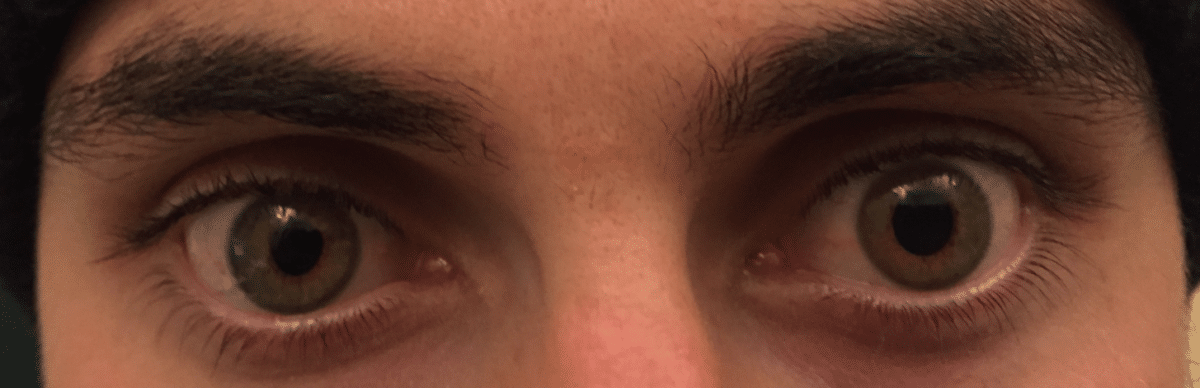
Common tests & procedures

Which nerve is damaged in Horner's syndrome?
In most cases, the physical findings associated with Horner syndrome develop due to an interruption of the sympathetic nerve supply to the eye due to a lesion or growth. The lesion develops somewhere along the path from the eye to the region of the brain that controls the sympathetic nervous system (hypothalamus).
Can horners cause double vision?
While vision and health normally aren't harmed by Horner's syndrome, the nerve damage that triggers this disorder may be a sign of other health problems. Symptoms that may accompany Horner's disease, but are not directly caused by it, include: Vertigo, coupled with nausea and vomiting. Double vision.
Can an eye exam detect Horner's syndrome?
Tests to confirm Horner syndrome An eye specialist (ophthalmologist) may also confirm a diagnosis by putting a medicated eye drop in both eyes — either a drop that will dilate the pupil of a healthy eye or a drop that will constrict the pupil in a healthy eye.
How long does Horner's syndrome last?
If the lesion is not due to any pathological cause, a slow recovery lasting up to several weeks to 4 months can be expected.
What is the most common cause of Horner's syndrome?
The most common causes of Horner syndrome in children include: Injury to the neck or shoulders during delivery. Defect of the aorta present at birth. Tumor of the hormonal and nervous systems (neuroblastoma)
Is Horner's syndrome a disability?
In July 2004 the RO granted a 10 percent disability rating for Horner's syndrome, effective August 20, 2002. The veteran's Horner's syndrome is characterized by anhydrosis, slight ptosis, and right eye irritation; symptoms that are reflective of no more than moderate, incomplete paralysis.
Can surgery fix Horner's syndrome?
Treatment depends on the underlying cause of the condition. There is no treatment for Horner syndrome itself. Ptosis is very mild and in rare cases affects vision in Horner syndrome. This can be corrected by cosmetic surgery or treated with eyedrops.
Is Horner's syndrome serious?
It can affect people of all races and ethnic groups. The symptoms associated with Horner's syndrome, in and of themselves, generally do not cause significant problems with a person's health or vision. However, they can indicate the presence of an underlying health problem that may be very serious.
How do they diagnose Horner's syndrome?
Clinical diagnosis Horner's syndrome is diagnosed clinically by observing ptosis (of upper and lower lids), miosis of the ptotic eye and demonstration of dilation lag in the affected eye, and anhidrosis on the same side as the ptosis and/or mitosis.
What cranial nerve causes Horner's?
Horner syndrome (Horner's syndrome or oculosympathetic paresis) results from an interruption of the sympathetic nerve supply to the eye and is characterized by the classic triad of miosis (ie, constricted pupil), partial ptosis, and loss of hemifacial sweating (ie, anhidrosis), as well as enophthalmos (sinking of the ...
Can Horner's syndrome cause headaches?
The trigeminal autonomic cephalalgias are a group of primary headache syndromes marked by severe head pain and associated cranial autonomic symptoms which can include a full or partial Horner's syndrome. Rarely, the eye-related symptoms will become fixed even between headache attacks.
Can surgery fix Horner's syndrome?
Treatment depends on the underlying cause of the condition. There is no treatment for Horner syndrome itself. Ptosis is very mild and in rare cases affects vision in Horner syndrome. This can be corrected by cosmetic surgery or treated with eyedrops.
Can MS cause Horner's syndrome?
In cases of Horner's syndrome, consider the age of the patient. In younger patients, demyelinating disease, including MS, can be a potential cause of Horner's syndrome. In older patients, stroke, zoster and GCA are etiologies that practitioners should consider.
What percentage of Horners syndrome are idiopathic?
The most common etiologies were idiopathic (20 patients, 25.6%), followed by internal carotid artery (ICA) dissection (15 patients, 19.2%), stroke (12 patients, 15.4%), surgical (12 patients, 15.4%), and neoplastic (11.5%).
What is Horner's syndrome and what causes it?
It is caused by damage to the sympathetic nerves of the face. The underlying causes of Horner's syndrome vary greatly and may include a tumor, stroke, injury, or underlying disease affecting the areas surrounding the sympathetic nerves.