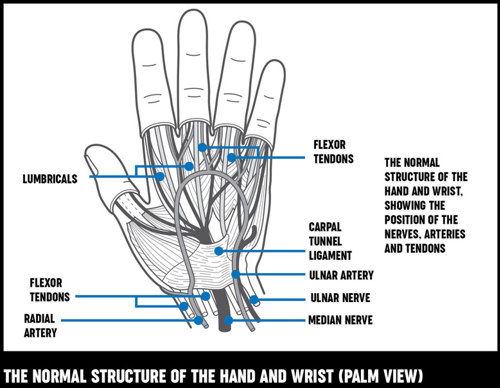
What is the function of ligaments in bones?
The ligament function is to provide stability to the skeleton by attaching bone to bone. In anatomy, a ligament definition is a rope-like band of strong connective tissue that stabilizes a joint during movement. A ligament does not allow a joint to overextend or move too far with activity.
What is the difference between ligaments&tendons?
You can think of your ligaments like ropes that stabilize the bones and joints. This tissue helps you avoid twisting too much, preventing dislocation. While ligaments help hold your bones and joints in place, tendons connect muscles to bone, according to the Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care.
Are ligaments related to tendons and muscles?
We tend to group ligaments and tendons are together, and think of them of as closer relatives than muscles and tendons; after all, ligaments and tendons are both connective tissue, made from sub-units of parallel collagen fibers. However muscles and tendons, the “muscle-tendon unit”, would more appropriately be grouped together.
Are ligaments tight enough to keep joints in joint?
The latter responsibility is usually attributed to ligaments, but ligaments are actually back-up to muscle-tendon units; if they were tight enough to keep movable skeletal joints “in joint”, we wouldn’t be able to move, because ligaments lack elasticity.

Do ligaments cause movement?
Your musculoskeletal system includes bones, muscles, tendons, ligaments and soft tissues. They work together to support your body's weight and help you move.
What is the function of a ligament?
A ligament is a fibrous connective tissue that attaches bone to bone, and usually serves to hold structures together and keep them stable.
Do ligaments aid in movement?
The system of ligaments in the vertebral column, combined with the tendons and muscles, provides a natural brace to help protect the spine from injury. Ligaments aid in joint stability during rest and movement and help prevent injury from hyperextension and hyperflexion (excessive movements).
How does a ligament act during movement?
A ligament functions by holding joints in place while allowing movement. Ligaments are made of tight bands of collagen fibers. The elasticity of the fibers allow for flexibility, while the protein, collagen, also maintains strength.
Which type of joint allows for the most movement?
Ball and Socket Joints1. Ball and Socket Joints: These joints allow for the greatest range of motion. The joint involves a ball fitting into a concave surface. Because these joints allow for more motion, they are at greater risk for instability.
What is a characteristic of ligaments?
Description. Ligaments are short bands of tough, flexible tissue, made up of lots of individual fibres, which connect the bones of the body together, being a dense type of connective tissue. Ligaments can be found connecting most of the bones in the body.
What is the difference between muscles tendons and ligaments?
A ligament connects bone to bone whilst a tendon attaches muscle to bone, acting like an anchor for the muscle. The Achilles tendon, for example, attaches the calf muscles to the calcaneus (heel bone), while a ligament holds the shin and foot bones (tibia and fibula with the talus) together at the ankle joint.
Which type of joint is not movable?
(Fibrous)Immovable (Fibrous) Joints Immovable or fibrous joints are those that do not allow movement (or allow for only very slight movement) at joint locations. Bones at these joints have no joint cavity and are held together structurally by thick fibrous connective tissue, usually collagen.
How are tendons and ligaments similar and different?
Ligaments and tendons are both made of connective tissue and both can be torn or overstretched, but they differ in function. Ligaments attach one bone to another. Tendons attach a muscle to a bone.
How are joints different from ligaments?
Ligaments connect the ends of bones together to form a joint. Tendon: A tough, flexible band of fibrous connective tissue that connects muscles to bones. Joints: Structures that connect individual bones and may allow bones to move against each other to cause movement.
How do joints move?
Muscles move our joints by pulling on tendons, which then pull on bones resulting in action: arm bend, knee lift. Many muscles work in pairs (synergy). The brain sends a message via nerves to the muscles.
