
What are the symptoms of spinal MS?
Symptoms often affect movement, such as:
- Numbness or weakness in one or more limbs that typically occurs on one side of your body at a time, or your legs and trunk
- Electric-shock sensations that occur with certain neck movements, especially bending the neck forward (Lhermitte sign)
- Tremor, lack of coordination or unsteady gait
What causes spinal lesions?
These growths can develop for a variety of different reasons, including:
- Acute trauma
- Repetitive trauma over time
- Spinal cord injury
- Infections
- Genetics
What symptoms do thoracic lesions cause?
Your thoracic nerves may have been damaged if you are experiencing any of these symptoms:
- Pain that starts from the lower neck to the shoulder, back, and chest
- Back pain that increases with activity
- Numbness and tingling in the same area of the shoulder, back, and chest
- Radiating weakness
- Difficulty breathing
- Muscle spasms in the upper or mid-back
- Tenderness in the upper or mid-back
- Difficulty and discomfort when sitting
What is spinal MS?
NMO is a demyelinating disease of the central nervous system which primarily affects the optic nerves and spinal cord. In conclusion, if you read the phrase “spinal MS,” know that it simply refers to the presence of lesions in the spinal cord in a patient diagnosed with MS.
Can you have MS with just spinal lesions?
If a patient does have lesions in the spinal cord, he/she may be said to have Spinal MS. A smaller number of MS patients, approximately 20 percent, may have only spinal lesions and not brain lesions. I am an example of one of those 20 percent of MS patients who only have spinal lesions.
Can you have spinal lesions without MS?
It's not known why some people with MS may have more lesions in their brain than their spinal cord, or vice versa. However, it should be noted that spinal lesions do not necessarily indicate a diagnosis of MS, and can sometimes lead to a misdiagnosis of MS.
Can MS lesions be on the spine and not the brain?
But the brain isn't the only area where lesions can develop — MS can also attack the spinal cord. Because finding these lesions involves more elaborate imaging tests, spinal cord lesions in MS are studied less often, and many people with MS aren't aware of the role these lesions may play in the disease process.
What part of spine are MS lesions found?
In particular, high lesion probability was found in the posterior columns in RRMS, posterior and lateral cord in SPMS and posterior, lateral and central regions in PPMS (Figure 2). Interestingly, high disability levels were associated with lateral and central cord involvement.
What do lesions on the spine indicate?
The causes of spinal lesions include trauma, infections, tumors (benign or malignant), and inflammatory diseases affecting the spine. They can also be caused by autoimmune, congenital, degenerative, or vascular disorders affecting the spine.
Is a lesion on the spine serious?
The different kinds of spinal lesions can cause a wide array of dysfunctions — such as motor and sensory deficits. Spinal lesions can be either benign or malignant depending on their severity, location, and if they're caused caused by cancers of the spine such as osteosarcoma or osteochondroma.
Where are most MS lesions found?
MS can cause a wide variety of neurologic symptoms since it can affect numerous areas of the brain, optic nerve, and spinal cord (Figure 3). Characteristic lesions are located in the periventricular and juxtacortical regions, in addition to the brainstem, cerebellum, spinal cord, and optic nerve.
What type of lesions indicate MS?
The pathologic hallmark of multiple sclerosis is multiple focal areas of myelin loss within the CNS called plaques or lesions, accompanied by variable gliosis and inflammation and by relative axonal preservation. Active multiple sclerosis lesions are infiltrated by macrophages containing myelin debris.
Are spinal lesions common?
Primary spinal tumors, which begin in your spine, are uncommon. Benign (noncancerous) primary spinal tumors account for 0.5% of all newly diagnosed tumors. Malignant (cancerous) primary spinal tumors are even less common.
How many lesions indicate MS?
The clinical diagnosis of MS is based on a history of at least two separate episodes of focal neurological dysfunction supported by evidence of at least two lesions within CNS white matter which have been disseminated in space and time.
Can you see MS on MRI of spine?
MS lesions are present throughout the spinal cord, and spinal cord MRI may play an important role in the diagnosis and follow-up of MS patients.
What indicates possible multiple sclerosis during an MRI?
