
Actually, yeah. They can reproduce asexually when some part of the plant falls off, especially the leaves. After falling to the ground, they would start to grow the necessary structures to create another cactus plant.
What is vegetative asexual reproduction?
Vegetative asexual reproduction involves a plant creating new plant material that goes on to become a new plant. This can be through budding, tillering, or other processes. The other type of asexual plant reproduction is called apomixis.
How common is asexual reproduction in plants?
Asexual reproduction in plants is actually quite common! This might be surprising given that many other organisms like mammals, fish, and reptiles typically reproduce sexually. Plants are interesting in that some plants that reproduce sexually can also reproduce asexually.
Can cactus reproduce asexually?
Actually, yeah. They can reproduce asexually when some part of the plant falls off, especially the leaves. After falling to the ground, they would start to grow the necessary structures to create another cactus plant. Is not that amazing?
Which edible plants use asexual reproduction?
Sweet potatoes make their home in kitchens all over the world. Just like onions, this is another edible plant that uses asexual reproduction. However, the sweet potato is another plant on our list that can use both sexual and asexual reproduction.
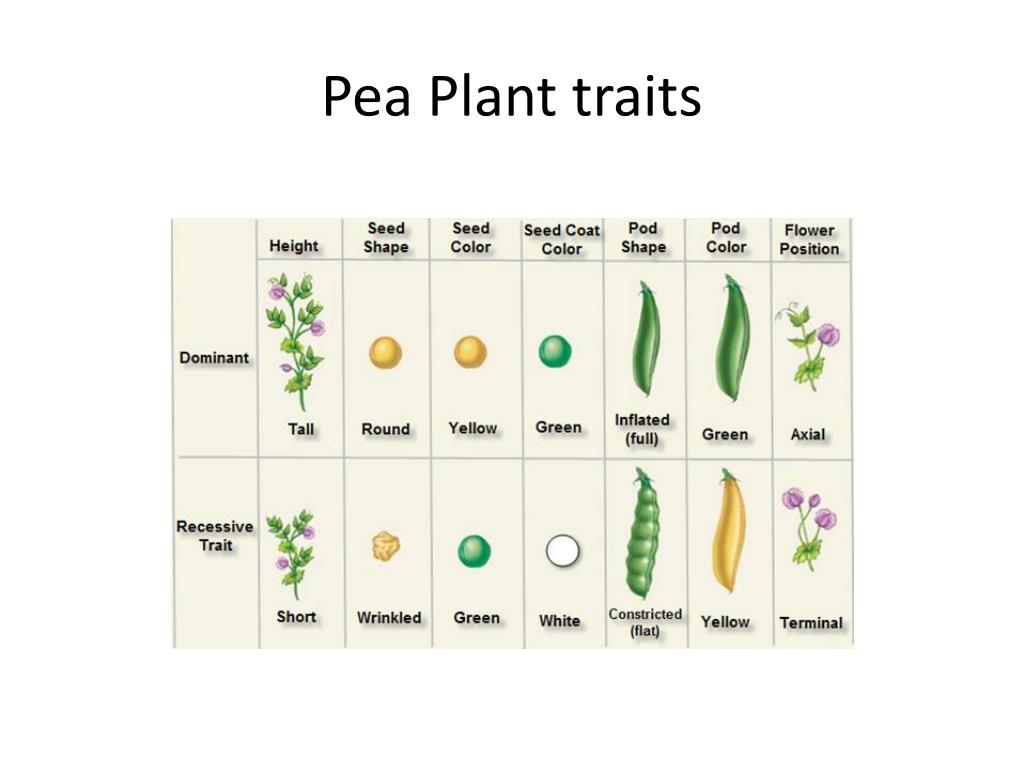
How do pea plants reproduce?
Peas usually reproduce by self-pollination, in which pollen produced by a flower fertilizes eggs in the same flower. Pea plants grow quickly and do not require much space.
Do pea plants reproduce self-pollination?
Pea flowers are perfect and self- pollinating. The flowers open early in the morning and do not shut. The anthers shed pollen the night before the flower opens, but this does not reach the stigma until the flower is tripped, usually by the wind.
