How might sunspot activity affect Earth's global climate?
Sunspots have been observed continuously since 1609, although their cyclical variation was not noticed until much later. At the peak of the cycle, about 0.1% more Solar energy reaches the Earth, which can increase global average temperatures by 0.05-0.1℃ .
Do sunspots increase temperature?
What effect do sunspots have on Earth’s temperature? Sunspots have been observed continuously since 1609, although their cyclical variation was not noticed until much later. At the peak of the cycle, about 0.1% more Solar energy reaches the Earth, which can increase global average temperatures by 0.05-0.1℃.
How do the sunspots affect us on Earth?
- Solar storms cause auroras which are cool to watch.
- Solar storms cause the ionosphere to heat, which allows people with short-wave radios to talk to people much further away.
- Big solar storms can damage satellites. Depending on what the satellite does as to how it affects us.
- Big solar storms can damage the electrical grid. ...
How does the sun affect the atmosphere and climate?
The Sun-climate connection. The Sun is the source of most of the energy that drives the biological and physical processes in the world around us—in oceans and on land it fuels plant growth that forms the base of the food chain, and in the atmosphere it warms air which drives our weather. The rate of energy coming from the Sun changes slightly day to day.

Do sunspots reduce temperature?
This in turn lowers the temperature relative to its surroundings because the concentrated magnetic field inhibits the flow of hot, new gas from the Sun's interior to the surface. Sunspots tend to occur in pairs that have magnetic fields pointing in opposite directions.
Why do sunspots affect climate?
This increase in UV rays affects chemistry of the outer atmosphere and the energy balance of Earth. The idea that sunspots affect Earth's climate is still largely debated, but it is believed that the increase of sunspots on the surface of the sun can reduce the amount of energy and light distributed to Earth.
How do sunspots affect global temperatures?
Sunspots have been observed continuously since 1609, although their cyclical variation was not noticed until much later. At the peak of the cycle, about 0.1% more Solar energy reaches the Earth, which can increase global average temperatures by 0.05-0.1℃. This is small, but it can be detected in the climate record.
Are sunspots related to weather?
A new study in the journal Science by a team of international of researchers led by the National Center for Atmospheric Research have found that the sunspot cycle has a big effect on the earth's weather.
Are sunspots hotter or cooler?
Sunspots are areas that appear dark on the surface of the Sun. They appear dark because they are cooler than other parts of the Sun's surface. The temperature of a sunspot is still very hot though—around 6,500 degrees Fahrenheit!
Is Sun Causing Global Warming?
No. The Sun can influence Earth's climate, but it isn't responsible for the warming trend we've seen over recent decades. The Sun is a giver of life; it helps keep the planet warm enough for us to survive. We know subtle changes in Earth's orbit around the Sun are responsible for the comings and goings of the ice ages.
How does the Sun play an important role in the change of temperature?
Sun plays a vital role in changes in climate. The heat provided by the sun causes the water to evaporate and become clouds. The heat also causes the air to get hot and causes winds and tornados.
Why are sunspots cooler?
As well as being a darker area on the sun, a sunspot is an area that temporarily has a concentrated magnetic field. This magnetic force inhibits the convective motion, which ordinarily brings hot matter up from the interior of the sun, so the area of the sunspot is cooler than the surrounding plasma and gas.
Do solar cycles affect climate?
What Effect Do Solar Cycles Have on Earth's Climate? According to the United Nations' Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), the current scientific consensus is that long and short-term variations in solar activity play only a very small role in Earth's climate.
Why is the Sun getting hotter?
The Sun is getting hotter, adding heat to the global warming that has been linked to greenhouse gases that trap heat in the atmosphere. Solar radiation reaching the Earth is 0.036 percent warmer than it was in 1986, when the current solar cycle was beginning, said a study published on Friday in the journal Science.
How does solar minimum affect weather?
People closely observing the Sun will see more sunspots during solar maximum. At solar minimum, solar ultraviolet radiation decreases, but the effect of this primarily hits the stratosphere and higher altitudes. It causes Earth's atmosphere to shrink slightly, which reduces drag on satellites.
How do solar cycles affect climate?
The Sun's irradiance has its greatest effect on Earth's upper atmosphere, while the lower atmosphere insulates Earth from the increased heat. If the Sun were driving Earth's warming, one would expect to see that upper atmosphere getting increasingly hot.
