When you import the zone file, Route 53 ignores the statement of authority (SOA) record. Any name server (NS) records in the zone file that have the same name as the hosted zone are also ignored.
Full Answer
What is the Amazon Route 53 service?
The name server (NS) record Amazon Route 53 automatically creates a name server (NS) record that has the same name as your hosted zone. It lists the four name servers that are the authoritative name servers for your hosted zone. Except in rare circumstances, we recommend that you don't add, change, or delete name servers in this record.
What is the NS record in Route 53?
Amazon Route 53 supports the DNS record types that are listed in this section. Each record type also includes an example of how to format the Value element when you are accessing Route 53 using the API. Note For record types that include a domain name, enter a fully qualified domain name, for example, www.example.com.
Does Amazon Route 53 cache DNS records?
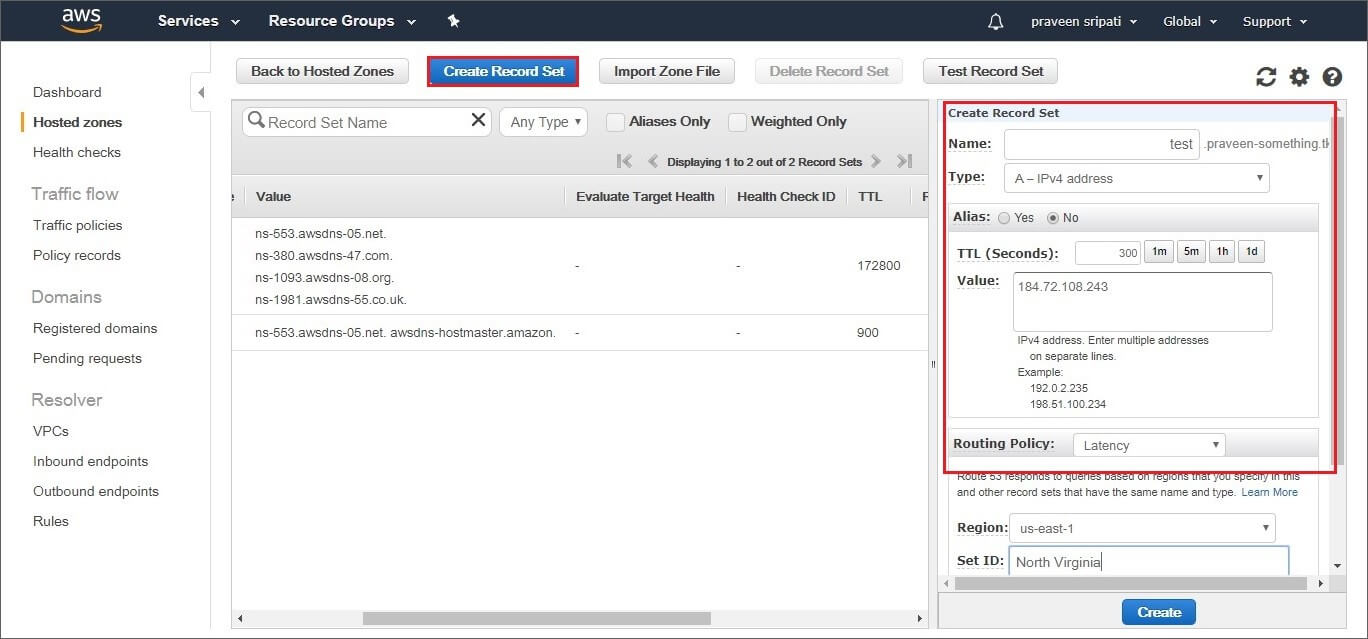
To lower the TTL setting on the NS record in a Route 53 hosted zone. Sign in to the AWS Management Console and open the Route 53 console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/route53/. Choose Hosted Zones in the navigation pane. Choose the name of the hosted zone. Choose the NS record, and choose Edit. Change the value of TTL …
Do I have to use Route 53 as the DNS service?
To make it even easier for you to configure DNS settings for your domain, Amazon Route 53 supports wildcard entries for all record types, except NS records. A wildcard entry is a record in a DNS zone that will match requests for any domain name based on the configuration you set.
