Does myasthenia gravis ever go away?
With treatment, most individuals with myasthenia can significantly improve their muscle weakness and lead normal or nearly normal lives. Some cases of myasthenia gravis may go into remission—either temporarily or permanently— and muscle weakness may disappear completely so that medications can be discontinued.
Will my myasthenia gravis ever go away?
myasthenia gravis can significantly improve their muscle weakness and lead normal or nearly normal lives. Some cases of myasthenia gravis may go into . remission—either temporarily or permanently— and muscle weakness may disappear completely so that medications can be discontinued. Stable, long-lasting complete remissions are the goal of
Does myasthenia gravis Make you Sleepy?
Sleep Problems. return to top. MG patients often have sleep problems, either with the quantity or quality of sleep. You might experience insomnia, or symptoms of sleep apnea such as loud snoring, daytime sleepiness, and repeated stops in breathing as you sleep.
Why are beta blockers contraindicated in myasthenia gravis?
Commonly-used medications like ciprofloxacin or certain other antibiotics, beta-blockers like propranolol, calcium channel blockers, Botox, muscle relaxants, lithium, magnesium, verapamil and more, can worsen the symptoms of myasthenia gravis. Some medications should be avoided altogether (unless there is no alternative).

Does myasthenia gravis affect sensory?
Sensory systems from receptors to brain are found to be affected in myasthenia gravis. Altered cholinergic neural transmission in myasthenia gravis downregulate motor, sensory and autonomic functions.
Which nerves are affected in myasthenia gravis?
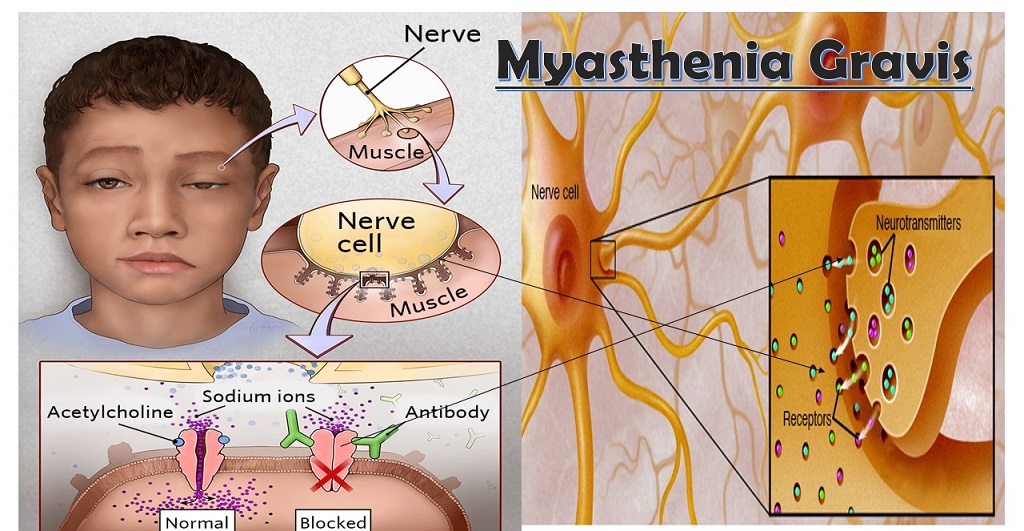
In myasthenia gravis, your immune system produces antibodies that block or destroy many of your muscles' receptor sites for a neurotransmitter called acetylcholine (as-uh-teel-KOH-leen). With fewer receptor sites available, your muscles receive fewer nerve signals, resulting in weakness.
Does myasthenia gravis cause numbness and tingling?
Numbness, heaviness, muscular spasm, or loss of control of the limb can be experienced by the myasthenic. Limb weakness is often not symmetrical, with one side being weaker than the other.
Does myasthenia gravis affect the nervous system?
Myasthenia gravis is caused by an error in the transmission of nerve impulses to muscles. It occurs when normal communication between the nerve and muscle is interrupted at the neuromuscular junction—the place where nerve cells connect with the muscles they control.
What body part is most commonly affected by myasthenia gravis?
Myasthenia gravis is a rare long-term condition that causes muscle weakness. It most commonly affects the muscles that control the eyes and eyelids, facial expressions, chewing, swallowing and speaking.
What is the most serious complication of myasthenia gravis?
