
What is the difference between Aci and VXLAN?
C 412 0050.5688.cbec dynamic 0 F F nve1 (4.0.0.1) Nowlet's move to VXLAN's prettier, more sophisticated sister, ACI. Application Centric Infrastructure, or ACI, is a spine-leaf topology running VXLAN over an IS-IS underlay.
What is the TEP algorithm for VXLAN mode traffic in ACI?
For Cisco Application Centric Infrastructure (ACI) Virtual Edge, VXLAN mode traffic always uses the source IP address as the TEP IP address. To ensure proper load balancing, we recommend the algorithm Source and Destination TCP/UDP Port.
What is the transport infrastructure for VXLAN traffic?
The transport infrastructure for VXLAN traffic is known as Overlay-1, which exists as part of tenant Infra. The Overlay-1 VRF in ACI contains /32 routes to each VTEP, vPC virtual IP address, APIC as well as spine proxy IP address.
What is the difference between Cisco ACI and VTEP?
In Cisco ACI, the endpoint’s IP address is the identifier, and a VTEP address designates the location (leaf) where end points are connected.Cisco ACI uses a dedicated VRF and interfaces of the uplinks as the infrastructure to carry VXLAN traffic.
Does Cisco ACI use EVPN?
EVPN is a standards-based way to implement a fabric that is functionally similar to ACI. EVPN works on the Cisco Nexus 9300/9500 in NX/OS mode, but it has also been adopted on other Cisco platforms, as well as on switches from Arista, Juniper and others.
What are the three main components of Cisco ACI?
The three core components of Cisco ACI architecture:APIC: APIC is considered the brain of the ACI architecture. ... ANP: ... Cisco ACI Fabric: Cisco Nexus Portfolio.
What is Cisco VXLAN?
VXLAN is a solution to support a flexible, large-scale multitenant environment over a shared common physical infrastructure. The transport protocol over the physical data center network is IP plus UDP.
How does Cisco ACI work?
Cisco Application Centric Infrastructure (ACI) is a software-defined networking (SDN) solution designed for data centers. Cisco ACI allows network infrastructure to be defined based upon network policies – simplifying, optimizing, and accelerating the application deployment lifecycle.
What is the difference between Cisco ACI and Cisco DNA?
In effect, Cisco ACI allows your environment to deploy new networks virtually, adjust application policies on the network, and gain greater network visibility. The Cisco DNA Center takes these ideas a step further and builds upon the achievements of Cisco ACI.
What are ACI components?
There are only three types of components in ACI, the Application Policy Infrastructure Controller (APIC), the spine switches, and the leaf switches.
Where is VXLAN used?
VXLAN is an encapsulation protocol that provides data center connectivity using tunneling to stretch Layer 2 connections over an underlying Layer 3 network. In data centers, VXLAN is the most commonly used protocol to create overlay networks that sit on top of the physical network, enabling the use of virtual networks.
Why would you use VXLAN?
VXLAN is a powerful tool for extending layer 2 subnets across layer 3 network boundaries. It solves VM portability/vMotion limitations by encapsulating traffic and extending it across L3 gateways, allowing VMs to be hosted by servers residing on foreign IP subnets.
Is VXLAN the same as VLAN?
VxLAN is very similar to VLAN, which also encapsulates layer 2 frames and segments networks. The main difference is that VLAN uses the tag on the layer 2 frame for encapsulation and can scale up to 4000 VLANs.
Why do we use Cisco ACI?
ACI will allow the network team to have visibility into both physical and virtual workloads on the network (with VMM integration, fabric can see VM attributes). You can also integrate Containers for microservices management. It improves the ease and speed of deployment.
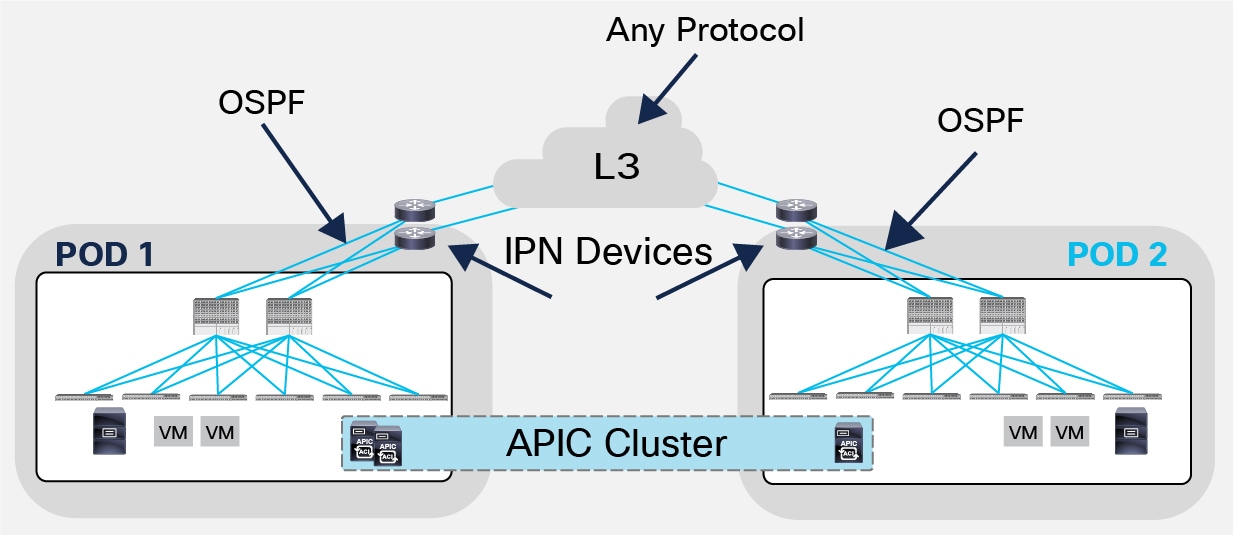
What is a Cisco ACI pod?
