Infusion rate (Ro): The steady state drug concentration is proportional to the infusion rate. Thus, a higher infusion rate will result in a higher steady state plasma drug concentration. Clearance: Higher clearance of the drug will result in lower plasma drug concentration at plateau.
What happens when you change the rate of an infusion?
Does changing infusion rate change clearance? As the infusion continues, C increases, initially quickly, but then more slowly, as the rate of excretion is initially slow but increases with increasing plasma concentration. Thus the concentration at equilibrium is determined by the ratio of the infusion rate to the clearance of the drug (C = f/Cl mg ml−1).
How is the drug infusion rate adapted to patient clearance?
The serum lipid clearance rate may reach its maximum limit at an infusion exceeding 250 mL/hour. Symptoms such as nausea and vomiting associated with hypertriglyceridemia can be reduced if the infusion rate is less than 250 mL/hour. Reducing the infusion rate to 50% (125 mL/hour) in the FineS study resulted in resolution of nausea and vomiting.
What is the relationship between infusion rate and drug concentration?
The intravenous administration of dolasetron 100 mg over 0.5-2 minutes did not significantly alter the pharmacokinetic profiles of either dolasetron or hydrodolasetron. In addition, the safety profile of dolasetron did not change with increasing rate of infusion. Therefore, the rate of infusion of d …
What is a constant rate infusion regimen?
Because the intensity of surgical stimulation changes rapidly, titration by manually changing a constant infusion rate is suboptimal. Changes in the rate of a constant infusion do not result in sufficiently rapid changes in concentration to keep up with rapid changes in stimulus intensity. Changing infusion rates instead yields an appreciable and often undesirable lag between the …
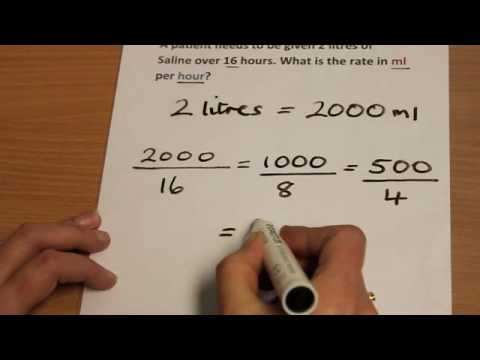
What affects clearance rate?
Clearance does not represent an actual volume; rather, it is a virtual volume of plasma that is completely cleared of the substance per unit of time. The value for clearance is related to the efficiency of elimination: the greater the rate of elimination, the higher the clearance.
What factors affect drug clearance?
Clearance can be affected by body weight, body surface area, cardiac output, hepatic function, renal function, plasma protein binding, concomitant medications, and variation in expression of drug metabolizing enzymes.
Is clearance same as rate of elimination?
In addition, for first-order elimination processes, clearance is a constant, whereas the rate of drug elimination is not constant. For example, clearance considers that a certain portion or fraction (percent) of the distribution volume is cleared of drug over a given time period.
Is clearance dependent on half-life?
3.2. Half-life is dependent on both clearance and volume of distribution, such that a decrease in clearance, as might be seen with a CYP1A2 or CYP2C19 substrate, or an increase in volume of distribution will prolong the half-life and lead to a longer dosage interval.
Is drug clearance affected by rate of absorption?
It does not require consideration of absorption or first-pass metabolism to determine adequate dosage. Drug clearance can be thought of as the metabolic and excretory factors on the rate and extent an active drug leaves the systemic circulation.Sep 3, 2021
What is meant by drug clearance How is it measured discuss the factors affecting drug clearance?
Clearance is equal to the rate at which a drug is removed from plasma(mg/min) divided by the concentration of that drug in the plasma (mg/mL). The total ability of the body to clear a drug from the plasma is renal clearance plus hepatic clearance plus clearance from all other tissues.Aug 29, 2021
What is the difference between clearance and excretion?
Usually, clearance is measured in L/h or mL/min. The quantity reflects the rate of drug elimination divided by plasma concentration. Excretion, on the other hand, is a measurement of the amount of a substance removed from the body per unit time (e.g., mg/min, μg/min, etc.).
