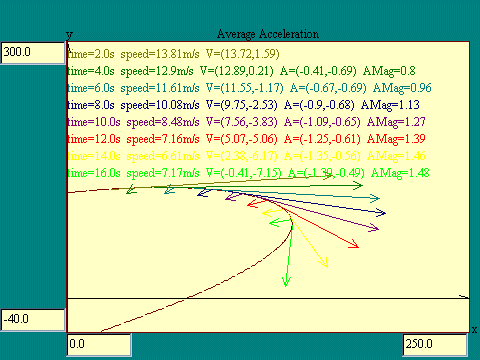
How does mass affect angular acceleration?
Physics How does mass affect angular acceleration? Angular acceleration is inversely proportional to mass. For rotational motion, adapting Newton's second law to describe the relation between torque and angular acceleration: where τ is the total torque exerted on the body, and I is the mass moment of inertia of the body. α = τ I ...................
What is meant by angular acceleration?
Angular acceleration. In physics, angular acceleration refers to the time rate of change of angular velocity. As there are two types of angular velocity, namely spin angular velocity and orbital angular velocity, there are naturally also two types of angular acceleration, called spin angular acceleration and orbital angular acceleration ...
What happens when angular acceleration is maximum in a circular orbit?
Suppose angular acceleration is maximum, the radius of the rotational path matters. Greater the radius of the orbit, the object’s attraction towards the center becomes less. This results in the decrease of the velocity and hence the acceleration. Why does the angular acceleration is zero in a uniform circular orbit?
How does torque affect angular acceleration?
The torque determines the angular acceleration: Since the tension work in opposite directions, the tensions, T 1 and T 2, act in opposite directions (where T 1 is on the side of block 1 and T 2 is on the side of block 2). Here is where I start to get more unsure.
What is angular acceleration?
Is torque a rotational analogue of force?
Does angular acceleration occur in non-rigid bodies?
About this website
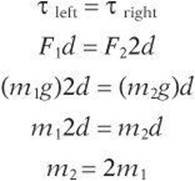
Does angular acceleration change with mass?
The first example implies that the farther the force is applied from the pivot, the greater the angular acceleration; another implication is that angular acceleration is inversely proportional to mass.
Does angular velocity depend on mass?
Thus, the angular momentum depends on the mass, velocity, and radius.
What increases angular acceleration?
In two dimensions, angular acceleration is a pseudoscalar whose sign is taken to be positive if the angular speed increases counterclockwise or decreases clockwise, and is taken to be negative if the angular speed increases clockwise or decreases counterclockwise....Angular acceleration.Radians per second squaredSymbolrad/s22 more rows
How is mass related to angular velocity?
While linear momentum is P = MV, where M is mass and V is velocity, angular momentum L = Iw, where I is rotational inertia and w (we use w instead of small Omega, the conventional symbol) is angular velocity. Angular velocity is just the angle the mass rotates in an interval of time. w has the units of radians/second.
What factors affect angular velocity?
In particular, three factors are considered: (1) the extent to which perceived angular velocity is determined by edge transitions of surface elements, (2) the extent to which angular velocity estimates are influenced by instantaneous linear velocities of surface elements, and (3) whether element-velocity effects are ...
How does mass affect rotational speed?
Indeed, the rotational inertia of an object depends on its mass. It also depends on the distribution of that mass relative to the axis of rotation. When a mass moves further from the axis of rotation it becomes increasingly more difficult to change the rotational velocity of the system.
How do mass length or gravity affects the relationship between angular acceleration?
Question: How do mass, length, or gravity affect the relationship between angular acceleration and angle? Answer: From equation (1) we see that: Mass doesn't affect the motion at all. The amplitude of the sine relationship is proportional to gravity.
Does angular acceleration change?
People sometimes forget that angular acceleration does not change with radius, but tangential acceleration does.
Does mass affect torque?
The amount of torque required to produce an angular acceleration depends on the distribution of the mass of the object.
How do you find angular acceleration?
Angular acceleration (α) can be defined as angular velocity (ω) divided by acceleration time (t). Alternatively, pi (π) multiplied by drive speed (n) divided by acceleration time (t) multiplied by 30. This equation yields the standard angular acceleration SI unit of radians per second squared (Rad/sec^2).
How does doubling the mass affect angular velocity?
When mass is doubled, angular momentum doubles, so precession frequency decreases. B) If you increase radius, you increase angular momentum, and thus decrease the precession frequency.
