Do schizophrenic patients experience impaired learning?
We assessed skill learning in young and older schizophrenic patients using the rotary pursuit task. Schizophrenic patients displayed impaired learning on this task compared with normal control subjects, but older patients were not more impaired than young ones.
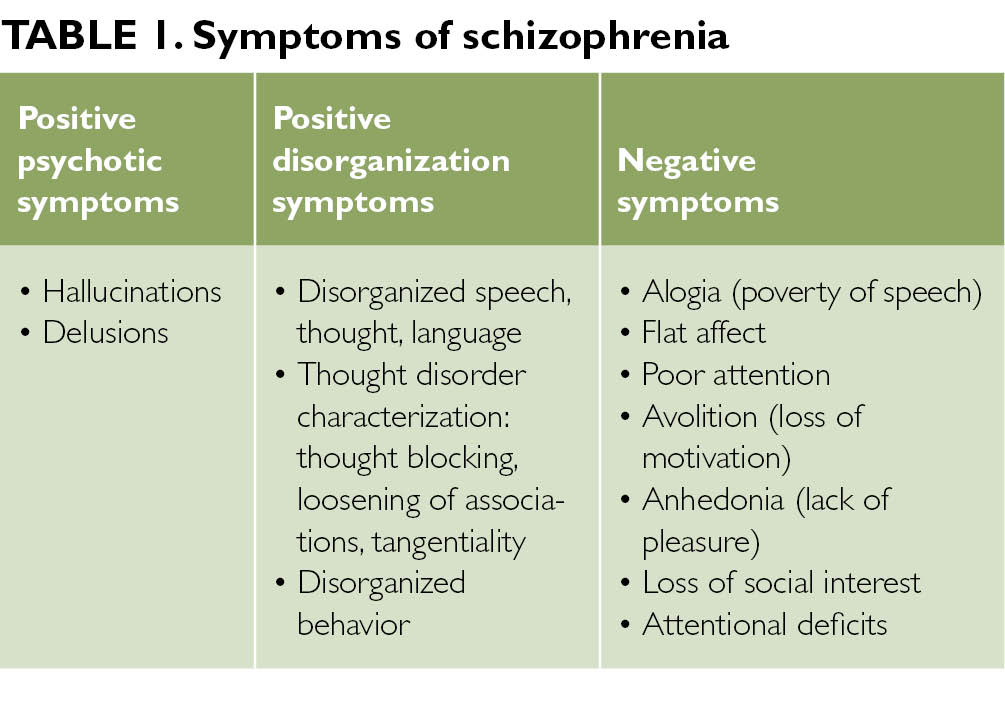
What are the symptoms of schizophrenia?
Schizophrenia is a complex brain disorder. It often runs in families and can cause troubling symptoms. These may include hearing voices, and having trouble thinking clearly and relating to others. It often starts suddenly in early adulthood.
How does schizophrenia affect your perception of the world?
With schizophrenia, your perception of the world can impact how you interpret new stimuli and people, which can be overwhelming. But living with schizophrenia doesn’t have to be lonely. Establishing a strong support system can be a powerful way to take on many symptoms of schizophrenia.
What is flat affect in schizophrenia?
Coping and Support Flat affect (diminished emotional expression) is a hallmark symptom of schizophrenia, although it may also affect those with other conditions. It is a lack of showing emotion characterized by an apathetic and unchanging facial expression and little or no change in the strength, tone, or pitch of the voice.

How does schizophrenia affect movement?
Parkinsonism is another common movement disorder associated with schizophrenia and is a 'hypo-kinetic' (reduced movement) disorder, characterised by slowness of movement and rigidity. These movement disorders are associated with antipsychotic medications but can arise independent of medication status.
Does schizophrenia have motor symptoms?
However, most schizophrenia patients also display a wide range of symptoms characterized by aberrant motor functioning. Symptoms of schizophrenia that fit this description are catatonic features, the motoric neurological soft signs (NSS), extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS), psychomotor slowing, and reduced motor activity.