How is clearance rate calculated?
A clearance rate is calculated by dividing the number of crimes cleared by the number of crimes reported; the result is multiplied by 100. For example, in 2010 there were 1,154 homicides cleared and 1,809 homicides reported. This equals a homicide clearance rate of 63.8 percent.
Does clearance affect volume of distribution?
Volume of distribution per se has no effect on clearance or on average steady-state blood levels.
What is the term for the time the body takes to clear one half of a drug from the body?
Introduction. The duration of action of a drug is known as its half life. This is the period of time required for the concentration or amount of drug in the body to be reduced by one-half. We usually consider the half life of a drug in relation to the amount of the drug in plasma.Dec 18, 2015
How many half-lives does it take to clear a drug?
4 to 5 half-livesEven further, 94 to 97% of a drug will have been eliminated after 4 to 5 half-lives. Thus, it follows that after 4 to 5 half-lives, the plasma concentrations of a given drug will be below a clinically relevant concentration and thus will be considered eliminated.Aug 23, 2021
What does 5 half-lives mean?
The half-life can also be a guide for how long a drug will take to reach a stable level in your body when you first start taking it. Generally, it will take about five times the drug's half-life to build a stable level in your body.
How much infusion rate for IDPN?
Care should be taken to keep the IDPN infusion rate to less than a maximum infusion rate of 250 mL/hour. The serum lipid clearance rate may reach its maximum limit at an infusion exceeding 250 mL/hour. Symptoms such as nausea and vomiting associated with hypertriglyceridemia can be reduced if the infusion rate is less than 250 mL/hour. Reducing the infusion rate to 50% (125 mL/hour) in the FineS study resulted in resolution of nausea and vomiting. After a 2-week period, the infusion rate was increased to 250 mL/hour with no recurrence of symptoms.
What is the initial infusion rate for sodium nitroprusside?
The initial infusion rate for sodium nitroprusside is 0.5 to 1.0 µg/kg per minute.51 4,515 The rate can be increased as needed to achieve the desired MAP. 516,517 A satisfactory reduction in systemic perfusion pressure can usually be obtained well below the recommended maximum rate of 10 µg/kg per minute.
What is cyanide toxic?
Cyanide toxicity is characterized by an unexplained metabolic acidosis, increased blood lactate, and an increased mixed venous oxygen content. 517,518 The nitroprusside radical interacts with the sulfhydryl groups of erythrocytes, releasing cyanide. If the amount of cyanide released overwhelms the capacity of the rhodanese system, cyanide toxicity (i.e., binding to the cytochrome electron transport system) results. This produces a change to anaerobic metabolism, metabolic acidosis, an increase in mixed venous oxygen content, and eventually death 517,519–523; several pediatric anesthetic-related deaths have resulted from cyanide toxicity and its treatment. 520–522
What is TCI in an IV?
Anything that can go wrong during IV anesthesia applies also to TCI. A TCI system is an IV infusion pump, as would be used with conventional IV anesthesia, with additional software to track drug delivery using a pharmacokinetic model. The user interface is modified to enter a desired drug concentration rather than a desired infusion rate.
What is TCI in anesthesia?
TCI was commercially launched at the 1996 World Congress of Anaesthesiologists in Sydney, Australia. Anesthesiologists had to learn a new dosing paradigm. In anesthesia, perhaps more than in other medical specialties, drug is titrated to effect. Fortunately, TCI administration of IV anesthetics leverages the training that anesthesiologists have in titration of volatile anesthetics. Most anesthesiologists have no idea of the actual dose of volatile anesthetic delivered to a patient. Instead, they set a concentration (partial pressure) on a vaporizer. This is the steady-state partial pressure to which the patient’s lungs, blood, and brain eventually equilibrate. For anesthesiologists, concentration-based dosing is intuitive. 23 This likely explains the finding that educated anesthesiologists would prefer to use TCI to conventional infusions if the devices were available. 24