About Cisco ACI Multi-Pod A 'Pod' is a set of interconnected ACI leaf and spine switches that are under the control of a specific APIC cluster. ACI fabric could have multiple Pods and all these Pods are part of the same fabric and are under the control of the same APIC cluster.
What is EPG in Cisco ACI?
Cisco Application Centric Infrastructure (ACI) - Endpoint Groups (EPG) Usage and Design - Cisco.
What is domain in Cisco ACI?
A domain is configured to be associated with a VLAN pool. EPGs are then configured to use the VLANs associated with a domain. EPG port and VLAN configurations must match those specified in the domain infrastructure configuration with which the EPG associates. If not, the APIC will raise a fault.
What is Cisco ACI application profile?
Application profiles (APs) are containers for the grouping of endpoint groups (EPGs). We can have more than one EPG with an AP. For example, an AP could group a web server with the backend database, with storage, and so on. EPGs are assigned to different bridge domains.
What is Cisco ACI bridge domain?
PASS:cisco. A Bridge Domain (BD) is a Layer 2 representation inside the ACI fabric. The BD is where users will define their Anycast Gateway/subnet which would provide the default gateway for their host attached to the fabric.
What is tenant in Cisco ACI?
Cisco ACI Tenant. Overall, a tenant is a logical container for application policies and it includes one or more virtual routing and forwarding (VRF) instances or contexts which can be associated with multiple bridge domains. This concept is very similar to the Private VLAN which is being used in traditional networking.
What is the easy button in VXLAN?
The easy button is VXLAN. How does VXLAN make things easy? Because when you look at what’s going on in an ACI network, you are essentially looking at a VXLAN network with a centralized policy-based management system. There are a few minor differences in the protocols being run across the network, but it is still a VXLAN network at its core.
How to configure VXLAN?
As shown in the VXLAN frame image, these are complex frames with layers of encapsulation and in a legacy NXOS or IOS setup, this requires a complex setup process. A high-level overview of setting up VXLAN looks like this: 1 Configure layer 3 links between the switches in your VXLAN environment. 2 Configure a link-state routing protocol (OSPF or IS-IS) between your switches. 3 Configure BGP between the switches and set up BGP route reflectors on non-VTEP devices. 4 Configuring multicasting across your VXLAN network 5 Enabling VXLAN on the switches 6 Mapping VLANs to VXLAN VNIDs 7 Creating NVE interfaces for the VNIs 8 Configure BGP EVPN 9 Connect devices to the network and set them into the correct VLANs/VNIDs
What does VXLAN mean?
A brief overview of VXLAN is that it stands for V irtual e X tensible LAN (Local Area Network) and it takes the logical separation of a layer 2 bridge domain that you would get from VLANs and pushes it further.
Does ACI work for VXLAN?
In truth, they are the easy buttons for each other. ACI does the work for you in setting up VXLAN, and by understanding how VXLAN works, the ACI learning curve is greatly reduced and when you look at the configuration elements in the ACI GUI, you see VXLAN elements.
Can BGP be used on non-VTEP devices?
Configure BGP between the switches and set up BGP route reflectors on non-VTEP devices.
Who developed VXLAN?
The standards for VXLAN were developed by VMware, Cisco, and Arista to be able to extend a layer 2 bridge domain across a layer 3 routing domain and to provide more logical segmentation versatility.
What is the difference between ACI and VXLAN?
The big difference between ACI and stand-alone VXLAN is that ACI is a centrally managed, completely programmable software defined network... OK, one of the big differences. ACI can be pretty intimidating at first, because it approaches network engineering from a completely novel way, but take a deep breath, and just remember that ACI is just a different way of achieving the same results.[iv]
How to verify vPC?
The quick-n-dirty way to verify a vPC pair is to go to the Fabric Quick Start page <Fabric><Quick Start>. From there, click the link for " Configure Interface, PC, and vPC". That wizard brings up its own window, and in that window is an inventory of the vPC pairs in the fabric. Like so...