What is angular acceleration in physics?
The angular acceleration is the time rate of change of the angular velocity and is usually designated by α and expressed in radians per second per second.
How does doubling the mass affect angular velocity?
When mass is doubled, angular momentum doubles, so precession frequency decreases. B) If you increase radius, you increase angular momentum, and thus decrease the precession frequency.
Does mass affect angular frequency?
where m is mass, k is the constant of Hook's Law, and ω is angular frequency. The equation clearly indicates that angular frequency is inversely proportional to the mass. So increasing the mass would decrease angular frequency and decreasing the mass would increase angular frequency.
How does mass affect oscillation?
Increasing the mass increases the period of oscillation. For example, a heavy car with springs in its suspension bounces more slowly when it hits a bump than a light car with identical springs.
How does mass affect linear momentum?
Linear momentum is defined as the product of a system's mass multiplied by its velocity. Momentum is directly proportional to the object's mass and also its velocity. Thus the greater an object's mass or the greater its velocity, the greater its momentum.
Angular Acceleration Formula - BYJUS
What is Angular Acceleration? Angular Acceleration Formula - basic equation determining the function of angular position. Explore more with solved examples.
Angular Acceleration Calculator - Symbolab
Free Angular Acceleration Calculator - calculate angular acceleration step by step
Angular Acceleration Formula | Equation & Solved Examples
Average Angular Acceleration. The blade of a fan is at rest; it starts rotating after 10 seconds at a speed of 5 radians per second. We can calculate angular acceleration from the slope of any line on this graph, which is y/x.
Angular Acceleration Formula – Definition, Types and Solved Questions
The angular acceleration in three dimensions may not be associated with a change in angular speed. If the particle's position vector twists in space, then even if the angular speed is constant, there will still be a nonzero angular acceleration because there is a continuous change in the direction of the angular velocity vector with time.
What is angular acceleration?
In physics, angular acceleration refers to the time rate of change of angular velocity. As there are two types of angular velocity, namely spin angular velocity and orbital angular velocity, there are naturally also two types of angular acceleration, called spin angular acceleration and orbital angular acceleration respectively.
Is torque a rotational analogue of force?
Torque is the rotational analogue of force: it induc es change in the rotational state of a system , just as force induces change in the translational state of a system. As force on a particle is connected to acceleration by the equation. F = m a {displaystyle mathbf {F} =mmathbf {a} }.
Does angular acceleration occur in non-rigid bodies?
For rigid bodies, angular acceleration must be caused by a net external torque. However, this is not so for non-rigid bodies: For example, a figure skater can speed up her rotation (thereby obtaining an angular acceleration) simply by contracting her arms and legs inwards, which involves no external torque.
Why does the angular acceleration is zero in a uniform circular orbit?
Angular acceleration refers to a change in the Angular velocity; either the magnitude has to be changed or the speed.
Can the angular acceleration be negative?
The negative angular acceleration depends on the coordinate axis in which the angular velocity is acting.
Does the radius affect the angular acceleration?
Suppose angular acceleration is maximum, the radius of the rotational path matters.
Why does the pulley have a mass?
Because the pulley has a mass, the tension forces on each side of the rope are different (if the pulley were massless then the tensions on each side would be the same, to my knowledge). The torque determines the angular acceleration:
Does angular acceleration increase with weight?
It seems angular acceleration increases as the mass of block 1 increases. This makes sense because if the weight of block 1 is greater, the pulley will rotate faster. However, the denominator also increases as m 1 increases and decreases as m 2 increases, which seems counterintuitive to me.
What is angular acceleration?
In physics, angular acceleration refers to the time rate of change of angular velocity. As there are two types of angular velocity, namely spin angular velocity and orbital angular velocity, there are naturally also two types of angular acceleration, called spin angular acceleration and orbital angular acceleration respectively.
Is torque a rotational analogue of force?
Torque is the rotational analogue of force: it induc es change in the rotational state of a system , just as force induces change in the translational state of a system. As force on a particle is connected to acceleration by the equation. F = m a {displaystyle mathbf {F} =mmathbf {a} }.
Does angular acceleration occur in non-rigid bodies?
For rigid bodies, angular acceleration must be caused by a net external torque. However, this is not so for non-rigid bodies: For example, a figure skater can speed up her rotation (thereby obtaining an angular acceleration) simply by contracting her arms and legs inwards, which involves no external torque.