Classically, the MRI shows lesions in the white matter deep in the brain near the fluid spaces of the brain (the ventricles). The test may also show changes in the cortex or near the cortex. MRI can also show changes in the brainstem and in the spinal cord.
Can you have MS lesions without symptoms?
Finding of white matter spots (lesions) in the brain that are classic for multiple sclerosis without having symptoms can occur. Not a surprising fact since many of people with MS have many old MRI spots when diagnosed.
Can you have MS with normal MRI and spinal tap?
MS can be present even with a normal MRI and spinal fluid test although it's uncommon to have a completely normal MRI. Sometimes the MRI of the brain may be normal, but the MRI of the spinal cord may be abnormal and consistent with MS, so this also needs to be considered.
Can spinal tumor mimic MS?
Rarely, another structural problem within the spine like a tumor can mimic symptoms of MS. Again, an MRI of the spine can help differentiate these structural spine problems from an inflammatory disease like MS.
Are spinal lesions common?
Primary spinal tumors, which begin in your spine, are uncommon. Benign (noncancerous) primary spinal tumors account for 0.5% of all newly diagnosed tumors. Malignant (cancerous) primary spinal tumors are even less common.
Can you have MS without lesions on the spine?
It is possible that a person may not have lesions on either the spine or brain during their initial diagnosis. However, the longer a person goes wi...
What causes MS lesions?
MS causes the immune system to attack the myelin sheath that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. Over time, inflammation can cause damage and scar...
Can you have MS lesions on the brain but not the spine?
It is possible that a person diagnosed with MS may have lesions on their brain but not on their spine. The opposite is also true. To avoid misdiagn...
Are multiple sclerosis lesions permanent?
MS lesions are dynamic and can change as time goes on. Over time, an individual lesion or area of abnormal tissue may remain the same size, it may...
Are multiple sclerosis lesions always visible?
While MRI scans are the gold standard for imaging MS lesions, some lesions may not always be clearly visible on scans. For example, some lesions ma...
Can a CT scan show multiple sclerosis lesions?
Unlike an MRI, which uses powerful magnetic fields to image the body's internal structures, a computed tomography (CT) scan images the body using a...
Can stress cause more multiple sclerosis lesions?
There is no solid answer at this point. Some research suggests that MS lesions are more likely to develop after periods of heightened stress. Furth...
Do brain lesions always mean multiple sclerosis?
To be diagnosed with multiple sclerosis, a person must show evidence of MS-like lesions that affect multiple areas of the nervous system and develo...
How to tell if someone has MS?
The most effective and non-invasive way to determine if a person has MS is to scan for brain and spinal cord lesions using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Why do we need MRIs for MS?
MRIs are used to determine if brain and spinal lesions are associated with MS. It’s not entirely understood why more spinal lesions may form over brain lesions, or vice versa.
What is the purpose of MRI scans?
MRI uses strong magnetic and radio waves to produce detailed pictures of the brain and spinal cord. This scan can effectively show any scarring or damage to the myelin sheath associated with MS.
What is the role of myelin coating in MS?
In addition to protecting the nerve cells, the myelin coating facilitates nerve transmission signals, or impulses. The resulting decrease in myelin leads to the symptoms of MS.
Does MS cause brain lesions?
Since myelin coats the nerve fibers that travel through both the brain and the spinal cord, demyelination creates lesions in both areas. This means that if someone with MS has brain lesions, they are also likely to have spinal lesions as well. Spinal cord lesions are common in MS.
Can MS cause more brain lesions than spinal cord?
It’s not known why some people with MS may have more lesions in their brain than their spinal cord, or vice versa. However, it should be noted that spinal lesions do not necessarily indicate a diagnosis of MS, and can sometimes lead to a misdiagnosis of MS.
Can an MRI show a spinal lesions?
Sometimes the number of spin al lesions identified from an MRI can provide the doctor with an idea of the severity of the MS and the likelihood of a more serious episode of demyelination occurring in the future. However, the exact science behind the number of lesions and their location is still not entirely understood.
How Do Spine Lesions Cause MS Symptoms?
