Can meteorites come back to Earth from space?
Most meteor showers come from comets, whose material is quite fragile. Small comet fragments generally won’t survive entry into our atmosphere. In theory, the Taurids and Geminids could send meteorites down to our surface every once in a while, but no remnants have been traced to them definitively.
What percentage of meteors fall to the ground?
Typically less than 5 percent of the original object will ever make it down to the ground. These meteorites, pieces of meteors that are found, typically range between the size of a pebble and a fist. Don’t expect to find meteorites after a meteor shower. Most meteor showers come from comets, whose material is quite fragile.
How many meteors can you see in an hour?
Several meteors per hour can usually be seen on any given night. When there are lots more meteors, you’re watching a meteor shower. Some meteor showers occur annually or at regular intervals as the Earth passes through the trail of dusty debris left by a comet (and, in a few cases, asteroids).
Can meteorites be found in the atmosphere?
These meteorites, pieces of meteors that are found, typically range between the size of a pebble and a fist. Don’t expect to find meteorites after a meteor shower. Most meteor showers come from comets, whose material is quite fragile. Small comet fragments generally won’t survive entry into our atmosphere.

Do meteors go in different directions?
Meteors do come from one direction;as the earth moves through comet debris, the various 'chunks' that form meteors are moving parallel to each other. But just like a railroad track, although the rails are parallel to each other, they appear to spread out as they approach someone standing on the track.
Why do shooting stars go in different directions?
The dust and rocks that cause meteor showers come primarily from the Earth passing through the debris stream left behind by a comet as it orbits the Sun. Usually, the Earth's orbit and the comet's orbit are slightly tilted relative to one another. So the paths only intersect on one side!
How do asteroids change direction?
An object with a high mass close to the Earth could be sent out into a collision course with the asteroid, knocking it off course. When the asteroid is still far from the Earth, a means of deflecting the asteroid is to directly alter its momentum by colliding a spacecraft with the asteroid.
Do meteors go upwards?
Meteors light up almost as soon as they hit Earth's atmosphere. On average, when you see a meteor, you're looking at a piece of dust burning bright about 50 to 75 miles (80 to 120 km) in altitude above Earth's surface. But the height at which they entirely burn up in the atmosphere varies.
What is the difference between a meteor and a meteorite?
When meteoroids enter Earth's atmosphere (or that of another planet, like Mars) at high speed and burn up, the fireballs or “shooting stars” are called meteors. When a meteoroid survives a trip through the atmosphere and hits the ground, it's called a meteorite.
How rare is a shooting star?
How common is it to see a shooting star? Shooting stars are very common. Rock from space regularly enters the Earth's atmosphere, with around one million shooting stars occurring every day around the world. To try to see a shooting star, the sky should ideally be clear.
When did the last asteroid hit Earth?
66 million years agoThe last known impact of an object of 10 km (6 mi) or more in diameter was at the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event 66 million years ago. The energy released by an impactor depends on diameter, density, velocity, and angle.
How big would a meteor have to be to destroy Earth?
60 milesUltimately, scientists estimate that an asteroid would have to be about 96 km (60 miles) wide to completely and utterly wipe out life on our planet.
How big was the meteor that killed the dinosaurs?
between 10 and 15 kilometres wideThe impact site, known as the Chicxulub crater, is centred on the Yucatán Peninsula in Mexico. The asteroid is thought to have been between 10 and 15 kilometres wide, but the velocity of its collision caused the creation of a much larger crater, 150 kilometres in diameter - the second-largest crater on the planet.
How rare is it to see a meteor?
Due to the combination of all of these factors, only a handful of witnessed meteorite falls occur Each year. As an order of magnitude estimation, each square kilometer of the earth's surface should collect 1 meteorite fall about once every 50,000 years, on the average.
How many meteors hit the Earth every day?
Every year, the Earth is hit by about 6100 meteors large enough to reach the ground, or about 17 every day, research has revealed. The vast majority fall unnoticed, in uninhabited areas. But several times a year, a few land in places that catch more attention.
Can shooting stars go downwards?
This is called a meteor or shooting star (or a falling star). In general, the meteors travel in a (approximately) straight path. We usually see only the large ones travel down towards the horizon while the small ones are burnt up long before that (giving the impression of coming from the horizon).
What is the difference between a shooting star and a falling star?
The phrase falling stars, or shooting stars as they are called in different regions, describes meteors or other pieces of matter that burn up and disintegrate as they hit the Earth's surface and pass through it.
What does it mean when you see a shooting star alone?
Regardless of your relationship status, a shooting star has been an omen of love entering one's life for many years. If you are single and see a shooting star it could mean that the stars are aligning for you in your love life.
Do shooting stars go straight across the sky?
A satellite will move in a straight line and take several minutes to cross the sky. A meteor, or shooting star, will move in less than a fraction of a second across the sky. Observe the kind of light from the "star". A satellite will brighten and dim in a regular pattern as it crosses the sky.
What does it mean if you see a shooting star spiritual?
Spiritual Meaning of a Shooting Star Whatever you wish for when you see a shooting star is thought to be more likely to come true and bring about some sort of change to your life. Shooting stars are also a reminder of your connection to the universe, as stars and humans are made up of the same building blocks of life.
