
Type I diabetics require the use of insulin to live. The use of insulin is implied in the diagnosis of Type I diabetes
Type 1 Diabetes
A chronic condition where the pancreas produces little or no insulin.
What is the ICD 10 code for insulin?
ICD-10 Code Z79. 4, Long-term (current) use of insulin should be assigned to indicate that the patient uses insulin for Type 2 diabetes mellitus (Category E11* codes). Z79. 4 should NOT be used for Type 1 diabetes mellitus (Category E10* codes).
What is the ICD 10 code for Type 1 diabetes mellitus?
Assigning and sequencing diabetes codes and associated conditions: Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (Juvenile Diabetes) Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus is an “insulin” dependent disease; therefore, DO NOT add the ICD-10 code Z79.4 (long term, current insulin use) with Type 1 Diabetes. mellitus (Category E10* codes).
Do I need to code for diabetic patients who are using insulin?
Don’t the coding guidelines say I need to report this code for diabetic patients who are using insulin? The use of code Z79.4 to indicate long-term current use of insulin is only used for patient’s who are type II diabetic. Some type II diabetics require insulin use to control their blood sugars and others do not.
Why is it called insulin-dependent diabetes?
Because people with type 1 diabetes rely on insulin, it was formerly called insulin-dependent diabetes. To learn about how the hormone insulin works, we have an article that explains the role of insulin.
What is the code for type 1 diabetes?
ICD-10 code E10. 9 for Type 1 diabetes mellitus without complications is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases .
How do you code type 1 and type 2 diabetes?
E08, Diabetes mellitus due to underlying condition. E09, Drug or chemical induced diabetes mellitus. E10, Type 1 diabetes mellitus. E11, Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Is type 1 or 2 insulin Dependant?
The necessity for treatment with insulin is why type 1 is classified as insulin-dependent. In type 2, some insulin is released but the locks on the cells are damaged. Insulin's keys no longer fit, and the cells refuse to unlock.
Should diabetes be coded first?
These codes, found under categories E08, E09, and E13, should be listed first, followed by the long-term therapy codes for insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents. Follow the instructions in the Tabular List of ICD-10-CM for proper sequencing of these diagnosis codes.
Can you code hyperglycemia and diabetes together?
According to American Hospital Association Coding Clinic, “Any combination of the diabetes codes can be assigned together, unless one diabetic condition is inherent in another.” 4 For example, diabetic retinopathy documented with hyperglycemia would be reported with two ICD-10 codes: E11.
Which diabetes is insulin independent?
Type 2 diabetes mellitus is also called non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM), since it can be treated with lifestyle changes and/or types of medication other than insulin therapy. Type 2 diabetes is significantly more common than type 1 diabetes.
How do doctors tell the difference between type 1 and 2 diabetes?
Blood tests used to diagnose type 1 and type 2 diabetes include fasting blood sugar, a hemoglobin A1C test, and a glucose tolerance test. The A1C test measures the average blood sugar level over the past few months. The glucose tolerance test measures blood sugar after a sugary drink is given.
Which type of diabetes is not insulin dependent?
Type 2 diabetes (formerly called adult-onset or non–insulin-dependent diabetes) can develop at any age. It most commonly becomes apparent during adulthood. But type 2 diabetes in children is rising.
How is uncontrolled type 1 or Type 2 diabetes mellitus codes in ICD-10-CM?
For example, the most common code used for type 2 diabetes is E11. 65 (type 2 diabetes with hyperglycemia), which reflects suboptimal control. The most common codes for type 1 diabetes are E10. 65 (type 1 diabetes with hyperglycemia) and E10.
Can you code E11 21 and E11 22 together?
21 and E11. 22 have an excludes 1 notes therefore they can be coded together as long as a separate renal manifestation is present, I would just be careful when coding the actual renal condition as there are some renal codes that are excluded when using CKD codes.
Can you code E11 40 and E11 42 together?
If you look in the alphabetical index under diabetes/diabetic with neuropathy it is E11. 40 (type 2 DM with diabetic neuropathy, unspecified). You cannot go with E11. 42 because that is specifically with polyneuropathy which is not documented.
What is the ICD-10 code for Diabetes type 2?
ICD-Code E11* is a non-billable ICD-10 code used for healthcare diagnosis reimbursement of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Its corresponding ICD-9 code is 250.