Why must ligaments stretch?
Stretch those ligaments! In short, our fascial tissues are designed both to facilitate movement and restrain too much of it. And, just like our muscles, they are elastic: They build up internal tension when stretched and can release that energy back into strong, quick movements in the opposite direction.
What are ligaments made of?
Ligaments are tough fibrous cords composed of connective tissue that contains both collagen and elastic fibers. The elastic fibers allow the ligaments to stretch to some extent. Ligaments surround joints and bind them together. They help strengthen and stabilize joints, permitting movement only in certain directions.
What are the fibrous cords that contain collagen and elastic fibers?
Ligaments . Ligaments are tough fibrous cords composed of connective tissue that contains both collagen and elastic fibers. The elastic fibers allow the ligaments to stretch to some extent.
What is the function of ligaments?
Ligaments can be found connecting most of the bones in the body. The function of a ligament is to provide a passive limit to amount of movement between your bones.
Which joint has ligaments?
The image shows the shoulder joint, which has many ligaments. Ligaments are specialized connective tissues with very interesting biomechanical properties. The basic building blocks of a ligament are collagenfibers. These fibers are very strong, flexible, and resistant to damage from pulling or compressing stresses.
What are the components of ligaments?
The solid components of ligaments are principally type 1 collagen(image is of the triple helix, collagen) which accounts for approximately 75% of the dry weight with the balance being made up by proteoglycans (<1%), elastin and other proteins and glycoproteins. Ultrastructural studies have revealed that collagen fibres are actually composed ...
How do ligaments heal?
Ligaments heal by a process which includes three phases: 1 Hemorrhage with inflammation - involves retraction of the disrupted ligament ends, formation of a blood clot, which is subsequently resorbed, and replaced with a heavy cellular infiltrate. Subsequently, a considerable hypertrophic vascular response takes place in the gap between the disrupted ends and results in an increase in both vascularity and blood flow, both of which decrease with time. 2 Matrix and cellular proliferation - defined as the production of "scar tissue" (dense, cellular, collagenous connective tissue matrix) by hypertrophic fibroblastic cells. This scar tissue is initially quite disorganized with more defects. After a few weeks of healing, the collagen becomes quite well aligned with the long axis of the ligament despite the fact that the types of collagen are abnormal and the collagen fibrils have smaller diameters in the proliferating tissue. 3 Remodeling and maturation (matrix remodeling) - defects in the scar become filled in but although the matrix becomes more ligament-like with time, some major differences in composition, architecture and function persist. Differences which persist include altered proteoglycan and collagen types, failure of collagen crosslinks to mature, persistence of small collagen fibril diameters, altered cell connections, increased vascularity, abnormal innervation, increased cellularity and the incomplete resolution of matrix "flaws"[3]
What is the purpose of non surgical ligament injury?
The aim is to allow for ligament healing in a short/non-stressful position. Rehabilitation is be slowly progressed as the ligament repairs and a gradually return to normal activities can occur.
What is collagen attached to?
The bundles of collagen are attached to the outer covering that surrounds all bones, the periosteum. [2] They have the ability to adapt to the complex functions that each are required to perform. Once thought to be inert, they are in fact responsive to many local and systemic factors that influence their function.
What is the best treatment for a ligament injury?
These injuries require load protection during the early healing phase. Depending on the ligament injury this may include the use of a weight-bearing brace or some supportive taping is common in early treatment (helps to ease the pain and avoid stretching of the healing ligament).
What ligaments hold the entire joint in place?
Extracapsular ligaments hold the entire joint in place and in this way prevent dislocation injuries. There are two types of extracapsular ligaments based on their distance from the joint capsule – proximate and remote. Proximate ligaments pass over at least two joints, close to their capsules.
Why are ligaments arranged parallel?
The fibers are arranged parallel (regularly) to each other. Since ligaments are stretched in a predictable direction, this arrangement is parallel to that direction and gives ligaments maximum strength to resist mechanical distress and prevent injuries.
What are the three types of articulation ligaments?
There are three types of the articulation ligaments: capsular, extracapsular and intracapsular. They differ by their location within a joint. Ligaments that are presented as the local thickening of the articular capsule are called the capsular ligaments, while the ligaments located outside or inside the capsule are called extracapsular and intracapsular ligaments respectively.
