Nondisjunction
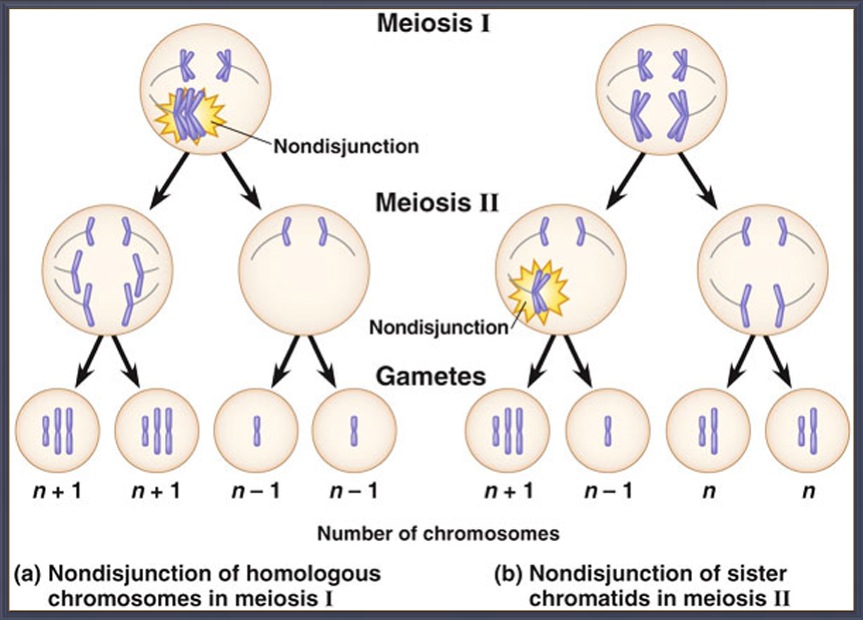
Nondisjunction is the failure of homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids to separate properly during cell division. There are three forms of nondisjunction: failure of a pair of homologous chromosomes to separate in meiosis I, failure of sister chromatids to separate during meiosis II, and failure of sister chromatids to separate during mitosis. Nondisjunction results in daughter cells with abnorm…
Which genetic disorder can only result from nondisjunction?
Turner syndrome (TS) is a genetic disorder caused by the partial or complete absence of one X chromosome. This is called monosomy and is typically caused by chromosomal nondisjunction. It is a very common abnormality among the sex chromosome disorders, with an incidence of 1 in 2000 liveborn females. Is Down syndrome caused by nondisjunction?
What are disorders caused by nondisjunction?
Nondisjunction may occur any time a cell divides, so it can happen during mitosis, meiosis I, or meiosis II. Conditions associated with nondisjunction include mosaicism, Down syndrome, Turner syndrome, and Klinefelter syndrome. Nondisjunction may occur whenever a cell divides its chromosomes.
What are the consequences of nondisjunction?
Nondisjunction results in an uneven distribution of chromosomes during cell replication. If nondisjunction occurs during meiosis I, the homologous chromosomes do not separate. If nondisjunction happens in meiosis II, sister chromatids do not separate.
What happens when nondisjunction occur?
What happens when Nondisjunction occurs? Nondisjunction Produces Abnormal Gametes If nondisjunction occurs during anaphase I of meiosis I, this means that at least one pair of homologous chromosomes did not separate. The end result is two cells that have an extra copy of one chromosome and two cells that are missing that chromosome.

What is the consequence of nondisjunction in meiosis?
Nondisjunction in meiosis results in gametes with incorrect numbers of chromosomes . There are two possible outcomes, depending on the timing of...
What is an example of a non disjunction?
The following are examples of genetic disorders caused by nondisjunction: Down Syndrome (Trisomy 21) Edwards Syndrome (Trisomy 18) Patau Syndr...
What is nondisjunction and its effects?
Nondisjunction is a lack of separation of chromosomes during anaphase of cell division (either during mitosis or either round of meiosis). The ef...
What is nondisjunction in biology?