What are the routes shared among the VTEPs in VRF green?
Here are the routes that are shared among the VTEPs in VRF GREEN. This output is Leaf3's BGP table for GREEN. You can see Type 2 routes for two endpoints (MAC 8847 and ea66). Each endpoint route points to the vPC's vIP as the next-hop. There are also two Type 5 routes for the two subnets. The Type 5 routes actually point to each VTEP that has been configured with the VNI associated with the subnet, including the vIP of the vPC.
What is a type 5 route?
The Type 5 routes actually point to each VTEP that has been configured with the VNI associated with the subnet, including the vIP of the vPC. Once a route has been shared among the VTEP peers and made its way into each VTEP's BGP table, the route goes into the remote VTEP's L2RIB, and from there the MAC table.
How to verify VPC member ports?
You can also verify vPC member ports by navigating to <Fabric><Access Policies><Leaf Policy Groups>. By clicking on the <Leaf Policy Groups> folder in the Navigation Pane, and then the sub-tab <PC/VPC> on the upper right of the Work Pane, you can call up an inventory of all port-channels and vPC member ports. vPC member ports are auto-named with the suffix "-VPC" and if that isn't enough of a hint, they are Link Aggregation Type VPC.
How many member ports are there in NX-OS?
As in NX-OS mode, the output of show vpc tells us that there are two member ports--Po1 and Po3. show port-channel summaryworks to verify what the GUI told us already, that e1/5-6 were in one port-channel, and e1/7-8 in another.
Do NVE switches share the same IP address?
You can see here that the individual nve interfaces have their own IP, and both switches share the same secondary IP. It will be the secondary IP address that will be used as the vPC pair's vIP. What router MAC do they use? Take a look at show nve peer.
How much more expensive is ACI than Nexus?
In terms of cost, ACI is just 5-10% more than the equivalent Nexus 9K EVPN fabric, and only 20-30% more than the equivalent VPC/STP design. That's a wash, easily justified by ACI's single point-of-management alone! Plenty of ACI customers buy it expecting nothing more than a really good L2/L3 fabric.
Is NSX a VXLAN?
VXLAN (NSX) over eVXLAN (ACI) seems to be a uneccessary complication but on the other hand both can play a different roles. ACI can provide a secured/automated fabric and NSX end-to-end network services available in multiple locations including a public cloud. So there are examples where EVPN or TRILL is a transport and on top of that NSX is running. It is similar to CsC services with MPLS-TE FRR or Segment Routing in the core. Of course VXLANoVXLAN imposes a bigger overhead but this is just a number of bytes. From the ASIC perspective incoming VXLAN is an IP/UDP packet so no performance impact apart from processing and serialization of additional 50 bytes per packet.
Is VXLAN a data plane?
VXLAN is just a data-plane protocol (like IP or Ether net). The problem is the control plane - how do you figure out where everyone is (think OSPF or BGP). I think the intersection of NSX and ACI control plane protocols is still zero.
Does HiGig2 leave ACI?
Just like HiGig2 or other internal switching encaps, it doesn't leave the ACI fabric. Whether it's VXLAN or VLAN (or untagged), the packets get decapsulated and re-encapulsated into that iVXLAN header as it bounces around inside ACI. That header is removed by the time it leaves the ACI fabric. Each bridge domain is its own iVXLAN segment. Cisco refers to this as normalization, so that different encaps can be used on the same network.
Does ACI use VXLAN?
ACI uses VXLAN but not in a way that would be (AFAIK) interoperable with any non -Cisco product. While they do use some proprietary tagging bits, the real challenge is the control plane.
Does NSX support EVPN?
The problem is still that NSX does not support EVPN - EVPN support would make this easy
Does NSX double per VM?
In contrast to ACI's chump change, NSX doubles your per-VM cost (based on several real-world scenarios I've done with and without ELA's). As a result, many NSX customers are limiting their deployments to narrow high-security areas, such as PCI, HIPAA, or IP.
More Shenanigans: vPC, VXLAN and ACI...Just for Fun!
In my last installment of "...Just for Fun!" we began our exploration into virtual port channels. First, we looked at a vPC pair in complete isolation, and then some failure scenarios. Let's continue our exciting adventure by exploring vPCs in a VXLAN environment and then round out the day with a peek into vPCs in ACI.
Vexing VXLAN... or maybe not
VXLAN offers both Layer 2 and Layer 3 forwarding. But the other really cool thing that VXLAN offers above and beyond a fabric like FabricPath is a distributed anycast gateway. That is, every leaf in a VXLAN leaf/spine topology can offer a default gateway to its attached hosts, and each leaf uses the same IP and MAC address.
Tricking the ACI..
Now let's move to VXLAN's prettier, more sophisticated sister, ACI. Application Centric Infrastructure, ACI, is a spine-leaf topology running VXLAN over an IS-IS underlay. The big difference between ACI and stand-alone VXLAN is that ACI is a centrally managed, completely programmable software defined network...OK, one of the big differences.
