
How to thicken your uterine lining naturally?
Tips to improve endometrial thickness
- Foods to eat. A balanced diet can help women increase endometrial receptivity thanks to the action of estrogen, balanced hormones, and blood flow.
- Rest. Sleeping has a direct effect on reproductive hormones and causes them to be properly balanced. ...
- Doing exercise. ...
- Femoral massage. ...
- Acupuncture. ...
- Castor oil packs. ...
Does a thick uterine lining always mean cancer?
Thickening of the lining of the uterus, called endometrial hyperplasia, may lead to cancer, but is not always a sign of cancer, according to the American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Endometrial hyperplasia occurs when there is an excess of the hormone estrogen compared to the hormone progesterone.
What are the common causes of a thin uterus lining?
What Is A Thin Endometrial Lining?
- Low estrogen level. If you don’t have enough estrogen, this can cause thinning of your endometrial lining. ...
- Damaged endometrial lining. If your estrogen level is normal, a thin endometrial lining may be the result of a previous uterine infection which has damaged the lining of the ...
- Decreased blood flow. ...
- Uterine fibroids. ...
Why does the uterus lining need to become thick?
This inner lining of the uterus begins to thicken to prepare for an embryo to implant, or for pregnancy to occur. If pregnancy occurs, the lining helps to maintain the pregnancy. If pregnancy does not occur, the lining sheds (you get your period), and the process begins again for the following cycle.
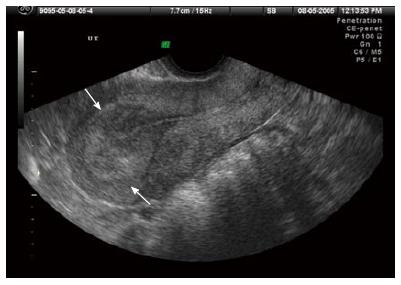
How is endometrial thickness measured?
Endometrial thickness is measured in millimeters using an ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
What is the condition where the endometrium grows outside the uterus?
Endometriosis: Endometriosis is a condition in which the endometrium grows outside the uterus. This can cause inflammation, irritation, and swelling and can lead to scarring and damage of the tissue surrounding the uterus. 4
What is the endometrium?
The endometrium is the inner lining of the uterus. It plays an important role in women's reproductive health. The uterine lining changes throughout the month, along with the menstrual cycle, in response to your body's reproductive hormones, estrogen and progesterone.
Why is endometrial lining important?
Your endometrial lining is important to your health, whether you are trying to get pregnant, notice changes to your menstrual cycle, or experience bleeding after menopause. You may try lifestyle or natural treatments to help with managing symptoms of thick endometrial lining or be a candidate for medical treatment to improve your chances of getting pregnant.
What is the purpose of the endometrial lining?
The main function of the endometrial lining is during a woman's reproductive years. This inner lining of the uterus begins to thi cken to prepare for an embryo to implant, or for pregnancy to occur. If pregnancy occurs, the lining helps to maintain the pregnancy. If pregnancy does not occur, the lining sheds (you get your period), and the process begins again for the following cycle. 1
How to help endometrial hyperplasia?
Exercise may be beneficial in increasing blood flow to the uterine lining. It may also help decrease stress and pain from endometrial hyperplasia.
Where is the endometrial lining located?
The endometrial lining is located in the innermost layer of the uterus, a hollow, pear-shaped organ in a woman's pelvis. 2
What Is Endometrial Hyperplasia?
Your endometrium is the lining of your uterus (womb). During your menstrual cycle, your endometrium changes. The estrogen that your ovaries produce makes your endometrium thicken. This prepares your uterus for possible pregnancy.
Are There Risk Factors for Getting Endometrial Hyperplasia?
You’re at a higher risk for endometrial hyperplasia if you have these risk factors:
What is the term for a condition in which the lining of the uterus is abnormally thick?
Endometri al hyperplasia is a condition in which the endometrium (lining of the uterus) is abnormally thick. There are four types of endometrial hyperplasia. The types vary by the amount of abnormal cells and the presence of cell changes.
What does it mean when your uterus is bleeding?
Abnormal uterine bleeding can be a symptom for many things. Your doctor can perform an exam and tests to diagnose the main condition. A transvaginal ultrasound measures your endometrium. It uses sound waves to see if the layer is average or too thick. A thick layer can indicate endometrial hyperplasia. Your doctor will take a biopsy of your endometrium cells to determine if cancer is present.
What causes endometrial hyperplasia?
Endometrial hyperplasia is caused by too much estrogen or not enough progesterone . Both of these hormones play roles in the menstrual cycle. Estrogen makes the cells grow, while progesterone signals the shedding of the cells. A hormonal imbalance can produce too many cells or abnormal cells.
Can endometrial hyperplasia cause cancer?
Atypical types of endometrial hyperplasia, especially complex, increase your risk of getting cancer. If you have these types, you might consider a hysterectomy. This is a surgery to remove your uterus. Doctors recommend this if you no longer want to become pregnant.
Is endometrial hyperplasia a treatable condition?
In most cases, endometrial hyperplasia is very treatable. Work with your doctor to create a treatment plan. If you have a severe type or if the condition is ongoing, you might need to see your doctor more often to monitor any changes.
Can endometrial hyperplasia be prevented or avoided?
You are more likely to have endometrial hyperplasia if you have gone through menopause. This is because your body’s hormones and menstrual cycles change. Other risk factors for this condition are:
Why is it important to pay attention to endometrial thickness?
Paying attention to endometrial thickness can help women who are trying to become pregnant understand the best way to optimize their chances of successful conception. Changes in endometrial thickness are common throughout a person’s life.
Why is endometrial thickness important?
Healthcare experts link the best chances for a healthy, full-term pregnancy to an endometrium that is neither too thin nor too thick. This allows the embryo to implant successfully and receive the nutrition it needs. The endometrium gets thicker as the pregnancy progresses.
What hormones cause endometrial growth?
Two hormones, estrogen and progesterone, prompt these cycles of endometrial growth and its shedding through menstruation if a pregnancy does not develop. In this article, we look at the normal range for endometrial thickness, causes of changes, and when to see a doctor.
What is the endometrium?
Outlook. The endometrium is the lining of the uterus. It is one of the few organs in the human body that changes in size every month throughout a person’s fertile years. Each month, as part of the menstrual cycle, the body prepares the endometrium to host an embryo. Endometrial thickness increases and decreases during the process.
What hormones are used to reduce endometrial thickness?
Treatments for excessive endometrial thickness include progestin, a female hormone that prevents ovulation and hysterectomy.
What is the best way to measure the thickness of the endometrium?
Ultrasound is the most common way to measure the thickness of the endometrium. It is the method that healthcare providers use first, especially if an individual has reported abnormal vaginal bleeding.
What hormone is produced by the placenta after an embryo implants in the uterus wall?
human chorionic gonadotrophin, which is a hormone that the placenta produces after an embryo implants in the uterus wall