The most serious complications of myasthenia gravis is a myasthenia crisis. This is a condition of extreme muscle weakness, particularly of the diaphragm and chest muscles that support breathing. Breathing may become shallow or ineffective.
What causes myasthenia gravis to get worse?
Infections and respiratory illnesses can produce increased weakness that lasts for a while after the illness is gone. The stress of surgery can make MG temporarily worse. The disease may intensify during certain times of a woman's menstrual cycle.
What are the stages of myasthenia gravis?
Myasthenia gravis (MG), a neuromuscular disease characterized by weakness and fatigue, is typically divided into five types: generalized, congenital, ocular, juvenile, and transient neonatal myasthenia gravis, depending on time of disease onset, the cause of the neuromuscular dysfunction, and the muscle groups affected ...
Why is myasthenia gravis worse at night?
In patients with myasthenia gravis, the body's immune system mistakenly interferes with the muscles' receptors for acetylcholine. When these receptors cannot work properly, the affected muscles tire easily. The amount of weakness typically fluctuates and may be worse at the end of the day.
Does myasthenia gravis show up on brain MRI?
Problems with the gland are closely associated with myasthenia gravis. Sometimes an MRI brain scan may also be carried out to check that your symptoms are not being caused by a problem in your brain.
What does myasthenia gravis do to the brain?
Myasthenia Gravis Brain Science MG interferes with the brain's ability to communicate effectively with muscles, but the interference happens at the junction between nerve endings and muscle cells, not in the brain itself. MG patients do often suffer from brain-related problems such as depression and sleep disorders.
Is myasthenia gravis a neurological disorder?
General Discussion. Myasthenia gravis is a neuromuscular disorder primarily characterized by muscle weakness and muscle fatigue. Although the disorder usually becomes apparent during adulthood, symptom onset may occur at any age.
Which cranial nerve is responsible for ptosis?
Oculomotor Nerve (Cranial Nerve III) Ptosis (a droopy eyelid) and diplopia are the hallmark symptoms of third nerve palsies. Disruption may occur at any location along the path of the nerve and subsequent paresis may occur in any muscle or combination of muscles innervated by the oculomotor nerve.
How does myasthenia gravis affect the somatic nervous system?
MG is an autoimmune disorder that causes weakness and fatigue of skeletal muscles due to an antibody-mediated attack directed against AChRs at neuromuscular junctions (1).
Where does myasthenia gravis start?
In myasthenia gravis, muscle weakness often first appears in the muscles of the face, neck and jaw. The arm and leg muscles are affected later.
What is the difference between Lambert Eaton syndrome and myasthenia gravis?
The difference between LEMS and myasthenia gravis (MG) This is very similar to myasthenia gravis, however the target of the attack is different in MG as the acetylcholine receptor on the nerve is affected, whereas in LEMS it's the voltage-gated calcium channel on the nerve.
How to diagnose myasthenia gravis?
A common way to diagnose myasthenia gravis is to test how you respond to certain medicines. Muscle weakness often dramatically improves for a brief time when you are given an anticholinesterase medicine. If you respond to the medicine, it confirms myasthenia gravis.
What are the complications of myasthenia gravis?
The most serious complications of myasthenia gravis is a myasthenia crisis. This is a condition of extreme muscle weakness, particularly of the diaphragm and chest muscles that support breathing. Breathing may become shallow or ineffective. The airway may become blocked because of weakened throat muscles and build up of secretions. Myasthenia crisis may be caused by a lack of medicine or by other factors, such as a respiratory infection, emotional stress, surgery, or some other type of stress. In severe crisis, a person may have to be placed on a ventilator to help with breathing until muscle strength returns with treatment.
How is myasthenia gravis diagnosed?
Your doctor can diagnose myasthenia gravis based on your symptoms and certain tests. During the physical exam, your doctor will ask about your medical history and symptoms.
How long does it take for myasthenia gravis to resolve?
Generally, it resolves in 2 to 3 months.
Why does myasthenia cause breathing problems?
Myasthenia crisis may be caused by a lack of medicine or by other factors, such as a respiratory infection, emotional stress, surgery, or some other type of stress.
What is MG in medical terms?
Myasthenia gravis (MG) is a chronic autoimmune disorder in which antibodies destroy the communication between nerves and muscle, resulting in weakness of the skeletal muscles. Myasthenia gravis affects the voluntary muscles of the body, especially those that control the eyes, mouth, throat and limbs. The disease can strike anyone ...