Can schizophrenia affect mobility?
One of the main causes of functional disability in patients with schizophrenia is impairment in functional mobility (FM) (2). FM is the ability to move from one place to another independently in the environment (3) and requires complex physical processes such as walking, transferring, and turning (4).
How does schizophrenia affect a person physically?
Compared with the general population, schizophrenia patients are at increased risk of weight gain, abdominal obesity, diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and cardiovascular disease.
Does schizophrenia cause movement disorder?
Spontaneous Movements Disorders (SMDs) or dyskinetic movements are often seen in patients with schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders, and are widely considered to be adverse consequences of the use of antipsychotic medications.
What is psychomotor schizophrenia?
Psychomotor problems may appear as clumsiness, unusual mannerisms or repetitive actions, and in extreme cases, motionless rigidity held for extended periods of time. Negative symptoms reflect a loss of functioning in areas such as emotion or motivation.
Does psychosis affect motor skills?
In psychosis, deficits in a variety of motor behaviors are present, including postural control,31,32 motor learning,33 and eye-blink conditioning.
Is schizophrenia a physical disability?
The SSA can assist a person with schizophrenia as the administration considers it a disability. To qualify for disability benefits, a person with schizophrenia will have to meet the SSA criteria and show that their condition is persistent and severe and prevents them from engaging in substantial gainful activity.
Do schizophrenics have trouble walking?
Patients with schizophrenia have decreased walking speed because of a smaller stride length. Reduced muscular power is associated with a reduction in the walking speed in persons without mental disorders.
What are some common behaviors associated with schizophrenia?
SymptomsDelusions. These are false beliefs that are not based in reality. ... Hallucinations. These usually involve seeing or hearing things that don't exist. ... Disorganized thinking (speech). Disorganized thinking is inferred from disorganized speech. ... Extremely disorganized or abnormal motor behavior. ... Negative symptoms.
When does schizophrenia worsen?
When people with schizophrenia live without adequate treatment, their mental health can worsen. Not only can the signs of schizophrenia get more severe, but they can also develop other mental health disorders, including: Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) Anxiety Disorders.
Does a schizophrenic know they are sick?
Early Warning Signs of Schizophrenia One is that people with the disorder often don't realize they're ill, so they're unlikely to go to a doctor for help. Another issue is that many of the changes leading up to schizophrenia, called the prodrome, can mirror other normal life changes.
Do schizophrenics have tics?
Certain movement problems such as tremors, facial tics, rigidity, and unusually slow movement (bradykinesia) or an inability to move (akinesia) are common in people with schizophrenia. In most cases these are side effects of medicines prescribed to help control the disorder.
What are psychomotor symptoms?
Psychomotor agitation is a symptom related to a wide range of mood disorders. People with this condition engage in movements that serve no purpose. Examples include pacing around the room, tapping your toes, or rapid talking. Psychomotor agitation often occurs with mania or anxiety.
Does schizophrenia cause muscle spasms?
Some patients report muscle spasms and cramps in the head and neck area, as well as stiff muscles throughout their body. Tardive dyskinesia (TD) is a type of EPS that can occur after months or years of treatment with antipsychotic medications.
Can schizophrenia cause shaky hands?
Shaking hands or tremor can be related to nervous system disorders. Examples include benign essential tremor. Hallucinations can be related to dementia or psychotic disorders like schizophrenia. Shaking can sometimes be a side effect of medications.
How are schizophrenia and autism related?
