Does Neptune have a hard surface?
Neptune does not have a solid surface. Its atmosphere (made up mostly of hydrogen, helium, and methane) extends to great depths, gradually merging into water and other melted ices over a heavier, solid core with about the same mass as Earth. Neptune's atmosphere is made up mostly of hydrogen and helium with just a little bit of methane.
Is Neptune made of gas?
What is Neptune made of? Neptune’s atmosphere is made up of a lot of gas. This atmosphere is primarily hydrogen and helium, with some methane in there too. The methane is what gives Neptune its blue colored appearance. Hydrogen, helium and methane make up most of Neptune’s atmosphere.
Is Neptune made of rock?
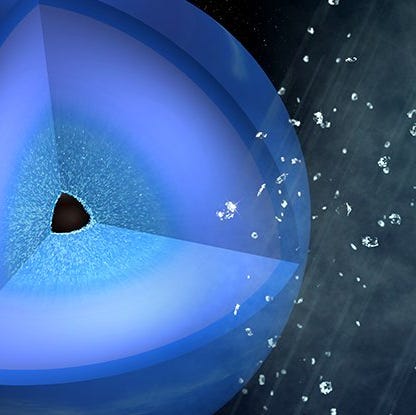
Of the large planets, Neptune is the densest. What is the internal core of Neptune? Neptune’s core, which is roughly the dimensions of the Earth, is believed to be composed of rock and ice. The core is roofed with a thick mantle that accommodates water, liquid ammonia and methane, combined with gases.
Is Neptune made of ice?
Neptune, like Uranus, is one of the two outer planets known as an "ice giant." Made up of more ices than Jupiter and Saturn, the chilly body almost seems to be in a class by itself. Different images emphasize the features on Neptune.
See more

Does Neptune have a cold core?
But as with all gas and ice giants, temperatures vary on Neptune due to depth and pressure. In short, the deeper one goes into Neptune, the hotter it becomes. At its core, Neptune reaches temperatures of up to 7273 K (7000 °C; 12632 °F), which is comparable to the surface of the Sun.
Is there a core in Neptune?
Like Earth, Neptune has a rocky core made up of iron and other metals, with a mass just greater than our planet. Temperatures in the core could reach 9,260 F (5,127 C). Like the other gas giants, Neptune boasts a series of rings.
Could you stand on Neptune?
But temperatures at this region would be thousands of degrees; hot enough to melt rock. And the pressure from the weight of all the atmosphere would be crushing. In short, there is simply no way one could stand on the “surface of Neptune”, let alone walk around on it.
Is Neptunes core as big as Earth?
Neptune has a radius of 24.764 km / 15.387 mi, and a diameter of 49.244 km / 30.598 mi. The core of Neptune is about 1.5 times the size of Earth.
Does Jupiter have a core?
According to most theories, Jupiter has a dense core of heavy elements that formed during the early solar system. The solid core of ice, rock, and metal grew from a nearby collection of debris, icy material, and other small objects such as the many comets and asteroids that were zipping around four billion years ago.
What if you fell into Neptune?
5:046:57What If You Fell Into Neptune? - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipUp fast as you make your way through all of neptune's 3 000 kilometer thick hydrogen and heliumMoreUp fast as you make your way through all of neptune's 3 000 kilometer thick hydrogen and helium atmosphere don't worry about smashing into the ground neptune doesn't have one per se.
What planets can humans land on?
It could be possible for humans to walk on 3 planets of the Solar system besides Earth: Mercury, Venus, and Mars. These are rocky planets with solid surfaces unlike the outer planets like Jupiter, Saturn, Neptune, and Uranus that are mostly made out of gas.
Which planet can humans live on?
Kepler-62e and Kepler-62f are thought capable of hosting life. The planet Kepler-69c is located about 2,700 light-years from Earth in the constellation Cygnus. This is an illustration of the planet, which is the smallest yet found to orbit in the habitable zone of a sun-like star.
Can humans land Pluto?
To travel the billions of miles between Earth and Pluto, the amount of fuel you would have to bring with you isn't a major problem for New Horizons, but for a manned mission, it would be prohibitive. Chemical fuels are heavy and you eventually hit a limit on how much mass a rocket can lift off the planet.
