?
Amylase is an enzyme, or special protein, that helps you digest carbohydrates. Most of the amylase in your body is made by your pancreas and salivary glands.
What is the role of amylase in carbohydrates digestion?
The digestion of carbohydrates begins in the mouth. The salivary enzyme amylase begins the breakdown of food starches into maltose, a disaccharide. As the bolus of food travels through the esophagus to the stomach, no significant digestion of carbohydrates takes place.
What happens if enzymes stop working?
Digestive enzymes speedup reactions that break down large molecules of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats into smaller molecules the body can use. Without digestive enzymes, animals would not be able to break down food molecules quickly enough to provide the energy and nutrients they need to survive.
What would happen if there were no enzymes in the human body?
If there were no enzymes in the human body, we would die. Enzymes serve as a catalyst for biochemical reactions. Without them, we would be unable to perform vital reactions like DNA copying and food digestion.
How is starch broken down?
The digestion of starch begins with salivary amylase, but this activity is much less important than that of pancreatic amylase in the small intestine. Amylase hydrolyzes starch, with the primary end products being maltose, maltotriose, and a -dextrins, although some glucose is also produced.
How do you break starch?
Chewing breaks food into small molecules that combine with saliva secreted by the salivary glands in the mouth. Along with mucin and buffers, saliva contains the enzyme salivary amylase, which acts on the starch in food and breaks it down to maltose.
What enzyme breaks down starches into simple carbohydrates?
amylaseamylase, any member of a class of enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis (splitting of a compound by addition of a water molecule) of starch into smaller carbohydrate molecules such as maltose (a molecule composed of two glucose molecules).
Why can't enzymes break down cellulose?
Why can't humans digest cellulose? Humans cannot digest cellulose because they lack the enzymes essential for breaking the beta-acetyl linkages. The undigested cellulose acts as fibre that aids in the functioning of the intestinal tract.
How does amylase break down starch GCSE?
The saliva in your mouth contains an enzyme called amylase. As you chew the cracker, the amylase triggers the starch to react with water to create a type of sugar called glucose, which tastes sweet. And the amylase reaction carries on making glucose even if you spit out the mush.
Can amylase break down glucose?
amylase, any member of a class of enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis (splitting of a compound by addition of a water molecule) of starch into smaller carbohydrate molecules such as maltose (a molecule composed of two glucose molecules).
Can amylase break down glycogen?
Amylase can't digest glycogen because of its inability to attack the branching (1→6) linkages. Perhaps, another very important reason is controlling the rate of glycogen metabolism through glycogen phosphorylase.