Why are yellow ligaments more stretchy than white ligaments?
For instance, a sudden 30 degree inward rotation of the knee can cause the anterior cruciate ligament to tear, while the ligamentum flavum can handle any possible angle of spinal flexion without tearing.
What is the difference between a white and yellow ligament?
On the other hand, yellow (elastic) ligaments are mostly comprised of elastic fibers, like the ligamentum flavum in the spinal column.
What is the difference between ligaments and tendons?
The difference between ligaments and tendons lies simply in the type of elements they connect and support: Ligaments connect two bones and stabilize organs;
What are ligaments made of?
Ligaments are made out of dense regular connective tissue. This implies two of the histological properties that this tissue has: Its fibers are densely packed next to one another and leave very little open space in between. The fibers are arranged parallel (regularly) to each other.
What are ligaments and tendon?
Summary. Tendons and ligaments are fibrous bands of connective tissue. Both play roles in stabilizing the skeleton and allowing movement. Tendons and ligaments commonly sustain injuries, which usually have similar symptoms and treatments. Both of these types of structure may get weaker with age, and injury may become more common as people get older.
What is the difference between tendons and ligaments?
The main difference between tendons and ligaments is that they connect different parts of the anatomy. Tendons connect muscles to bones, while ligaments connect bones to other bones. In addition, there are some other minor anatomical differences.
What causes tendon and ligament injuries?
Tendon and ligament injuries are common. Several factors can increase the risk of injury, including: 1 overuse, such as through playing sports 2 trauma from a fall or blow 3 twisting the tendon or ligament into an awkward position 4 weakness in the surrounding muscles due to a sedentary lifestyle
Why do tendons snap out of place?
Subluxation is more likely in people with certain genetic anatomical differences, but tendons can also snap out of place as a result of an injury. Tendon ruptures can also occur. These injuries may be due to a combination of immediate trauma and chronic trauma.
What is bursitis in a ligament?
Bursitis is a type of inflammation that may feel like an injury to the tendon or ligament. Bursitis happens when bursae— small, gel filled sacs that cushion the bones, tendons, and muscles near the joints — become inflamed. This inflammation often happens because of overuse or extreme stress on the joint.
Where are ligaments and tendons located?
Ligaments are located at joints , whereas tendons provide the connection between muscle and bone that allows the muscles to move different parts of the body. Ligaments and tendons can stretch or tear relatively easily. The symptoms of tendon and ligament injuries tend to be very similar.
How to treat a ligament injury?
Applying a compress may help treat a ligament or tendon injury. The treatments for ligament and tendon injuries are very similar. For minor strains, sprains, inflammation, and other injuries, most doctors will recommend the RICE method: Rest the injured area and avoid putting weight on it.
What is a Ligament?
What is a ligament? Ligaments are fibrous bands that hold a skeleton together. A ligament's function is to provide stability of a joint by connecting one bone to another bone.
Ligament Function
What do ligaments do? Ligaments connect one bone to another and are the primary bond to stabilize a joint. The knee joint is an example of a location where ligaments provide strong connections. Ligaments allow the knee to bend and twist while ensuring the knee remains stable while jumping and running.
Types of Ligaments
In order to understand the different types of ligaments, it is important to understand the structure of a joint. Over 900 ligaments support the human body. Ligaments stabilize the skeleton, allowing people to stand erect, move fluidly and avoid collapse .
What are ligaments made of?
Ligaments are made of connective tissue and contain high amounts of collagen, a protein that helps the ligaments stretch and heal after injury, according to the Nemours Foundation. Ligaments help keep structures of the body in place, often connecting two bones together at the joints.
What are the muscles that help you move?
Muscles Help Everything Move 1 Skeletal muscle: The tissue attached to your bones that helps control movement. These are the muscles you can see and control. 2 Smooth muscle: The tissue found inside hollow organs like the stomach or intestines. 3 Cardiac muscle: The muscles found in the heart that help pump blood around the body.
What connects muscles and bones?
Tendons Connect Muscles and Bones. While ligaments help hold your bones and joints in place, tendons connect muscles to bone, according to the Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care. Like ligaments, tendons are made up of connective tissue and are highly resistant to tearing and stretching. The reason you can take a sip of coffee ...