Spine lesions can cause dysfunction in motor and sensory skills due to nerve damage. The loss of myelin surrounding the nerve cells of the spinal cord slows down the electrical signals in the CNS and can impair communication between different nerves. Spinal cord wasting (atrophy), or the loss of white matter tissue in the spinal cord, which contains neurons and myelin, can also cause symptoms.
What are spine lesions?
In MS, immune cells attack the fatty coating on the outside of nerve cells. This nerve coating is known as myelin. When damage occurs, it leaves behind scar tissue that forms into lesions on the brain and spinal cord. These lesions are called plaques.
How Do Spine Lesions and Brain Lesions Differ?
Multiple sclerosis is characterized by the presence of lesions (sclerosis) on the brain and spinal cord. People with primary progressive MS (PPMS) typically have more spinal cord lesions than brain lesions. Researchers have also found that spinal cord involvement may predict worse neurological outcomes. Spine lesions have also been shown to predict long-term disability in people with clinically isolated syndrome (CIS) and relapsing-remitting MS (RRMS). Another way that brain and spine lesions differ is in the symptoms they may cause. MS symptoms depend on the location of the lesion. For example, brain lesions can cause symptoms such as impaired coordination or issues with vision. In contrast, spinal cord lesions can cause muscle weakness, numbness and tingling, and pain.
How Do Doctors Detect Spine Lesions?
The most common method for detecting lesions is through magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). This is a highly sensitive imaging method that can take detailed pictures of the body’s organs and tissues. MRI scans use radio waves and magnetic fields to measure the water content in tissues. Myelin is a fatty substance and repels water. Therefore, in areas affected by MS, the myelin will be gone. These areas will fill with water and look abnormal on the scan, showing neurologists where the damage is in the spinal cord. It is important to note, that unlike an X-ray, MRI does not involve any radiation.
What is the name of the nerve coating that forms on the brain and spinal cord?
This nerve coating is known as myelin. When damage occurs, it leaves behind scar tissue that forms into lesions on the brain and spinal cord. These lesions are called plaques. The spine contains 33 individual bones and is divided into five distinct regions: Cervical, starting at the base of the head through the neck.
How to detect lesions in the body?
The most common method for detecting lesions is through magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). This is a highly sensitive imaging method that can take detailed pictures of the body’s organs and tissues. MRI scans use radio waves and magnetic fields to measure the water content in tissues.
What is MS team?
MyMSTeam is the social network for people with multiple sclerosis and their loved ones. On MyMSTeam, more than 169,000 members come together to ask questions, give advice, and share their stories with others who understand life with MS.
Why do people with MS have more brain lesions?
And in cases with spinal cord damage , there are sometimes actually fewer brain lesions, he adds.
How long does it take for MS to show asymptomatic spinal lesions?
A study published in the Journal of Clinical Medicine in February 2021 looked at a large group of relapsing and progressive MS patients and found that asymptomatic spinal lesions can be seen in about 15 percent of clinically stable MS patients over a median period of 14 months.
How do spinal cord lesions form?
How MS Lesions Form. Spinal cord lesions in MS “probably” form through the same mechanisms as those in the brain, says Dr. Reder. “For some unknown reason, white blood cells escape from the bloodstream, go through the blood–brain barrier, and get into the brain tissue,” he explains. These cells cause inflammation of the brain ...
What is the FDA approved treatment for MS?
Developing Potential Therapies for MS. In 2017, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved Ocrevus (ocrelizumab) to treat adults who have relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis and primary progressive multiple sclerosis ( PPMS ). It was the first drug approved by the FDA for PPMS.
What causes inflammation in the brain and spinal cord?
These cells cause inflammation of the brain and spinal cord — mostly in the white matter — but also the gray matter. According to Reder, toxic chemicals produced by these cells strip the myelin insulation off the connections between nerves. The resulting lesions tend to affect multiple nerves and tend to be 1 to 2 centimeters in length or diameter.
Can MS attack the spinal cord?
But the brain isn’t the only area where lesions can develop — MS can also attack the spinal cord. Because finding these lesions involves more elaborate imaging tests, spinal cord lesions in MS are studied less often, and many people with MS aren’t aware of the role these lesions may play in the disease process.