Schizophrenia (SZ) and autism spectrum disorder (ASD) share considerable clinical features and intertwined historical roots. It is greatly needed to explore their similarities and differences in pathophysiologic mechanisms. We assembled a large sample size of neuroimaging data (about 600 SZ patients, 1000 ASD patients, and 1700 healthy controls) to study the shared and unique brain abnormality of the two illnesses. We analyzed multi-scale brain functional connectivity among functional networks and brain regions, intra-network connectivity, and cerebral gray matter density and volume. Both SZ and ASD showed lower functional integration within default mode and sensorimotor domains, but increased interaction between cognitive control and default mode domains. The shared abnormalties in intra-network connectivity involved default mode, sensorimotor, and cognitive control networks. Reduced gray matter volume and density in the occipital gyrus and cerebellum were observed in both illne s ses. Interestingly, ASD had overall weaker changes than SZ in the shared abnormalities. Interaction between visual and cognitive regions showed disorder-unique deficits. In summary, we provide strong neuroimaging evidence of the convergent and divergent changes in SZ and ASD that correlated with clinical features.
How does schizophrenia affect improvisation?
In this study we focused on socio-motor improvisation in individuals with schizophrenia, one of the more debilitating mental disorder . This represents the ability to improvise gestures during an interaction to promote sustained communication and shared attention. Using a novel paradigm called the mirror game and recently introduced to study joint improvisation, we recorded hand motions of two people mirroring each other. Comparing Schizophrenia patients and healthy controls skills during the game, we found that improvisation was impaired in schizophrenia patients. Patients also exhibited significantly higher difficulties to being synchronized with someone they follow but not when they were leaders of the joint improvisation game. Considering the correlation between socio-motor synchronization and socio-motor improvisation, these results suggest that synchronization does not only promote affiliation but also improvisation, being therefore an interesting key factor to enhance social skills in a clinical context. Moreover, socio-motor improvisation abnormalities were not associated with executive functioning, one traditional underpinning of improvisation. Altogether, our results suggest that even if both mental illness and improvisation differ from normal thinking and behavior, they are not two sides of the same coin, providing a direct evidence that being able to improvise in individual situations is fundamentally different than being able to improvise in a social context.
What are the most common motor disorders attributed to neuroleptic drugs?
A factor analysis on the most frequently occurring motor disorders generated the following symptom clusters: (1) tremor, bradykinesia, rigidity, and attendant symptoms; (2) buccolingual-masticatory dyskinesia, astasia, dyskinesia of the lower extremities and posture in extension; and (3) dyskinesia of the upper extremities and postural disorder. The classification and the factors were used to study the effects of drug withdrawal on a sample of patients over a sixmonth period. Symptoms of cluster 1 decreased while those of cluster 2 increased in severity. In a control group receiving standard drugs during a comparable period, no significant changes were noted.
What is the NSS in schizophrenia?
Neurological soft signs (NSS) are related to grey matter and functional brain abnormalities in schizophrenia. Studies in healthy subjects suggest, that NSS are also linked to white matter. However, the association between NSS and white matter abnormalities in schizophrenia remains to be elucidated. The present study investigated, if NSS are related to white matter alterations in patients with schizophrenia. The total sample included 42 healthy controls and 41 patients with schizophrenia. We used the Neurological Evaluation Scale (NES), and we acquired diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging to assess white matter on a voxel-wise between subject statistic. In patients with schizophrenia, linear associations between NES with fractional anisotropy (FA), radial, axial, and mean diffusivity were analyzed with tract-based spatial statistics while controlling for age, medication dose, the severity of the disease, and motion. The main pattern of results in patients showed a positive association of NES with all diffusion measures except FA in important motor pathways: the corticospinal tract, internal capsule, superior longitudinal fascicle, thalamocortical radiations and corpus callosum. In addition, exploratory tractography analysis revealed an association of the right aslant with NES in patients. These results suggest that specific white matter alterations, that is, increased diffusivity might contribute to NSS in patients with schizophrenia.
What is the metabolic syndrome?