-disjunction is a lack of junction, or a separation or breaking apart. Disjunction is a normal process for both mitosis and meiosis — the chromosomes are supposed to split apart during anaphase so each daughter cells can receive a full and complete copy of the original cell's genome. Finally, nondisjunction, the full term, means there is a lack of separation. The chromosomes stay joined together so that too many migrate to one daughter cell while the other has a deficit.
How many rounds of cell division does meiosis occur?
Meiosis occurs in two rounds of cell division — Meiosis I and Meiosis II. The overall process is described in the steps below and outlined in the figure
How many chromosomes are produced during Meiosis I?
If nondisjunction occurs during Meiosis I in humans, two gametes with extra chromosomes will be produced (24 chromosomes each, or n+1) and two gametes lacking a chromosome will be produced (22 chromosomes each, n-1 ).
How many chromosomes are in a diploid cell?
In humans, diploid cells contain 46 chromosomes ( 2n = 46 ). Diploid cells, also called somatic cells, include all the non-reproductive cells of the body, including nerve cells, skin cells, muscle cells, bone cells, fat cells, etc. Humans only have two type of haploid cells — sperm and eggs, each of which contain only 23 chromosomes ( n = 23 ). During fertilization, the haploid number of chromosomes in the sperm (23) combine with the haploid number in the egg (23) to produce a diploid zygote (46; n + n = 2n ). This zygote cell will divide thousands of times through mitosis to produce all the diploid cells that make up the body of the new infant (and eventually the adult human).
What is the process of reducing the number of chromosomes in a cell?
Meiosis is the process responsible for reducing the chromosome number; i.e. for turning a diploid cell into four haploid cells.
When are sister chromatids joined?
Sister chromatids are joined together at their centromere, and will remain joined until Anaphase II during the second division in meiosis.
Can nondisjunction occur in both males and females?
Nondisjunction can occur in both males and females, so it is possible for both sperm and eggs with abnormal chromosome numbers to be produced.
What happens to nondisjunction in meiosis?
Nondisjunction in meiosis I occurs when the tetrads fail to separate during anaphase I. At the end of meiosis I, there will be 2 haploid daughter cells, one with n+1 and the other with n-1. Both of these daughter cells will then go on to divide once more in meiosis II, producing 4 daughter cells, 2 with n+1 and 2 with n-1.
What causes mitotic nondisjunction?
Mitotic nondisjunction can occur due to the inactivation of either topoisomerase II, condensin, or separase. This will result in 2 aneuploid daughter cells, one with 47 chromosomes (2n+1) and the other with 45 chromosomes (2n-1).
How does meiosis change into haploid?
Meiosis goes through all 4 phases of mitosis twice, with modified mechanisms that ultimately create haploid cells instead of diploid. One modification is in meiosis I. Homologous chromosomes are separated instead of sister chromatids, creating haploid cells. It is during this process where we see crossing over and independent assortment leading to the increased genetic diversity of the progeny. Meiosis II progresses the same way as mitosis, but with the haploid number of chromosomes, ultimately creating 4 daughter cells all genetically distinct from the original cell.
When does nondisjunction occur?
Nondisjunction can occur during anaphase of mitosis, meiosis I, or meiosis II. During anaphase, sister chromatids (or homologous chromosomes for meiosis I), will separate and move to opposite poles of the cell, pulled by microtubules. In nondisjunction, the separation fails to occur causing both sister chromatids or homologous chromosomes to be pulled to one pole of the cell.
How many phases are there in mitosis?
Mitosis contains 4 phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. In prophase, the nuclear envelope breaks down and chromatin condenses. In metaphase, the chromosomes line up along the metaphase plate, and microtubules attach to the kinetochores of each chromosome. In anaphase, the chromatids separate and are pulled by the microtubules to opposite ends of the cell. Finally, in telophase, the nuclear envelopes reappear, the chromosomes unwind into chromatin, and the cell undergoes cytokinesis, which splits the cell into 2 identical daughter cells.
Why do most cases go undiagnosed?
Most cases go undiagnosed due to a lack of clinical abnormalities.
Can mitotic nondisjunction cause cancer?
This can cause some forms of cancer, including retinoblastoma.