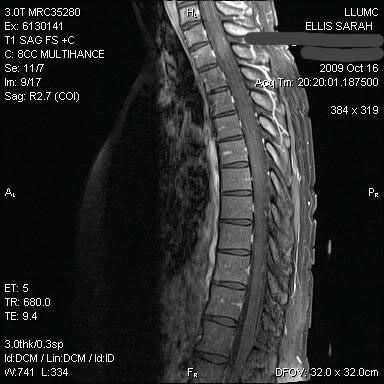
Can MS be seen on MRI?
Spinal cord lesions are more commonly seen in progressive forms of multiple sclerosis, and they can result in an increased risk of disability. MS lesions on the spinal cord can be seen on an MRI scan, as shown here. Getty Images.
What is spinal MS?
In conclusion, if you read the phrase “spinal MS,” know that it simply refers to the presence of lesions in the spinal cord in a patient diagnosed with MS. These lesions may cause various types of sensory and motor dysfunction below the level of the spinal cord involvement. The prognosis of spinal MS does not appear to be more dire than that of MS only affecting the brain. However, the higher incidence of spinal cord lesions often found in primary progressive multiple sclerosis (PPMS) does contribute to a more rapid development of disability.
Where do lesions occur in MS?
The lesions caused by multiple sclerosis can occur anywhere within the central nervous system, which includes the brain, the spinal cord, and the optic nerves. Approximately 55-75 percent of patients with MS will have spinal cord lesions at some time during the course of their disease.
What are the signs of a lesions in the corticospinal tract?
Lesions in this area often affect the corticospinal tract. Neurological signs which indicate lesions in the corticospinal tract include the Babinski Sign and the Hoffmann Sign. Additional indicators of lesions in the upper spine include the l’Hermittes phenomenon and the Romberg Sign.
What is the condition similar to MS?
Conditions similar to Spinal MS. An acute attack of myelitis is caused by inflammation in the spinal cord. Some patients may be diagnosed with Transverse Myelitis if they are experiencing their first attack of demyelination and inflammation.
Is spinal MS worse than MS?
The prognosis of spinal MS does not appear to be more dire than that of MS only affecting the brain. However, the higher incidence of spinal cord lesions often found in primary progressive multiple sclerosis (PPMS) does contribute to a more rapid development of disability.
Do spinal cord lesions cause bladder dysfunction?
Although the location of lesions do not always closely correlate to areas of clinical disability, there are cause/effect patterns which do emerge. Patients with spinal cord lesions are more likely to develop bladder dysfunction (e.g., urinary urgency or hesitancy, partial retention of urine, mild urinary incontinence), bowel dysfunction (e.g., ...
What is spinal lesion?
Lesion is a general term for tissue that has been injured, destroyed, or otherwise has a problem. Spinal lesions affect the nervous tissue of the spine. They may be due to: Symptoms and treatment depend on the spinal-lesion type and cause.
Which disease produces spinal cord lesions in a majority of cases?
Multiple sclerosis, which produces spinal cord lesions in a majority of cases 3
How to tell if you have a spinal cord injury?
However, if the lesion affects the spinal nerve roots or spinal cord, you are likely to have nerve symptoms, which can include: 1 Weakness 2 Numbness 3 Tingling 4 Electrical shock-like feelings down one leg or arm 5 Difficulty with fine motor skills (such as writing) or with walking, balance, or coordination
What is the diagnostic process for spinal cord injury?
The diagnostic process starts with a medical history to assess trauma and risks for spinal infection, cancer, and congenital malformations. A physical exam will check for sensory and strength changes. Blood and urine tests may also be done to screen for underlying problems and general health.
Is physical therapy necessary for multiple sclerosis?
Treatment of the underlying condition, such as with antibiotics or antivirals for infections, or disease-modifying therapies for multiple sclerosis, may also be necessary . Physical therapy may be able to help restore function after treatment and initial recovery. Physical Therapy for Chronic Pain.
Can a spinal lesion cause back pain?
Spinal lesions may have symptoms of non-specific back pain, or myofascial pain syndrome. You may not be able to pinpoint where your pain is coming from. However, if the lesion affects the spinal nerve roots or spinal cord, you are likely to have nerve symptoms, which can include: Weakness. Numbness.