What happens if you land on Uranus?
As an ice giant, Uranus doesn't have a true surface. The planet is mostly swirling fluids. While a spacecraft would have nowhere to land on Uranus, it wouldn't be able to fly through its atmosphere unscathed either. The extreme pressures and temperatures would destroy a metal spacecraft.
What is the smallest gas giant?
NeptuneNeptune is the fourth largest planet in terms of diameter, making it the smallest in physical size of the gas giants.
What is the coldest planet in our solar system?
UranusThe coldest planet in our solar system on record goes to Uranus which is closer to the Sun and 'only' about 20 times further away from the Sun than the Earth is. The lowest temperature recorded there was minus 224 degrees Celsius.
What is the core temperature of Neptune?
Because of its great distance from the Sun, Neptune's outer atmosphere is one of the coldest places in the Solar System, with temperatures at its cloud tops approaching 55 K (−218 °C; −361 °F). Temperatures at the planet's centre are approximately 5,400 K (5,100 °C; 9,300 °F).
What is on Neptune's surface?
Surface. Neptune does not have a solid surface. Its atmosphere (made up mostly of hydrogen, helium, and methane) extends to great depths, gradually merging into water and other melted ices over a heavier, solid core with about the same mass as Earth.
Is there an atmosphere on Neptune?
Neptune's thick atmosphere is mostly hydrogen, with smaller amounts of helium and methane. It is the absorption of red light by methane which gives Neptune its very blue coloration.
Is Neptune a moon?
TritonThalassaHippocampNereidGalateaDespinaNeptune/Moons
How was Neptune discovered?
Neptune is not visible to the unaided eye and is the only planet in the Solar System found by mathematical prediction rather than by empirical observation. Unexpected changes in the orbit of Uranus led Alexis Bouvard to deduce that its orbit was subject to gravitational perturbation by an unknown planet. After Bouvard's death, the position of Neptune was predicted from his observations, independently, by John Couch Adams and Urbain Le Verrier. Neptune was subsequently observed with a telescope on 23 September 1846 by Johann Galle within a degree of the position predicted by Le Verrier. Its largest moon, Triton, was discovered shortly thereafter, though none of the planet's remaining 13 known moons were located telescopically until the 20th century. The planet's distance from Earth gives it a very small apparent size, making it challenging to study with Earth-based telescopes. Neptune was visited by Voyager 2, when it flew by the planet on 25 August 1989; Voyager 2 remains the only spacecraft to visit Neptune. The advent of the Hubble Space Telescope and large ground-based telescopes with adaptive optics has recently allowed for additional detailed observations from afar.
Why did Neptune migrate to its current orbit?
This hypothesis of migration after formation is favoured, due to its ability to better explain the occupancy of the populations of small objects observed in the trans-Neptunian region . The current most widely accepted explanation of the details of this hypothesis is known as the Nice model, which explores the effect of a migrating Neptune and the other giant planets on the structure of the Kuiper belt.
What is the name of the ocean science project that allows people to surf the seafloor?
Along with its sister project, VENUS, NEPTUNE offers a unique approach to ocean science.
How does Neptune's magnetic field compare to Uranus'?
Neptune resembles Uranus in its magnetosphere, with a magnetic field strongly tilted relative to its rotational axis at 47° and offset at least 0.55 radii, or about 13,500 km from the planet's physical centre. Before Voyager 2 's arrival at Neptune, it was hypothesised that Uranus's tilted magnetosphere was the result of its sideways rotation. In comparing the magnetic fields of the two planets, scientists now think the extreme orientation may be characteristic of flows in the planets' interiors. This field may be generated by convective fluid motions in a thin spherical shell of electrically conducting liquids (probably a combination of ammonia, methane and water) resulting in a dynamo action.
What was Galileo's first observation of Neptune?
Hence, he is not credited with Neptune's discovery. At his first observation in December 1612, Neptune was almost stationary in the sky because it had just turned retrograde that day. This apparent backward motion is created when Earth's orbit takes it past an outer planet. Because Neptune was only beginning its yearly retrograde cycle, the motion of the planet was far too slight to be detected with Galileo's small telescope. In 2009, a study suggested that Galileo was at least aware that the "star" he had observed had moved relative to the fixed stars.