Which DNS record types does Amazon Route 53 support?
Amazon Route 53 currently supports the following DNS record types:A (address record)AAAA (IPv6 address record)CNAME (canonical name record)CAA (certification authority authorization)MX (mail exchange record)NAPTR (name authority pointer record)NS (name server record)PTR (pointer record)More items...
What is NS record in AWS?
The name server (NS) record It lists the four name servers that are the authoritative name servers for your hosted zone. Except in rare circumstances, we recommend that you don't add, change, or delete name servers in this record.
How do I add NS to Route 53?
Sign in to the AWS Management Console and open the Route 53 console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/route53/ .Choose Hosted Zones in the navigation pane.Choose the name of the hosted zone.Choose the NS record, and choose Edit.Change the value of TTL (Seconds). ... Choose Save changes.
What are Route 53 nameservers?
Route 53 name servers are the authoritative name servers for every domain that uses Route 53 as the DNS service. The name servers know how you want to route traffic for your domain and subdomains based on the records that you created in the hosted zone for the domain.
What is SOA and NS records?
NS: Name server record, which delegates a DNS zone to an authoritative server. PTR: Pointer record, which defines a name associated with an IP address. SOA: Start of authority, used to designate the primary name server and administrator responsible for a zone.
What is an NS record DNS?
What is a DNS NS record? NS stands for 'nameserver,' and the nameserver record indicates which DNS server is authoritative for that domain (i.e. which server contains the actual DNS records). Basically, NS records tell the Internet where to go to find out a domain's IP address.
When you create a DNS you are provided with two records NS and SOA What does SOA mean here?
start of authorityThe DNS 'start of authority' (SOA) record stores important information about a domain or zone such as the email address of the administrator, when the domain was last updated, and how long the server should wait between refreshes.
Are SOA records required?
Every domain must have an SOA record. When you add a domain to the DNS, the email address that you enter is added to the SOA record for the domain. This publicly associates the email with the domain.Dec 18, 2018
Why is Amazon Route 53?
Amazon Route 53 is a highly available and scalable cloud Domain Name System (DNS) web service. It is designed to give developers and businesses an extremely reliable and cost effective way to route end users to Internet applications by translating names like www.example.com into the numeric IP addresses like 192.0.
Which services does Amazon Route 53 provide?
Amazon Route 53 is a highly available and scalable Domain Name System (DNS) web service. You can use Route 53 to perform three main functions in any combination: domain registration, DNS routing, and health checking. Your website needs a name, such as example.com.
Is AWS Route 53 region specific?
Route 53 is primarily a global service, but the following features support AWS Regions: If you're using Route 53 Resolver to set up hybrid configurations, you create endpoints in AWS Regions that you choose, and you specify IP addresses in multiple Availability Zones.
What are Amazon routes are built based on?
The order in which they are serviced is determined by their time in queue, on a first-come, first-served basis. If multiple agents are available, the contact is routed to the agent who has been in the Available status for the longest time.
A record type
You use an A record to route traffic to a resource, such as a web server, using an IPv4 address in dotted decimal notation.
AAAA record type
You use an AAAA record to route traffic to a resource, such as a web server, using an IPv6 address in colon-separated hexadecimal format.
CAA record type
A CAA record specifies which certificate authorities (CAs) are allowed to issue certificates for a domain or subdomain. Creating a CAA record helps to prevent the wrong CAs from issuing certificates for your domains.
CNAME record type
A CNAME record maps DNS queries for the name of the current record, such as acme.example.com, to another domain (example.com or example.net) or subdomain (acme.example.com or zenith.example.org).
DS record type
A delegation signer (DS) record refers a zone key for a delegated subdomain zone. You might create a DS record when you establish a chain of trust when you configure DNSSEC signing. For more information about configuring DNSSEC in Route 53, see Configuring DNSSEC signing in Amazon Route 53 .
MX record type
An MX record specifies the names of your mail servers and, if you have two or more mail servers, the priority order. Each value for an MX record contains two values, priority and domain name.