Why do I need a Z code for type 2 diabetes?
If a type II diabetic is using insulin it is important to report that with a Z code because the use of this medication will affect the physician’s management of the patient. Type I diabetics require the use of insulin to live.
Is it necessary to report a Z code for long term insulin use?
The use of insulin is implied in the diagnosis of Type I diabetes itself. Since this is the case, it is not necessary to report a Z code for long-term insulin use because it would be understood that this patient would be using insulin.
What is the code for gestational diabetes?
Codes for gestational diabetes are in subcategory O24.4. These codes include treatment modality — diet alone, oral hypoglycemic drugs, insulin — so you do not need to use an additional code to specify medication management. Do not assign any other codes from category O24 with the O24.4 subcategory codes.
What is the ICd 10 code for secondary diabetes?
Follow the instructions in the Tabular List of ICD-10-CM for proper sequencing of these diagnosis codes. For example, if a patient has secondary diabetes as a result of Cushing’s syndrome and no other manifestations, report code E24.9 Cushing’s syndrome, unspecified, followed by E08.9 Diabetes mellitus due to underlying condition without manifestations. If a patient is diagnosed with secondary diabetes due to the adverse effects of steroids, report codes E09.9 Drug or chemical induced diabetes without complications and T38.0X5A Adverse effect of glucocorticoids and synthetic analogues, initial encounter.
How does diabetes affect blood sugar?
In patients with type 2 diabetes, problems begin when the cells in their body start to not respond to insulin as well as they should. This is called insulin resistance, which causes high blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia). The pancreas responds by making more insulin to try and manage the hyperglycemia, but eventually, the pancreas can’t keep up and blood sugar levels rise. Left uncontrolled, the disease progresses into prediabetes and, eventually, type 2 diabetes. This is the most common type of diabetes and is initially treated with lifestyle modification including a healthy diet and exercise. If these measures are not effective, treatment generally starts with an oral hypoglycemic agent. If better control is needed, injectable medications or insulin may be initiated to help manage blood sugar levels and avoid complications.
What chapter do you report diabetes?
Report encounters related to pregnancy and diabetes using codes in Chapter 15 Pregnancy, Childbirth, and the Puerperium. If a pregnant woman has pre-existing diabetes that complicates the pregnancy, Chapter 15 guidelines instruct us to assign a code from O24 first, followed by the appropriate diabetes code (s) from Chapter 4 (E08–E13). Report codes Z79.4 or Z79.84 if applicable.
What is secondary diabetes?
Secondary diabetes — DM that results as a consequence of another medical condition — is addressed in Chapter 4 guidelines. These codes, found under categories E08, E09, and E13, should be listed first, followed by the long-term therapy codes for insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents.
What is type 1.5 diabetes?
Type 1.5 diabetes is a form of diabetes in which an adult has features of both type 1 and type 2 diabetes. These patients have also been described with the terms “latent autoimmune diabetes of adults” (LADA), and “slow-progressing type 1 diabetes.” The condition has also been called “double” diabetes, because individuals demonstrate both the autoimmune destruction of beta cells of type 1 diabetes and the insulin resistance characteristic of type 2 diabetes. People with type 1.5 diabetes have autoantibodies to insulin-producing beta cells and gradually lose their insulin-producing capability, requiring insulin within 5–10 years of diagnosis.
What is the most common type of diabetes?
Left uncontrolled, the disease progresses into prediabetes and, eventually, type 2 diabetes. This is the most common type of diabetes and is initially treated with lifestyle modification including a healthy diet and exercise. If these measures are not effective, treatment generally starts with an oral hypoglycemic agent.
Type 1 Diabetes: How Is It Treated?
KidsHealth / For Teens / Type 1 Diabetes: How Is It Treated? en espaolDiabetes tipo 1: Cul es el tratamiento? Your teachers follow a lesson plan that outlines what you'll study each day. Your parents may have a plan to help you pay for college.
Insulin And Type 2 Diabetes: What You Should Know
Insulin and Type 2 Diabetes If your health care provider offered you a medication to help you feel better and get your blood sugar under control, would you try it? If so, you might be ready to start taking insulin. Does insulin immediately make you think of type 1 diabetes? Think again.
Managing Diabetes
You can manage your diabetes and live a long and healthy life by taking care of yourself each day. Diabetes can affect almost every part of your body. Therefore, you will need to manage your blood glucose levels, also called blood sugar.