What is a Neptune?
NEPTUNE is the world's first regional-scale underwater ocean observatory that plugs directly into the Internet. NEPTUNE is the largest installation on the Ocean Networks Canada network of ocean observatories. Since December 2009, it has allowed people to "surf" the seafloor while ocean scientists run deep-water experiments from labs ...
How far does the magnetosphere slow the solar wind?
Neptune's bow shock, where the magnetosphere begins to slow the solar wind, occurs at a distance of 34.9 times the radius of the planet. The magnetopause, where the pressure of the magnetosphere counterbalances the solar wind, lies at a distance of 23–26.5 times the radius of Neptune. The tail of the magnetosphere extends out to at least 72 times the radius of Neptune, and likely much farther.
What is the magnetic field of Neptune?
Neptune has an unusual magnetic field which is tipped on its side in relation to the axis that the planet rotates around. The strong magnetic field, which is about 27 times more powerful than Earth's, is tipped at a 47 degree angle and is likely powered by the motions inside the mantle itself.
What is Neptune made of?
Made up of more ices than Jupiter and Saturn , the chilly body almost seems to be in a class by itself. Different images emphasize the features on Neptune. By tracking features such as the Great Dark Spot and South Polar Feature, astronomers were able to refine measurements of the length of Neptune's day.
Why are the rings on the blue planet red?
Instead, the clumpy rings contain prominent arcs, likely due to the influence of one of Neptune's moons. Made up of ice particles and silicates, the rings are reddish.
How did Neptune's rings come to be?
Neptune's rings were first discovered when it passed between a star while astronomers were attempting to study the planet. The star faded out, then returned to view. Unlike other rings, the arc-like nature meant that the fading did not repeat on the other side of the planet, which puzzled scientist.
What is the first layer of Neptune?
Beneath the clouds. The first layer of Neptune is its icy atmosphere , which is mostly hydrogen and helium. The bluish coloration comes from traces of methane in the air, but the planet is a more brilliant hue than the dull blue of Uranus, which implies something else could be affecting it.
What is the temperature of the mantle?
Temperatures inside the mantle range from 3,140 degrees Fahrenheit (1,727 degrees Celsius) to 8,540 F (4,727 F). At deep enough depths, the methane may transform into diamond crystals.
What is the temperature of Neptune's core?
Temperatures in the core could reach 9,260 F (5,127 C).
Why is the stratosphere of Neptune hazy?
Neptune’s spectra suggest that its lower stratosphere is hazy due to condensation of products caused by the interaction of ultraviolet radiation and methane (i.e . photolysis), which produces compounds such as ethane and ethyne. The stratosphere is also home to trace amounts of carbon monoxide and hydrogen cyanide, which are responsible for Neptune’s stratosphere being warmer than that of Uranus.
What is the temperature of Neptune?
Beneath the atmosphere is the planet’s large mantle. This is a superheated liquid region where temperatures can reach as high as 2,000 to 5,000 K (1727 – 4727 °C; 3140 – 8540 °F).
What is the core of Neptune made of?
In accordance with these theories, the core of Neptune is composed of iron, nickel and silicates, with an interior model giving it a mass about 1.2 times that of Earth. The pressure at the center is estimated to be 7 Mbar (700 GPa), about twice as high as that at the center of Earth, and with temperatures as high as 5,400 K.
How long does it take for Neptune to rotate?
Because Neptune is not a solid body, its atmosphere undergoes differential rotation. The wide equatorial zone rotates with a period of about 18 hours, which is slower than the 16.1-hour rotation of the planet’s magnetic field. By contrast, the reverse is true for the polar regions where the rotation period is 12 hours.
What is the composition of Neptune?
Neptune, like the rest of the gas giant planets in the Solar System, can be broken up into various layers. The composition of Neptune changes depending on which of these layers you’re looking at. The outermost layer of Neptune is the atmosphere, forming about 5-10% of the planet’s mass, and extending up to 20% of the way down to its core.
How was Neptune's rotation determined?