What would happen if a meteor broke in half?
No expert here but in theory perhaps if the meteor was spinning rapidly when it entered the atmosphere or the entry into the atmosphere caused it to spin rapidly and then at some point broke in half it might be able to make a drastic course change much like a curve ball but more extreme. if it broke in two with a now flat side and was still rapidly spinning I believe almost anything could happen. Also, when objects are in flight our perceptions are often skewed. Take for example that jet contrail that was spotted over the Pacific a few years ago. Most people who observed it thought it was a missile being launched in a vertical direction.
How does a meteoroid skip off the atmosphere?
The concept of a meteoroid "skipping" off the atmosphere has been suggested several times here. However, such skipping can only take place when the object's approach angle is nearly tangent to the atmosphere. The resulting "skip" will only alter the meteoroid's path slightly. It's a skip, not a bounce. Anyone who has ever tried skipping a flat stone across the surface of a pond will tell you that the stone must be thrown nearly parallel with the water's surface to make it skip. Increase the angle of approach just a little than the stone simply goes "ka plunk" and to the bottom of the pond! The situation is quite similar for a body skipping off the upper regions of the atmosphere.#N#I fully agree with Glenn, too, regarding splitting. Disruption, or break-up into two pieces, would produce no more than a very slight deviation from the object's original trajectory at the velocities involved here. The two fragments will follow essentially parallel paths. Simple physics.
How much does a meteor weigh?
Meteors generally run 10 - 250 mg in mass or so, a chunk of debris could weigh up into the kilogram range (but probably won't). There are approximately 500,000 pieces of debris in orbit between 1 and 10 cm (and thus in the multi-gram range).
Do meteors travel in a straight line?
Second: my money is on a perspective effect as you suggest. Remember in reality all meteors in a shower are travelling in a straight line together and the entire shower effect, with meteors shooting across the sky in different directions, and the apparent radiant point, etc. is due to perspective effects.
Is it possible to see the second meteor?
Perhaps just as the first meteor burned out, the second one started, with the endpoint of the first coincident with the starting point of the second? Unlikely maybe, but not impossible. Just a thought. Watching the Perseids one year, I kept seeing slow, faint meteors moving along a sort of wavy path. Then I realized they were pigeons.
Can meteors change their path of travel?
Neither meteors, nor in-coming satellite debris, can change their path of travel in the atmosphere almost instantly by 90 degrees. So, I'm afraid that pretty much absolutely eliminates the explanations so far advanced.
Can spin create a change?
Spinning can in fact create a change like this, if the object broke apart and pieces of similar mass went in opposite directions. If the spin axis is at a large angle w.r.t. the velocity vector, a piece could shoot off in a seemingly arbitrary direction.
Why do meteor showers occur?
Some meteor showers occur annually or at regular intervals as the Earth passes through the trail of dusty debris left by a comet (and, in a few cases, asteroids). Meteor showers are usually named after a star or constellation that is close to where the meteors appear to originate in the sky.
What are meteors called?
This is also when we refer to them as “shooting stars. ”. Sometimes meteors can even appear brighter than Venus -- that’s when we call them “fireballs.”.
Why Do We Care About Meteorites?
Meteorites that fall to Earth represent some of the original, diverse materials that formed planets billions of years ago. By studying meteorites we can learn about early conditions and processes in the solar system’s history. These include the age and composition of different planetary building blocks, the temperatures achieved at the surfaces and interiors of asteroids, and the degree to which materials were shocked by impacts in the past.
What Do Meteorites Look Like?
Meteorites may resemble Earth rocks, but they usually have a burned exterior that can appear shiny. This “fusion crust” forms as the meteorite’s outer surface melts while passing through the atmosphere.
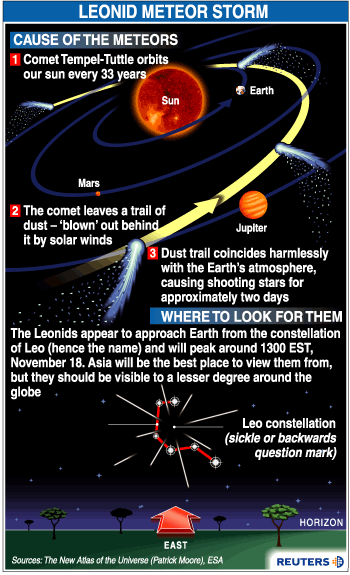
What is the name of the comet that swings by the Sun every 135 years?
Every Perseid meteor is a tiny piece of the comet Swift-Tuttle, which swings by the Sun every 135 years. Other notable meteor showers include the Leonids, associated with comet Tempel-Tuttle; the Aquarids and Orionids, linked to comet Halley, and the Taurids, associated with comet Encke.
How can scientists tell where meteorites originate?
Scientists can tell where meteorites originate based on several lines of evidence. They can use photographic observations of meteorite falls to calculate orbits and project their paths back to the asteroid belt. They can also compare compositional properties of meteorites to the different classes of asteroids.
How old are meteorites?
And they can study how old the meteorites are – up to 4.6 billion years. This rock encountered by NASA's Curiosity Mars rover is an iron meteorite called "Lebanon.".