What tests are done to check for myasthenia gravis?
Blood tests. These tests look for antibodies that may be present in people with myasthenia gravis. Genetic tests. These tests are done to check for conditions that run in families. Nerve conduction studies. A test called repetitive nerve stimulation is used to diagnose myasthenia gravis.
What are the symptoms of myasthenia gravis?
In more than half of people who develop myasthenia gravis, their first signs and symptoms involve eye problems, such as: Drooping of one or both eyelids (ptosis) Double vision (diplopia), which may be horizontal or vertical, and improves or resolves when one eye is closed.
How do you know if you have myasthenia gravis?
In about 15% of people with myasthenia gravis, the first symptoms involve face and throat muscles, which can: Impair speaking. Your speech might sound soft or nasal, depending on which muscles have been affected. Cause difficulty swallowing. You might choke easily, making it difficult to eat, drink or take pills.
What is the protein that causes myasthenia gravis?
This protein is involved in forming the nerve-muscle junction. Antibodies against this protein can lead to myasthenia gravis. Antibodies against another protein, called lipoprotein-related protein 4 (LRP4), can play a part in the development of this condition.
How long does it take for a child to recover from myasthenia gravis?
If treated promptly, children generally recover within two months after birth. Some children are born with a rare, hereditary form of myasthenia gravis, called congenital myasthenic syndrome.
Can myasthenia gravis be caused by antibodies?
Other antibodies have been reported in research studies and the number of antibodies involved will likely expand over time. Some people have myasthenia gravis that isn't caused by antibodies blocking acetylcholine, MuSK or LRP4.
Can myasthenia gravis cause muscle weakness?
Muscle weakness caused by myasthenia gravis worsens as the affected muscle is used. Because symptoms usually improve with rest, muscle weakness can come and go. However, the symptoms tend to progress over time, usually reaching their worst within a few years after the onset of the disease.
Can myasthenia gravis be treated?
It's caused by a breakdown in the normal communication between nerves and muscles. There's no cure for myasthenia gravis, but treatment can help relieve signs and symptoms, such as weakness of arm or leg muscles, double vision, drooping eyelids, and difficulties with speech, chewing, swallowing and breathing.
What causes weakness in myasthenics?
There are many factors that can trigger episodes of weakness in myasthenics, including other illnesses (e.g. viral respiratory infections), drugs that affect the neuromuscular junction, hot weather, pregnancy, and emotional upset. The undiagnosed myasthenic might not connect the various symptoms to one condition.
What is the weakness of the myasthenic limb?
Limb weakness is often not symmetrical, with one side being weaker than the other. Shoulder weakness is demonstrated by trouble holding up an arm to comb or shampoo one’s hair, or to shave or put on makeup. The grip may become weak opening jars (and child-proof medicine bottles), hips may be weak getting out of deep chairs or the bathtub, and legs may tire climbing stairs or when walking distances.
Why do myasthenics walk with their noses in the air?
For this reason, a number of myasthenics walk around with their noses in the air (when their neck muscles are strong enough to support their head )! Bright lights can aggravate the symptom. In a minority of myasthenics (around 15%), MG is limited to ocular problems.
What is MG in the eye?
Ocular myasthenia is when MG confines itself to the eye muscles. The impact of the condition on eye muscles include:
How long does it take for MG to move?
But for most whose first symptoms are ocular, MG eventually moves onto other parts of the body within a couple of years. Three different serial pictures to demonstrate fatigue of eyelid muscles as the patient keeps looking up. After a few minutes of rest, the eyelids have returned to near-normal position.
What is MG in myasthenics?
Generalised MG (Head, Neck, Arms and Legs) This is where many muscle groups are affected. The typical myasthenic may feel strong on awakening from a night’s rest or a nap, but experiences increasing muscle fatigue as the day progresses.
Where is muscle weakness in the pharynx?
Muscle weakness in the pharynx (the section of the alimentary canal that extends from the mouth and nasal cavities to the larynx , where it becomes continuous with the esophagus) is another early sign of MG.
Is MG a psychiatric disorder?
All chronic diseases, including MG, may have psychiatric consequences in terms of coping and adaptation. Psychiatric morbidity usually appears as anxiety disorders, such as panic disorder and generalised anxiety disorder, and as depressive disorders.
Is myasthenia gravis a psychiatric disorder?