Neptune’s rotation period was determined using measurements of radio emissions and Voyager 2 also showed that Neptune had a surprisingly active weather system. Six new moons were discovered during the flyby, and the planet was shown to have more than one ring.
How much of the atmosphere does Neptune have?
Neptune’s atmosphere forms about 5% to 10% of its mass and extends perhaps 10% to 20% of the way towards the core, where it reaches pressures of about 10 GPa – or about 100,000 times that of Earth’s atmosphere. At high altitudes, Neptune’s atmosphere is 80% hydrogen and 19% helium, with a trace amount of methane.
Why are Neptune and Uranus called Ice Giants?
Neptune and Uranus because of their differing interior compostion from the Jovian planets of Jupiter and Saturn, are frequently referred to as ice giants. Now if you were to parachute into the atmospheres of both of them, you’d still be crushed to death from the pressure and eventual heat.
How many years does it take for Pluto to orbit the Sun?
But that’s not what happens. Pluto orbits the Sun every 248 years ; Neptune orbits every 165 years. If you take two Pluto years, that is three Neptune years (rounding makes it tricky). This is close to exact; when objects do this, we call this an ‘orbital resonance’. Now, what it means is that Pluto and Neptune make a repeating pattern as they orbit. This does a number of things:
Why is Pluto above the rest of the solar system?
Basically because Neptune’s gravity always acts on Pluto in the same pattern of directions and strengths, it stabilizes the orbit.
What happened to Neptune?
What we think happened was that Neptune slowly moved outward in the early solar system. As it did, the places where its resonances were did as well. If an object happened to be orbiting at that distance when a resonance crossed it, it could get trapped, and start moving ahead of Neptune with the resonance.
What is the Neptune core made of?
Although Neptune is a gas giant its core is primarily made of silicates and nickel-iron.
What is the difference between ice giants and gas giants?
Smaller gas giants like Neptune have a slightly different layout, while it still has a thick atmosphere, ice giants likely have a mantle of water , ammonia, and methane ices, super heated and crushed like the liquid hydrogen of Jupiter and Saturn. The center of an ice giant would likely be the same as the mantle, except crushed to the point of a solid, like the center Jupiter. Again though, we don’t know this for certain, but it does give you a good idea of just how weird gas giants can be.
What is the core of Neptune?
Neptune has a core that consists of iron, nickel and various other silicates…
Why is Neptune blue?
Due to its smaller size and higher concentrations of volatiles relative to Jupiter and Saturn, Neptune (much like Uranus) is often referred to as an "ice giant" – a subclass of a giant planet. As with Uranus, the absorption of red light by the atmospheric methane is part of what gives Neptune its blue hue, although Neptune's is darker ...
What is the Neptune core made of?
Also like Uranus, Neptune's internal structure is differentiated between a rocky core consisting of silicates and metals; a mantle consisting of water, ammonia and methane ices; and an atmosphere consisting of hydrogen, helium and methane gas. It's atmosphere is also divided into four layers, consisting of (from innermost to outermost) ...
How long does it take for Neptune to rotate?
Because Neptune is not a solid body, its atmosphere undergoes differential rotation. The wide equatorial zone rotates with a period of about 18 hours, which is slower than the 16.1-hour rotation of the planet's magnetic field. By contrast, the reverse is true for the polar regions where the rotation period is 12 hours.
What are the two regions of Neptune's atmosphere?
The two main regions of Neptune's atmosphere are the two innermost ones: the lower troposhere, where temperatures decrease with altitude; and the stratosphere , where temperature increases with altitude. Within the troposphere, pressure levels range from one to five bars (100 and 500 kPa), hence the surface of Neptune is defined as being within this region.
What is the mass of Neptune?
Composition and Structure: With a mean radius of 24,622 ± 19 km, Neptune is the fourth largest planet in the Solar System. But with a mass of 1.0243 × 10 26 kg – which is roughly 17 times that of Earth – it is the third most massive, outranking Uranus. Due to its smaller size and higher concentrations of volatiles relative to Jupiter and Saturn, ...
Why is Neptune's color so intense?
Because Neptune's atmospheric methane content is similar to that of Uranus, some unknown atmospheric constituent is thought to contribute to Neptune's more intense coloring. The internal structure and composition of Neptune. Credit: NASA.