Do peas only reproduce by self fertilization?
The stigma is a female part of a flower. It passes the pollen grains to female gametes in the ovary. Pea plants are naturally self-pollinating.
How do pea flowers pollinate?
0:422:00How to Pollinate Peas : The Chef's Garden - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipMuch. And I'll just give it a little rub just like a beat would do or the wind. But like I saidMoreMuch. And I'll just give it a little rub just like a beat would do or the wind. But like I said these are pretty easy and simple they should be able to pollinate themselves.
Do peas require pollination?
Beans, peas and tomatoes are self-pollinating and do not need bees for fruit production. Their flowers have all the needed reproductive parts and can transfer and accept their own pollen for the development of their edible fruits.
Why do pea plants self fertilize?
Self-pollination assures that reproduction within the plant's flowers will take place. Peas do not depend on external pollinators such as wind, rain or insects to do the job.
Do sweet peas self-pollinate?
Sweet peas are self-pollinating - they fertilize themselves whilst the flower buds are still young and haven't opened. What is a Spencer Sweet Pea? Spencer type sweet peas have large, frilly flowers with a lovely scent and are easy to grow.
Are pea plants haploid or diploid?
In other words, peas are diploid organisms in that they have two copies of each chromosome. The same is true for many other plants and for virtually all animals.
Why do peas have adaptations?
It's all about surviving... Peas, like some other legumes, have developed specific adaptations to allow the continuation and reproduction of each different species. Pea plants have developed and adapted to self-pollinate when necessary.
What is a pea?
Peas are part of the Leguminosae family and are related to beans, groundnuts, and clovers. The genus Pisum is included in the Vicieae group which also contains broad beans, chick peas, and lentils. Pisum sativum is a plant that has been used in gardens for thousands of years. It is considered an important crop because it is used all over the world. Its importance can be seen by the continued use over thousands of years. On this page you will discover the ways in which Pisum sativum reproduces, its specific adaptations, and how it gains its nutrients.
Why is pisum sativum important?
It is considered an important crop because it is used all over the world. Its importance can be seen by the continued use over thousands of years. On this page you will discover the ways in which Pisum sativum reproduces, its specific adaptations, and how it gains its nutrients.
What are the relationships between peas and bacteria?
Pea plants have also developed relationships with bacteria and fungus. With the bacteria, the plant receives nitrogen which has been fixed into a form that is easily used by the plant and the bacteria receives extra sugars and other nutrients which the plant has made.
What happens when an organism enters a flower?
When the organism enters the flower it rubs against the pollen grains and takes some of the pollen with it as is travels to the next flower. When the organism arrives and enters the next flower, the pollen which was picked up can be transferred to the female portion of the pistil that is placed near the pollen anthers.
What is the male part of a flower called?
The male part is known as the stamen. The filament and anthers make up that stamen. The anthers contain the pollen grains. For pollination, or fertilization to occur, insects, usually, will enter the open petals of the flower to drink the nectar.
What is the male part of a sativum?
The female part is called the pistil. It contains the style, the stigma, and the enlarged base known as the ovary, which contains the eggs. The male part is known as the stamen. The filament and anthers make up that stamen.
What is asexual reproduction?
Asexual reproduction only requires DNA from one parent. It creates offspring that are genetically identical to the parent. Genetically identical offspring are called clones. Clones lack genetic diversity. This makes them more susceptible to disease. It also makes them less adaptable to changes in the environment.
Why do plants need to reproduce?
Plants are living organisms. That means they need to reproduce in order to pass on their genes to future generations. Plants can create offspring through either sexual or asexual reproduction.
What is the next step after pollination?
Bee covered in pollen (Source: USGS Bee Inventory and Monitoring Lab [public domain] via Wikimedia Commons). Fertilization is the next step after pollination. Once it reaches the pistil, the pollen needs to fertilize an egg inside the stigma.
How do liverworts reproduce?
They often use asexual reproduction through fragmentation to grow new plants. They do this by cutting a leaf off a plant and placing it in water or soil.
Can flowers be cross pollinated?
Plants can either self-pol linate or cross-pollinate. Self-pollination happens when a plant’s own pollen fertilizes its own ovules.