Myasthenia gravis (MG) is a chronic, autoimmune disease involving neuromuscular junctions. It is frequently associated with symptoms such as loss of muscle strength, difficulty in respiration and swallowing, diplopia and ptosis. All chronic diseases, including MG, may have psychiatric consequences in terms of coping and adaptation. Psychiatric morbidity usually appears as anxiety disorders, such as panic disorder and generalised anxiety disorder, and as depressive disorders. However, there are very few data on the prevalence and aetiology of such psychiatric symptoms in patients with MG, and those available in the literature are generally from old studies with poor methodology. The interaction between MG and psychiatric disorders needs to be appreciated, especially in the primary care setting, since the symptoms may overlap. MG may be under-recognised initially because the psychiatric symptoms may coincide with those of the actual disease, such as fatigue, lack of energy and shortness of breath. On the other hand, co-morbid psychiatric symptoms that appear during the course of the illness may be misdiagnosed as true myasthenic symptoms; thus, leading to unnecessary drug treatment. Differentiation of the aetiology of these symptoms might alter the treatment choice and, therefore, affect the treatment success rate and patients' well-being. Psychiatric treatments must be carefully planned because of the risk of aggravating the underlying neurological disease. Even though there appears to be an intricate relationship between MG and psychiatric symptoms, there is very limited information on this subject. As such, prospective, randomised, controlled pharmaco/psychotherapy studies are needed to better direct the management of patients and, thus, improve quality of life during the course of the illness.
Is MG a psychiatric condition?
All chronic diseases, including MG, may have psychiatric consequences i …. Myasthenia gravis (MG) is a chronic, autoimmune disease involving neuromuscular junctions. It is frequently associated with symptoms such as loss of muscle strength, difficulty in respiration and swallowing, diplopia and ptosis. All chronic diseases, including MG, may have ...
Why is pain so complicated?
Pain is complicated and can be caused by a variety of different things. It has physical and mental causes that often overlap with one another. Pain perception can also be impacted by different drugs.
What is MG in medical terms?
Myasthenia gravis (MG) is an autoimmune condition that affects how nerves and muscles talk to one another. This can lead to muscle weakness and fatigue. MG can affect specific parts of the body, or it can be more widespread.
Can MG cause pain?
It is also possible that people with MG who have pain have other underlying issues. For example, a pain-causing autoimmune condition, like rheumatoid arthritis, can occur alongside MG. 1,2
Is headache common in MG?
Headaches are not uncommon in MG, but they are also not uncommon in general. It is hard to determine whether headaches are directly related to a person’s MG.
Is fatigue a symptom of MG?
Although weakness and fatigue are the most commonly talked about symptoms, they are not the only ones. Every person’s experience with MG can differ, but 1 issue that may be more common than expected is pain.
Is it a symptom of MG?
MG is not thought to specifically impact pain pathways. However, a survey of people with MG found that a surprisingly high percentage experience regular pain. Specifically, about half of all survey respondents reported having pain that they thought was related to their MG. About 30 percent of those with pain rated it as moderate to severe. 1
Who Is At Risk For Myasthenia Gravis?
Myasthenia gravis tends to appear mainly in young women and men over the age of 50. Young people diagnosed with myasthenia gravis have a better chance at achieving remission than older patients.
What is the treatment for ocular myasthenia gravis?
Depending on the type and severity of the symptoms, treatment can include eyeglasses (with or without eyelid crutches) and surgery.
What is the condition called when the muscles in the eye are affected?
Ocular Myasthenia Gravis. In approximately 15 percent of people with myasthenia gravis, the only muscles affected are those in the eyes, in which case the condition is called ocular myasthenia gravis. Some of the first signs of ocular myasthenia gravis include a dropping eyelid and double vision. Symptoms affecting the eyes are extremely common in ...
What is the name of the disease that affects the muscles?
Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disease that affects the muscles, causing muscle weakness. The disease can affect various muscle groups in the body, and muscles in the face, the neck, and the limbs can exhibit symptoms of weakness and immobility. Myasthenia gravis is one of the better understood neurological disorders, ...
What are the causes of facial weakness?
Fatigue. Vocal changes. Weakness of the facial muscles, affecting speech and chewing or swallowing. Ophthalmoparesis and Ophthalmoplegia —respectively, weakening and paralysis or the muscles responsible for eye movement. Difficulty breathing.
Can medication help with myasthenia gravis?