Background Metabolic syndrome ( MBS) and especially diabetes mellitus type 2 (T2DM) are common comorbidities of patients with psychotic disorders. They are associated with the psychiatric disease itself and with the use of antipsychotics (AP). Selecting the appropriate antipsychotic medication is, thus, not only challenging for the practicing psychiatrists but also plays a role in the daily routine of physicians in internal and general medicine.QuestionWhat has to be considered in the treatment of patients suffering from primary psychosis and comorbid T2DM?Materials and methodsRecent findings, reviews, and basic literature are analyzed and an update is presented and discussed.ResultsMBS and T2DM have a negative impact on the already increased mortality and impaired life quality of patients with schizophrenic psychoses. Significant differences in the metabolic risk of several AP have been found. Detecting, assessing and treating T2DM is an often complicated task due to underuse of medical care and nonadherence of patients with schizophrenia.Conclusions The treatment of patients suffering from primary psychoses with AP has shown demonstrable positive effects on life expectancy, life quality, and disease progression. Given a high risk for T2DM, interdisciplinary internal medicine–psychiatric monitoring is essential. Pharmaceutical preparations with fewer metabolic side effects should be preferred. Simultaneously, antidiabetic therapy with metformin has proven to be advantageous and should be consequently established.
How does VR affect postural control?
Impairment in postural control is prevalent in patients with schizophrenia, and often limit occupational performance. Virtual reality (VR) has proven its benefits for improving postural control and among schizophrenia population. Remarkably, the effectiveness of a VR game-based intervention on postural control in this population has never been evaluated. The primary aim of this study is to examine the effects and impact of VR on postural control parameters in patients with schizophrenia. This is a single-blinded, randomised controlled trial with two parallel groups. Thirty-four patients with schizophrenia are randomly assigned to the virtual reality group (VR) or the inactive control group (CG). The intervention consists of 3 30 min sessions for 4 weeks. Assessments are performed at baseline, post-intervention and 1-month follow-up. The primary outcome is postural control. The center of pressure (COP) displacement and velocity in anteroposterior (AP) and mediolateral (ML) directions are measured by PhyisoSensing pressure platform. This study protocol comprises parameters that are thought to be crucial to the success of the intervention. There are used objective and quantitative measures to evaluate the outcomes for effectively plan postural control interventions in schizophrenia with more reliable and valid results. The results of the study will be useful to clarify the effect of VR on postural control in patients with schizophrenia and provide insight into the validity of this approach as an intervention technique. It is expected that the results confirm the positive findings supporting the therapeutic prospects of VR.
What is the dimensional structure of motor disorders?
This study aimed to ascertain the factor structure of motor signs and their clinical correlates in psychotic disorders. A sample of consecutive admissions of psychotic patients (n=187) was utilized to examine the factor structure of motor disorders as assessed by the Modified Rogers Scale (MRS). The relationship between motor dimensions and external variables was analyzed. A comparative examination of alternative factor solutions revealed that a six-factor structure, explaining 59% of the total variance, best fitted the 36 MRS items. This solution comprised the components of motor poverty, agitation, stereotypy/mannerisms, proskinetic, negativistic and dyskinetic. All the motor dimensions significantly improved over the psychotic episode. Motor dimensions differentially correlated with the syndromes of psychoses, with the association between motor poverty and the negative syndrome being particularly strong. Residual motor pathology, but not the acute one, was related to various clinical variables. Residual symptoms of motor poverty and stereotypy/mannerisms were associated with poor premorbid adjustment, more illness severity and a diagnosis of schizophrenia. It is concluded that the factor structure of motor disorders and its clinical correlates are rather more complex than generally acknowledged.
What are the symptoms of schizophrenia?
Each person may feel symptoms differently. These are the most common symptoms:
What is schizophrenia?
Schizophrenia is a complex brain disorder. It often runs in families and can cause troubling symptoms. These may include hearing voices, and having trouble thinking clearly and relating to others. It often starts suddenly in early adulthood. There is no cure for this illness, but it can be managed with medicine and supportive therapy.
How is schizophrenia treated?