How fast is Jupiter's wind?
Maximum wind speeds on Jupiter can be more than 500 km/hour. That's twice the speed of the strongest hurricanes on Earth. But that's nothing compared to Neptune. Astronomers have calculated winds blasting across the surface of Neptune at 2,100 km/hour.
Why is Neptune blue?
Due to its smaller size and higher concentrations of volatiles relative to Jupiter and Saturn, Neptune (much like Uranus) is often referred to as an “ice giant” – a subclass of a giant planet. As with Uranus, the absorption of red light by the atmospheric methane is part of what gives Neptune its blue hue, although Neptune’s is darker ...
What is the internal structure of Neptune?
Also like Uranus, Neptune’s internal structure is differentiated between a rocky core consisting of silicates and metals; a mantle consisting of water, ammonia and methane ices; and an atmosphere consisting of hydrogen, helium and methane gas. It’s atmosphere is also divided ...
What is the mass of Neptune?
Composition and Structure: With a mean radius of 24,622 ± 19 km, Neptune is the fourth largest planet in the Solar System. But with a mass of 1.0243 × 1026 kg – which is roughly 17 times that of Earth – it is the third most massive, outranking Uranus. Due to its smaller size and higher concentrations of volatiles relative to Jupiter and Saturn, ...
How fast is Jupiter's wind?
Maximum wind speeds on Jupiter can be more than 500 km/hour. That’s twice the speed of the strongest hurricanes on Earth. But that’s nothing compared to Neptune. Astronomers have calculated winds blasting across the surface of Neptune at 2,100 km/hour.
What are the two regions of Neptune?
The two main regions of Neptune’s atmosphere are the two innermost ones: the lower troposhere, where temperatures decrease with altitude; and the stratosphere , where temperature increases with altitude.
What was the first storm to be spotted on Jupiter?
The first to be spotted was a massive anticyclonic storm measuring 13,000 x 6,600 km and resembling the Great Red Spot of Jupiter. Known as the Great Dark Spot, this storm was not spotted five later (Nov. 2nd, 1994) when the Hubble Space Telescope looked for it. Instead, a new storm that was very similar in appearance was found in the planet’s northern hemisphere, suggesting that these storms have a shorter life span than Jupiter’s
What is the atmosphere of Neptune?
Atmosphere: Neptune’s “surface” can therefore be said to be composed of about 80% hydrogen and 19% helium, with a trace amount of methane. The surface layer is also permeated by roving bands of clouds with varying compositions, depending on altitude and pressure.

Namesake
- The ice giant Neptune was the first planet located through mathematical calculations. Using predictions made by Urbain Le Verrier, Johann Galle discovered the planet in 1846. The planet is named after the Roman god of the sea, as suggested by Le Verrier.
Potential For Life
- Neptune's environment is not conducive to life as we know it. The temperatures, pressures, and materials that characterize this planet are most likely too extreme and volatile for organisms to adapt to.
Size and Distance
- With a radius of 15,299.4 miles (24,622 kilometers), Neptune is about four times wider than Earth. If Earth were the size of a nickel, Neptune would be about as big as a baseball. From an average distance of 2.8 billion miles (4.5 billion kilometers), Neptune is 30 astronomical units away from the Sun. One astronomical unit (abbreviated as AU), is the distance from the Sun to Earth. From …
Orbit and Rotation
- One day on Neptune takes about 16 hours (the time it takes for Neptune to rotate or spin once). And Neptune makes a complete orbit around the Sun (a year in Neptunian time) in about 165 Earth years (60,190 Earth days). Sometimes Neptune is even farther from the Sun than dwarf planet Pluto. Pluto's highly eccentric, oval-shaped orbit brings it inside Neptune's orbit for a 20-y…
Moons
- Neptune has 14 known moons. Neptune's largest moon Triton was discovered on October 10, 1846, by William Lassell, just 17 days after Johann Gottfried Galle discovered the planet. Since Neptune was named for the Roman god of the sea, its moons are named for various lesser sea gods and nymphs in Greek mythology. Triton is the only large moon in the solar system that circl…
Rings
- Neptune has at least five main rings and four prominent ring arcs that we know of so far. Starting near the planet and moving outward, the main rings are named Galle, Leverrier, Lassell, Arago, and Adams. The rings are thought to be relatively young and short-lived. Neptune's ring system also has peculiar clumps of dust called arcs. Four prominent arcs named Liberté (Liberty), Egalité (Eq…
Formation
- Neptune took shape when the rest of the solar system formed about 4.5 billion years ago when gravity pulled swirling gas and dust in to become this ice giant. Like its neighbor Uranus, Neptune likely formed closer to the Sun and moved to the outer solar system about 4 billion years ago.