How does sun affect weather?
The Earth's climate system depends entirely on the Sun for its energy. Solar radiation warms the atmosphere and is fundamental to atmospheric composition, while the distribution of solar heating across the planet produces global wind patterns and contributes to the formation of clouds, storms, and rainfall.
How does volcanic eruptions cause climate change?
Volcanic gases react with the atmosphere in various ways; the conversion of sulfur dioxide (SO2) to sulfuric acid (H2SO4has the most significant impact on climate. Volcanoes can impact climate change.
How do volcanic eruptions affect climate?
The gases and dust particles thrown into the atmosphere during volcanic eruptions have influences on climate. Most of the particles spewed from volcanoes cool the planet by shading incoming solar radiation. The cooling effect can last for months to years depending on the characteristics of the eruption.
What happens to the Earth during a sunspot?
Therefore during sunspot maximums, the Earth will see an increase in the Northern and Southern Lights and a possible disruption in radio transmissions and power grids.
What is the magnetic field of a sunspot?
Sunspots are areas where the magnetic field is about 2,500 times stronger than Earth's, much higher than anywhere else on the Sun. Because of the strong magnetic field, the magnetic pressure increases while the surrounding atmospheric pressure decreases.
What is the period of sunspot minima?
One interesting aspect of solar cycles is that the sun went through a period of near zero sunspot activity from about 1645 to 1715 . This period of sunspot minima is called the Maunder Minimum. The "Little Ice Age" occurred over parts of Earth during the Maunder Minimum.
Why do scientists preposition satellites to a different orientation?
Therefore scientists will often times preposition satellites to a different orientation to protect them from increased solar radiation when a strong solar flare or coronal mass ejection has occur red. The Solar Cycle: Sunspots increase and decrease through an average cycle of 11 years.
What are solar flares?
Sunspots, Solar Flares, Coronal Mass Ejections and their influence on Earth: Coronal Mass Ejections (shown left) and solar flares are extremely large explosions on the photosphere. In just a few minutes, the flares heat to several million degrees F. and release as much energy as a billion megatons of TNT.
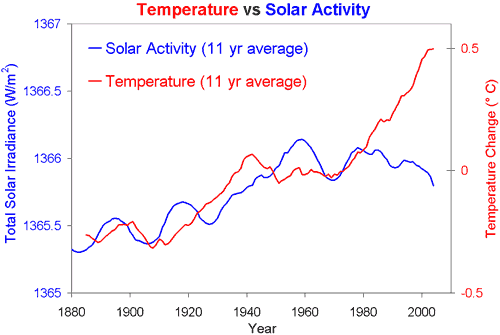
How does solar activity affect Earth's climate?
There is research which shows evidence that Earth's climate is sensitive to very weak changes in the Sun's energy output over time frames of 10s and 100 s of years. Times of maximum sunspot activity are associated with a very slight increase ...
What is the name of the dark region of a sunspot?
Sunspots tend to occur in pairs that have magnetic fields pointing in opposite directions. A typical spot consists of a dark region called the umbra, surrounded by a lighter region known as the penumbra .
What is the temperature of sunspots?
Sunspots are spots of cooler temperatures on the sun. They appear darker than the rest of the sun and occur in a region called the photosphere. The photosphere has a temperature of 5,778 kelvin compared to sunspots that have an average temperature of 3,500 kelvin.
Why do sunspots have less energy?
During high sunspot activity less energy would be coming from the sun because of the lower temperatures. However, this is not now thought to be the case. Sunspots have been linked to interference with magnetic instruments on Earth; increased activity of sunspots causes there to be more interference with magnetic instruments.
Why do sunspots occur?
Sunspots are not fully understood but are generally believed to be caused by a change in the sun’s magnetic field through the process of magnetic re-connection. Magnetic re-connection is where magnetic field lines are broken and reconnected causing inflowing magnetic energy to convert to kinetic energy. Sunspots occur in regions of intense magnetic ...
How does the sun affect the atmosphere?
The increase of ultraviolet rays from sunspots affects the outer atmosphere of the Earth. Ultraviolet rays also can cause skin cancer and skin related illnesses. The effect of sunspots on the climate of planet Earth is thought to be very small.