Medications: Several different medications may be used to treat generalized myasthenia gravis, but there is no good evidence that any of these are effective at treating ocular symptoms. There is some evidence that treatment with medication may prevent ocular myasthenia gravis from progressing to generalized myasthenia gravis.
Can ocular myasthenia gravis be seen in both eyes?
With ocular myasthenia gravis, the symptoms typically include ptosis and diplopia. Ptosis: A drooping eyelid can be seen in either eye or in both eyes. The drooping may not be always visible, but will often follow a pattern that can be seen on physical examination by an ophthalmologist or other eye care professional.
Why does MG get worse after surgery?
Infections and respiratory illnesses can produce increased weakness that lasts for a while after the illness is gone. The stress of surgery can make MG temporarily worse. The disease may intensify during certain times of a woman’s menstrual cycle.
What causes MG to get worse?
These factors can make MG worse: Extreme temperatures (hot or cold weather, hot showers or baths, sunbathing, saunas, hot tubs) Some medications, including beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, and some antibiotics. Some chemicals, including some household cleaners, insecticides and pet flea sprays. Infections and respiratory illnesses can ...
Can anesthesia worsen MG?
Because some anesthesia can worsen MG, your surgeon and anesthesiologist will want to be prepared to manage your symptoms.
Can medications make myasthenia gravis worse?
The University of Illinois at Chicago College of Pharmacy website describes medications that can make your MG worse. You also can find a list of medications to avoid on the Myasthenia Gravis Foundation of America website at www.myasthenia.org.
What happens when myasthenia gravis is not working?
When these receptors cannot work properly, the affected muscles tire easily . The amount of weakness typically fluctuates and may be worse at the end of the day.
How often does myasthenia gravis only affect the eyes?
In the other 85% of patients, however, symptoms of weakness will develop in another part of the body, usually within the next three years. At that time, these patients are considered to have generalized myasthenia gravis.
How is ocular myasthenia gravis different from generalized myasthenia gravis?
On the other hand, generalized myasthenia gravis affects muscles throughout the body. In addition to visual symptoms, generalized myasthenia gravis may cause trouble speaking, trouble swallowing, and weakness in the arms or legs.
Why does myasthenia gravis typically cause double vision?
Double vision is a common symptom of myasthenia gravis because this condition very frequently affects the strength of the eye muscles.
What is the condition that causes weakness in the body?
Myasthenia gravis is a condition that causes weakness of specific muscles in the body. Normally nerves send a signal to muscles using a chemical called acetylcholine, which tells the muscles when to move. In patients with myasthenia gravis , the body’s immune system mistakenly interferes with the muscles’ receptors for acetylcholine.
What is the best test for myasthenia gravis?
One important test to help diagnose myasthenia gravis is called a nerve conduction study/electromyogram (sometimes called “EMG” for short). In part of this test, a small electrical stimulation is delivered to a nerve, and the responses are measured from a muscle. The most accurate test to diagnose myasthenia gravis is called a single fiber ...
What are the side effects of pyridostigmine?
The side effects of pyridostigmine can include diarrhea, abdominal cramps, nausea, and vomiting. Another medication called glycopyrrolate can be used to reduce these effects. Corticosteroid medications, such as prednisone, can ...
What is the relationship between myasthenia gravis and hearing loss?
Studies of the pathophysiological basis of this relationship suggest that acetylcholine receptors (AChRs) on outer hair cells (OHCs) play a central role. In patients with MG, autoantibodies against AChRs induce a progressive loss of AChRs on OHCs, decreasing their electromotility. The stapedial reflex decay test can be altered in MG patients, and can be used as an additional tool for diagnosis and monitoring. Transient evoked and distortion product otoacoustic emissions are the main diagnostic tool for monitoring OHC functionality in MG patients, and can be used to record subclinical hearing alterations before the onset of clinically evident hearing loss. Understanding the association between MG and hearing dysfunction requires a multidisciplinary approach. Otolaryngologists should take this relationship into account when approaching patients with a diagnosis of myasthenia gravis and "in patients with MG" with ण128;in MG patients, and the progress of hearing alterations should always be monitored in patients with MG.
Is there a connection between hearing and myasthenia gravis?
There is increasing evidence of a connection between hearing function and myasthenia gravis (MG). Studies of the pathophysiological basis of this relationship suggest that acetylcholine receptors (AChRs) on outer hair cells (OHCs) play a central role. In patients with MG, autoantibodies against AChR …