Where do MS lesions appear?
Lesions in people with MS usually appear in the brain stem, cerebellum, spinal cord, and cranial nerves (including the optic nerve, trigeminal nerve, and facial nerve). Lesions can appear in one specific area of the brain, in multiple areas, or in large swathes of the central nervous system.
What causes brain lesions in multiple sclerosis?
Brain lesions in multiple sclerosis are caused by an abnormal immune system response. Lesions in the central nervous system cause different symptoms, depending upon their location, size, and severity. Disease-modifying medications and lifestyle changes can help prevent multiple sclerosis brain lesions from forming or worsening.
What Causes Brain Lesions?
Brain lesions can have many different causes. Age, a family history of brain lesions, trauma, and viral or bacterial infections are just a few things that can cause brain lesions. Autoimmune diseases, such as lupus and MS, are another. In the case of MS, brain lesions are the result of inflammation and damage caused by a misfiring immune response and the formation of scar tissue.
How Do Doctors Detect Brain Lesions?
Brain lesions appear as darker or lighter spots on a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan. Other times a person's neurologic symptoms bring them to the doctor’s office.
How to prevent brain lesions from forming?
Disease-modifying medications and lifestyle changes can help prevent multiple sclerosis brain lesions from forming or worsening. Lesions in multiple sclerosis (MS) are the result of damage to the cells of the central nervous system, which is made up of the brain and spinal cord. “Sclerosis” refers to the characteristic scar tissue ...
What is the parietal lobe?
The parietal lobes are located at the center of the brain. This is where sensory information is processed. Our parietal lobes allow us to feel temperature, taste, touch, and movement. The parietal lobes are also responsible for our ability to read and do math. Lesions in the parietal lobes may cause symptoms such as forgetting words for common objects and loss of sensations such as heat, cold, and pain. The parietal lobe also carries a portion of the nerve fibers originating from the eyes, so lesions in this area can affect the lower part of the visual field.
How to diagnose brain lesions?
Diagnosing lesions in the brain may involve a neurologist taking a complete medical history, conducting a physical examination, and performing a detailed neurological exam. The doctor may use vibration or hot or cold objects to assess the ability to detect sensations. The doctor may pinch a person’s cheek or other part of the body to check pain responses. These stimulus response tests may also help pinpoint the possible location of the lesion or lesions.
Which subtype of MS has the highest volume of brain lesion atrophy?
While patients with relapsing remitting MS showed the highest number of new lesions during the study, patients with progressive MS—the most severe subtype—had the most accelerated volume of brain lesion atrophy. This indicates that this new imaging biomarker could be particularly important in transitional phases between relapsing and progressive MS subtypes, researchers say.
What is brain lesions?
Brain lesions in general are a sign of damage to the brain, such as physical trauma, a stroke, normal aging, or chronic disease. Patients with MS receive MRI scans as part of their routine care so that doctors can track the appearance of new lesions and the enlargement of existing ones, typically seen as indicators of disease progression.
What does it mean when you see a brain lesions on an MRI?
For decades, clinicians treating MS have interpreted the appearance of new or expanding brain lesions on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans as a sign that a patient’s disease is getting worse.
What is the loss of myelin sheaths in the brain?
MS is characterized by the loss of myelin sheaths surrounding axons in the brain and disrupting the brain’s ability to send and receive neuronal messages. The growth of new myelin sheaths ...
How many patients were involved in the MS study?
The five-year study involved 192 patients with one of the three subtypes of MS: clinically isolated syndrome, the earliest stage; relapsing remitting, an intermediate stage; or progressive, the most severe stage. In that study, patients underwent imaging studies in the Center for Biomedical Imaging in the Clinical and Translational Science Institute at UB and BNAC.
Does brain lesion loss correlate with disability?
They found that the amount of lesion volume that atrophied was the only significant lesion parameter that correlated with clinical disability as measured by the Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS), the most widely used method of quantifying disability in MS.
Who funded the study of atrophied brain lesion volume?
The research on atrophied brain lesion volume received no external funding but was supported in part by BNAC and the Center for Biomedical Imaging at the Clinical and Translational Science Institute at UB.