Type 1 Diabetes
Print Diagnosis Diagnostic tests include: Glycated hemoglobin (A1C) test. This blood test indicates your average blood sugar level for the past two to three months. It measures the percentage of blood sugar attached to the oxygen-carrying protein in red blood cells (hemoglobin).
Type 1 Diabetes And Insulin
It’s necessary to take insulin when you have type 1 diabetes. Your body doesn’t produce the hormone insulin, and without that, your body can’t properly get the energy and fuel it needs from glucose. Because people with type 1 diabetes rely on insulin, it was formerly called insulin-dependent diabetes.
What Type Of Diabetes Requires Insulin Injections?
People with Type 1 diabetes always require insulin injections in order to control blood sugar readings because they make little or no insulin. Insulin is also prescribed for Type 2 diabetes when oral medications or other injectable meds are not controlling blood sugar levels adequately.
Type 1 Diabetes
Introduction Diabetes is a lifelong condition that causes a person's blood sugar (glucose) level to become too high. The hormone insulin – produced by the pancreas – is responsible for controlling the amount of glucose in the blood.
Should I Use Diabetes Pills Or Insulin?
Diabetes affects the way your body breaks down food. Treatment depends on which type of diabetes you have. In type 1 diabetes, your pancreas stops producing insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps regulate glucose, or sugar, in your blood. Type 2 diabetes starts with insulin resistance.
Managing Diabetes Without Insulin – Is It Possible?
It is widely believed that those with Type 2 diabetes may eventually need insulin if they have diabetes for long enough. However, only about 20-30 percent of people with Type 2 diabetes end up needing insulin injections. In this article, we will explore whether it is possible to manage your diabetes without insulin.
Insulin And Type 2 Diabetes: What You Should Know
Insulin and Type 2 Diabetes If your health care provider offered you a medication to help you feel better and get your blood sugar under control, would you try it? If so, you might be ready to start taking insulin. Does insulin immediately make you think of type 1 diabetes? Think again.
Managing Diabetes
You can manage your diabetes and live a long and healthy life by taking care of yourself each day. Diabetes can affect almost every part of your body. Therefore, you will need to manage your blood glucose levels, also called blood sugar.
Insulin For Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
Examples The different types of insulin are categorized according to how fast they start to work (onset) and how long they continue to work (duration). The types now available include rapid-, short-, intermediate-, and long-acting insulin.
Type 1 Diabetes Faqs
Do I need to take insulin for the rest of my life? Yes. People with type 1 diabetes are not making enough insulin from their own bodies. Most people inject insulin at least four times a day. However, the insulin pump, or continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII), is slowly replacing frequent injections as a preferred delivery system.
Type 1 Diabetes - Topic Overview
This topic covers type 1 diabetes, including information about symptoms, tests, and home treatment. For specific information about children who have type 1 diabetes, see the topic Type 1 Diabetes: Children Living With the Disease. Insulin is a hormone that helps the body's cells use sugar (glucose) for energy.
What is ICD-10 code for insulin dependent diabetes mellitus?
ICD-10 Code Z79. 4, Long-term (current) use of insulin should be assigned to indicate that the patient uses insulin for Type 2 diabetes mellitus (Category E11* codes).
What is the default code for diabetes?
Yes, we do have a default code in ICD-10-CM for those times the physician just doesn’t document anything more than “diabetes”—it’s E11. 9. Just like 250.00, E11.
How do you code diabetes history?
ICD-10 code Z83. 3 for Family history of diabetes mellitus is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range – Factors influencing health status and contact with health services .
What is the correct coding and sequencing for diabetic polyneuropathy in a person with type 1 diabetes?
42, and type 1 diabetes mellitus with diabetic autonomic (poly)neuropathy is assigned to code E10. 43.
Do you code insulin with type 1 diabetes?
Type I diabetics require the use of insulin to live. The use of insulin is implied in the diagnosis of Type I diabetes itself. Since this is the case, it is not necessary to report a Z code for long-term insulin use because it would be understood that this patient would be using insulin.
When coding secondary diabetes mellitus The sequencing of the codes is based on?
The sequencing of the secondary diabetes codes in relationship to codes for the cause of the diabetes is based on the Tabular list instructions for categories E08, E09, and E13. ? The note under categories E08, E09, and E13 states “Use additional code to identify any insulin use (Z79. 4.)” Code Z79.