Structure
- Neptune is one of two ice giants in the outer solar system (the other is Uranus). Most (80% or more) of the planet's mass is made up of a hot dense fluid of "icy" materials – water, methane, and ammonia – above a small, rocky core. Of the giant planets, Neptune is the densest. Scientists think there might be an ocean of super hot water under Neptune's cold clouds. It does not boil a…
Atmosphere
- Neptune's atmosphere is made up mostly of hydrogen and helium with just a little bit of methane. Neptune's neighbor Uranus is a blue-green color due to such atmospheric methane, but Neptune is a more vivid, brighter blue, so there must be an unknown component that causes the more intense color. Neptune is our solar system's windiest world. Despite its great distance and low e…
Overview
Neptune is the eighth planet from the Sun and the farthest known solar planet. In the Solar System, it is the fourth-largest planet by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. It is 17 times the mass of Earth, and slightly more massive than its near-twin Uranus. Neptune is denser and physically smaller than Uranus because its greater mass causes more gravitat…
Physical characteristics
Neptune's mass of 1.0243×10 kg is intermediate between Earth and the larger gas giants: it is 17 times that of Earth but just 1/19th that of Jupiter. Its gravity at 1 bar is 11.15 m/s , 1.14 times the surface gravity of Earth, and surpassed only by Jupiter. Neptune's equatorial radius of 24,764 km is nearly four times that of Earth. Neptune, like Uranus, is an ice giant, a subclass of giant planet, because t…
History
Some of the earliest recorded observations ever made through a telescope, Galileo's drawings on 28 December 1612 and 27 January 1613 contain plotted points that match up with what is now known to have been the positions of Neptune on those dates. On both occasions, Galileo seems to have mistaken Neptune for a fixed star when it appeared close—in conjunction—to Jupiter in the night …
Climate
Neptune's weather is characterised by extremely dynamic storm systems, with winds reaching speeds of almost 600 m/s (2,200 km/h; 1,300 mph)—nearly reaching supersonic flow. More typically, by tracking the motion of persistent clouds, wind speeds have been shown to vary from 20 m/s in the easterly direction to 325 m/s westward. At the cloud tops, the prevailing winds range i…
Orbit and rotation
The average distance between Neptune and the Sun is 4.5 billion km (about 30.1 astronomical units (AU)), and it completes an orbit on average every 164.79 years, subject to a variability of around ±0.1 years. The perihelion distance is 29.81 AU; the aphelion distance is 30.33 AU.
On 11 July 2011, Neptune completed its first full barycentric orbit since its disc…
Formation and migration
The formation of the ice giants, Neptune and Uranus, has proven difficult to model precisely. Current models suggest that the matter density in the outer regions of the Solar System was too low to account for the formation of such large bodies from the traditionally accepted method of core accretion, and various hypotheses have been advanced to explain their formation. One is tha…
Moons
Neptune has 14 known moons. Triton is the largest Neptunian moon, comprising more than 99.5% of the mass in orbit around Neptune, and it is the only one massive enough to be spheroidal. Triton was discovered by William Lassell just 17 days after the discovery of Neptune itself. Unlike all other large planetary moons in the Solar System, Triton has a retrograde orbit, indicating that it was capture…
Observation
Neptune brightened about 10% between 1980 and 2000 mostly due to the changing of the seasons. Neptune may continue to brighten as it approaches perihelion in 2042. The apparent magnitude currently ranges from 7.67 to 7.89 with a mean of 7.78 and a standard deviation of 0.06. Prior to 1980 the planet was as faint as magnitude 8.0. Neptune is too faint to be visible to the naked eye. …