NAPTR record type
A Name Authority Pointer (NAPTR) is a type of record that is used by Dynamic Delegation Discovery System (DDDS) applications to convert one value to another or to replace one value with another. For example, one common use is to convert phone numbers into SIP URIs.
Step 1: Get your current DNS configuration from the current DNS service provider (optional but recommended)
When you migrate DNS service from another provider to Route 53, you reproduce your current DNS configuration in Route 53. In Route 53, you create a hosted zone that has the same name as your domain, and you create records in the hosted zone. Each record indicates how you want to route traffic for a specified domain name or subdomain name.
Step 2: Create a hosted zone
To tell Amazon Route 53 how you want to route traffic for your domain, you create a hosted zone that has the same name as your domain, and then you create records in the hosted zone.
Step 3: Create records
After you create a hosted zone, you create records in the hosted zone that define where you want to route traffic for a domain (example.com) or subdomain (www.example.com).
Step 4: Lower TTL settings
The TTL (time to live) setting for a record specifies how long you want DNS resolvers to cache the record and use the cached information. When the TTL expires, a resolver sends another query to the DNS service provider for a domain to get the latest information.
Step 5: (If you have DNSSEC configured) Remove the DS record from the parent zone
If you've configured DNSSEC for your domain, remove the Delegation Signer (DS) record from the parent zone before you migrate your domain to Route 53.
Step 6: Wait for the old TTL to expire
If your domain is in use—for example, if your users are using the domain name to browse to a website or access a web application—then DNS resolvers have cached the names of the name servers that were provided by your current DNS service provider. A DNS resolver that cached that information a few minutes ago will save it for almost two more days.
Step 7: Update the NS records to use Route 53 name servers
To begin using Amazon Route 53 as the DNS service for a domain, use the method provided by the registrar, or the parent zone, to replace the current name servers in the NS record with Route 53 name servers.
Private DNS
Private DNS is a Route 53 feature that lets you have authoritative DNS within your VPCs without exposing your DNS records (including the name of the resource and its IP address (es) to the Internet.
Health Checks & DNS Failover
DNS Failover consists of two components: health checks and failover. Health checks are automated requests sent over the Internet to your application to verify that your application is reachable, available, and functional.
Route 53 Resolver
Route 53 Resolver is a regional DNS service that provides recursive DNS lookups for names hosted in EC2 as well as public names on the internet. This functionality is available by default in every Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC).
Maximum response size
To comply with DNS standards, responses sent over UDP are no more than 512 bytes in size. Responses exceeding 512 bytes are truncated and the resolver must re-issue the request over TCP.
Authoritative section processing
For successful queries, Route 53 appends name server (NS) records for the relevant hosted zone to the Authority section of the DNS response. For names that are not found (NXDOMAIN responses), Route 53 appends the start of authority (SOA) record (as defined in RFC 1035) for the relevant hosted zone to the Authority section of the DNS response.
Additional section processing
Route 53 appends records to the Additional section. If the records are known and appropriate, the service appends A or AAAA records for any target of an MX, CNAME, NS, or SRV record cited in the Answer section. For more information about these DNS record types, see Supported DNS record types .
Issue
I've configured my website to use Amazon Route 53 for DNS services, but I can't access my website from the internet. How do I troubleshoot this issue?
Short Description
Clients might be unable to access your website that uses Route 53 DNS services if:
Resolution
Be sure that the public hosted zone for your website's domain name in Route 53 contains the appropriate resource records sets. For more information, see Creating Records by Using the Amazon Route 53 Console and Editing Records. For record type-specific values, see Values That You Specify When You Create or Edit Amazon Route 53 Records.
Short description
To configure reverse DNS resolution for a Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) server, you must first determine the appropriate method for your use case:
Using on-premises SMTP servers
Note: This resolution uses the following example IP addresses for the SMTP server: 1.2.3.4 (IPv4) and 2000:1234:5678:9012:3456:7890:1234:5678 (IPv6).
Using SMTP servers hosted in Amazon VPC
Create a forward DNS record (record type A) that points to the appropriate Elastic IP address.