How do you code diabetes with chronic kidney disease?
22 for Type 2 diabetes mellitus with diabetic chronic kidney disease is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range – Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases .
When coding diabetic nephropathy which code is listed first?
These codes, found under categories E08, E09, and E13, should be listed first, followed by the long-term therapy codes for insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents. Follow the instructions in the Tabular List of ICD-10-CM for proper sequencing of these diagnosis codes.
When coding secondary diabetes mellitus The sequencing of the codes is based on?
The sequencing of the secondary diabetes codes in relationship to codes for the cause of the diabetes is based on the Tabular list instructions for categories E08, E09, and E13. ? The note under categories E08, E09, and E13 states “Use additional code to identify any insulin use (Z79. 4.)” Code Z79.
Do you code insulin with type 1 diabetes?
Type I diabetics require the use of insulin to live. The use of insulin is implied in the diagnosis of Type I diabetes itself. Since this is the case, it is not necessary to report a Z code for long-term insulin use because it would be understood that this patient would be using insulin.
What is the correct coding and sequencing for diabetic polyneuropathy in a person with type 1 diabetes?
42, and type 1 diabetes mellitus with diabetic autonomic (poly)neuropathy is assigned to code E10. 43.
Is there a combination code for diabetes and hypertension?
Guru. I would code it as I10 for hypertension and E11. 9 for diabetes.
Can you code type 1 and type 2 diabetes?
In this case, the provider specifically documented “combination Type 1 and 2 diabetes mellitus in poor control”; therefore, the coder should assign code E13.
What is the AHA Coding Clinic?
The Coding Clinic for ICD-9-CM was established in 1984 to help everyone who had an interest and dedication in improving the accuracy and uniformity of medical record coding. The newsletter was created to provide coding advice, official coding decisions, and news related to the use of ICD-9-CM.
Why is type 1 diabetes called insulin dependent?
Because people with type 1 diabetes rely on insulin, it was formerly called insulin-dependent diabetes. To learn about how the hormone insulin works, we have an article that explains the role of insulin. Insulin is a hormone produced by the beta cells of the pancreas whose role is to permit the body to use glucose for energy.
Why do people with type 1 diabetes need insulin?
Because people with type 1 diabetes rely on insulin, it was formerly called insulin-dependent diabetes.
Where Should You Inject the Insulin?
Insulin injected into the abdomen is absorbed (and therefore put to work) the most quickly.
What is the role of insulin in the pancreas?
Insulin is a hormone produced by the beta cells of the pancreas whose role is to permit the body to use glucose for energy. Image: 123rf. As soon as you are (or your child is) diagnosed with type 1 diabetes (T1D), you will be immersed in the world of insulin, and it may feel overwhelming at first.
What is the process of releasing insulin?
In someone without type 1 diabetes, the body releases insulin when they eat; it’s the insulin that should help them process and use the carbohydrates in the food. That release of insulin at mealtime is called the bolus secretion . Rapid-acting insulin imitates the bolus secretion.
What is pre-mixed insulin?
Pre-mixed: A pre-mixed insulin combines two other types of insulin— for example, a rapid-acting and intermediate-acting insulin. This assures that you have the right amount of insulin to cover the bolus and basal secretions.
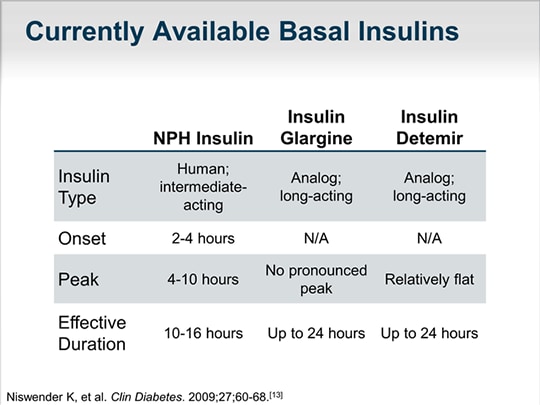
How long does insulin last?
Long-acting: Similar to intermediate-acting insulin, long-acting insulin replicates the basal secretion. Long-acting insulin lasts for 20-24 hours, so you usually take it once a day. Some people may take this type of insulin twice a day for better control of their blood sugar.