What are the three types of muscle tissue?
Muscles Help Everything Move. Your body has three different types of muscle tissue: skeletal muscle, smooth muscle and cardiac muscle , according to the Khan Academy. Skeletal muscle: The tissue attached to your bones that helps control movement. These are the muscles you can see and control.
Which muscle is the prime mover?
While a variety of muscles may be involved in a single motion, the primary muscle is known as the prime mover or agonist, ...
What is a sprain?
Sprains are a common injury and occur when a joint moves into an unnatural position, like twisting your ankle. While ligaments become injured by unnatural movement, tendons become injured from overuse or repetitive motion, according to UMMS.
What is the muscle opposite the prime mover called?
The muscle opposite the prime mover is called the antagonist, which maintains the body or limb position and controls rapid movement. Advertisement. For instance, when you extend your leg at the knee, your quads (a group of four muscles) are triggered, serving as the agonists in the motion — they're the reason the leg extends. ...
Why can't we move if we have ligaments?
The latter responsibility is usually attributed to ligaments, but ligaments are actually back-up to muscle-tendon units; if they were tight enough to keep movable skeletal joints “in joint”, we wouldn’t be able to move, because ligaments lack elasticity.
What is the difference between ligaments and tendons?
There are two main differences between tendons and ligaments. The first difference is in their structure. Structurally, both ligaments and tendons have sub-units of parallel collagen fibers; collagen fibers are inherently elastic because they are parallel fibers of helical crystals, which look like a coiled spring.
Why do tendon fibers twist?
The reason the tendon is twisting, by the way, is because each one of its collagen fibers is twisting, so when you put them together they tend to twist, just like the DNA helix.
What happens when you put DNA molecules together?
When you put DNA molecules together, each one twists the next, and that in turn twists the next one, and then finally by the third twist you’ve got a chromosome. In the same way, the inherent twisting of the collagen fiber creates the twisting in the tendon.
Does collagen make ligaments elastic?
The only elasticity in ligaments is white elastic fibers between each layer of the ligament, to allow some movement between the layers. But this doesn’t make the ligament itself elastic .
Is ligament a connective tissue?
We tend to group ligaments and tendons are together, and think of them of as closer relatives than muscles and tendons; after all, ligaments and tendons are both connective tissue, made from sub-units of parallel collagen fibers. However muscles and tendons, the “muscle-tendon unit”, would more appropriately be grouped together.
Do ligaments maintain elasticity?
As stated above, ligaments do not become involved in maintaining the integrity of movable joints unless the muscle-tendon units are breached. Because they act as backup to the muscle-tendon unit, elasticity is not a desirable quality. During normal range of motion, ligaments remain lax.
What are the functions of ligaments and tendon?
Tendons and ligaments are both types of connective tissue, but they perform different functions. Tendons connect your muscles to your bones. Ligaments hold your bones together in your joints. Tendons and ligaments both provide stability and allow you to move.
Why do tendon and ligament injuries increase with age?
Your risk of tendon and ligament injuries increases with age as your connective tissue becomes drier and less elastic. Additionally, as an athlete, you put your body, including your tendons and ligaments, under quite a bit of physical stress.
What is cartilage in knees?
It coats and cushions your joints, reducing friction and absorbing shock. You have discs of cartilage in your knees called menisci. Meniscus tears are also common sports injuries caused by sudden twisting movements. Weakness or damage in your ligaments, tendons, or muscles can increase your risk of injuring your menisci.
What are the most common ligament injuries?
Sprains are the most common ligament injuries. You can strain tendons or develop tendonitis, a painful inflammatory condition that develops when you gradually develop tiny tears in the tissue. You can injure your tendons and ligaments in many ways, including: 1 Overuse and repetitive movements 2 Trauma from collisions or forceful blows 3 Sudden twisting movements and awkward landings 4 Weakness in the surrounding muscles
Can you injure your tendons?
You can injure your tendons and ligaments in many ways, including: Your risk of tendon and ligament injuries increases with age as your connective tissue becomes drier and less elastic. Additionally, as an athlete, you put your body, including your tendons and ligaments, under quite a bit of physical stress.