How long is the Sunspot cycle?
The sunspots come and go, with huge fluctuations between times of maximum and minimum sunspot activity, the overall cycle being around 11 years in length. Sunspots usually occur in small groups in several different places all over the sun. Sunspots were first recorded as having been seen as far back as 28 BC.
How much would the temperature be reduced by 2100?
According to a study on the effects of low sunspot activity conducted by the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research, if there was a sudden reduction of sunspots now it is estimated that in the year 2100 the temperature would be reduced by 0.26 degrees Celsius.
Why is the sun important to plants?
The sun is the sole source that allows life to thrive on Earth. This is because it is the key driver of photosynthesis in plants. Without the sun there would be no life on Earth at all. Sunspots were thought to affect plants because of the light needed for photosynthesis.
How does solar flare affect the atmosphere?
Although solar flares, and associated coronal mass ejections, can bombard Earth’s outermost atmosphere with tremendous amounts of energy, most of that energy is reflected back into space by the Earth’s magnetic field.
Where does the extra heat from solar flares radiate?
A small fraction of the extra heat from the solar flare radiates to layers of the atmosphere below the thermosphere, but it is miniscule compared to the normal amount of heating the lower layers of the atmosphere already experience from incoming visible and ultraviolet sunlight.
Do solar flares cause heat waves?
Solar flares don’t cause heat waves, but they do have other impacts on Earth. Consequences include pretty auroras, as well as hazards. They can rain extra radiation on satellites, and increase the drag on satellites in low-Earth orbit. Increased electromagnetic activity due to solar storms can also disrupt power grids and radio communications.
Can solar storms disrupt power grids?
Increased electromagnetic activity due to solar storms can also disrupt power grids and radio communications. Passengers on commercial jets flying polar routes may be exposed to increased electromagnetic radiation.
Where do sunspots form?
However, there are some clues. For example, sunspots tend to form nearer the Sun’s equator as the cycle winds down (and at higher latitudes when a new cycle begins). Scientists measure solar cycles by keeping track of the number of sunspots appearing on the Sun’s surface as well as noting the location.
What does a sunspot mean?
Sunspots indicate active magnetic fields. The dark spots are cooler than the surrounding areas. Think of them as caps to a magnetic storm that is brewing just below the solar surface. The Sun’s magnetic fields are moving around, getting twisted and concentrated in these regions.
What happens to the sun after high activity?
After some years of high activity, the Sun will ramp down with fewer sunspots or almost no sunspots. The temperature cools. Conversely, solar maximum is the highest number of sunspots in any given cycle. A new cycle starts with a “solar maximum” littered with solar storms and sunspots. The temperature warms.
What is a black spot on the surface of the Sun?
In areas where the magnetic fields are particularly strong, we may see a black spot—called a sunspot —emerge on the surface of the Sun. This is indicative of a sunstorm and a lot of activity beneath the surface. More sunspots means more solar activity. There does seem to be an ebb and flow or “cycle” to this magnetic flow and movement.
What is the solar cycle?
What Solar Cycle Are We In Now? 1 By solar minimum, we mean the lowest number of sunspots. After some years of high activity, the Sun will ramp down with fewer sunspots or almost no sunspots. The temperature cools. 2 Conversely, solar maximum is the highest number of sunspots in any given cycle. A new cycle starts with a “solar maximum” littered with solar storms and sunspots. The temperature warms.
How long does the solar cycle last?
The total number of sunspots has long been known to vary with an approximately 11-year repetition known as the solar cycle—going from low to high and then high to low.
How long is the Sun's cycle?
Note: The exact length of the cycle is not always 11 years; it has been as short as eight years and as long as 14. Eleven years in the life of the Sun from 1980 (start of solar maximum) to 1986 (near minimum) to 1989 (near maximum again). Credit: NASA.
How often do sunspots peak?
Scientists believe that the number of spots on the sun cycles over time, reaching a peak—the so-called Solar Maximum—every 11 years or so. Some studies indicate that sunspot activity overall has doubled in the last century.
Is it a coincidence that the sunspots are increasing?
They say it’s no coinciden ce that an increase in sunspot activity and a run-up of global temperatures on Earth are happening concurrently, and view regulation of carbon emissions as folly with negative ramifications for our economy and tried-and-true energy infrastructure.