Managing schizophrenia is a lifelong process. It can't be cured. But symptoms can often be managed with medicine and therapy . Often, more than 1 method is needed. Types of treatment that may be helpful include:
What is the best medicine for paranoia?
Antipsychotic medicines. These are the main medicines used to reduce the most troubling symptoms such as delusions and paranoia.
Why do people with schizophrenia have attendance problems?
Patients with Schizophrenia may have attendance problems for a number of reasons including, hospitalizations, “drug holidays” (times when a drug is stopped for a period of time, often to give relief from side-effects), and frustration with progress.
What is schizophrenia?
Schizophrenia is a disease that strikes many people while they are young, while they are still in their learning and formative years. As a result, the deficits in attention and memory that result have long-lasting consequences for the remainder of their lives.
What does schizophrenia perceive?
Patients in an acute stage of Schizophrenia percieve the world as a mass of information, without an overlying view to bring it together.
Why do people have difficulty reacting to stimulus?
They have difficulty reacting, as they cannot compare the action that has been taken by the stimulus inducing person, to a historical perspective of “Does this mean they are mad, sad,etc.”
Can schizophrenia cause memory loss?
Memory deficits in Schizophrenia can be severe. One instructor says:
Does schizophrenia cure learning?
It has been shown that there are a number of treatments available for Schizophrenia, but none of them cure the underlying pathologies that result in impaired learning.
Does psychosis indicate recovery?
However, Green (1996) points out that in a literature review, it has been shown that the degree of psychosis does not act as an indicator of the subsequent recovery.
Psychotic Symptoms And Schizophrenia Diagnosis By Race
The lifetime prevalence of self-reported psychotic symptoms is highest in black Americans , Latino Americans , and white Americans .
What Is The Long
Without ongoing care, people with schizophrenia can be hospitalized multiple times, lose jobs and fall out of touch with their families.
Who Does It Affect
Schizophrenia affects about 1% of Canadiansthats about 40,000 people in British Columbia. While scientists are still working hard to figure out what causes schizophrenia, we do know that it affects:
Treatment Of Cognitive Deficits In Schizophrenia
As mentioned above, the traditional characteristic signs and symptoms of psychosis are less stable than cognitive impairments. They tend to fluctuate naturally throughout the course and have been found to be more treatment responsive.
What Are The 4 Main Types Of Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia looks different from one person to the next. But there are four main categories into which patients fall:
The Warning Signs Of Suicide
The warning signs that people with depression and schizophrenia may be considering suicide include:
When To See A Doctor
As schizophrenia usually develops gradually, it can be difficult to pinpoint when changes in behavior start or know whether they are something to worry about. Identifying that you are experiencing a pattern of concerning behaviors can be a sign you should consult with a professional.
What is the best therapy for schizophrenia?
Social skills training, a type of behavioral therapy , can also be used to teach people with schizophrenia to express feelings and needs, ask questions, and control their voice, body, and facial expressions. Speech therapy can help with tone and modulation of voice to convey more emotion. How Behavioral Therapy Works.
What antipsychotics help with flat affect?
The newer "atypical" antipsychotics also influence other neurotransmitters in the brain and may help with a flat affect. Clozaril (clozapine) is one of these agents shown to help combat flat affect in people with schizophrenia and other mental illnesses for which this is a concern. 5 . Atypical Antipsychotics for Schizophrenia.
Why do people have flat affect?
It is hypothesized that it is due to differences in brain functioning —and some of the neurocognitive deficiencies that accompany schizophrenia. 2
What is the purpose of antipsychotics?
Typical antipsychotics function by blocking receptors for dopamine.
What is flat affect?
Coping and Support. Flat affect (diminished emotional expression) is a hallmark symptom of schizophrenia, although it may also affect those with other conditions. It is a lack of showing emotion characterized by an apathetic and unchanging facial expression and little or no change in the strength, tone, or pitch of the voice.
Can a man with schizophrenia not smile?
For instance, upon hearing the great news, someone with schizophrenia may not smile, laugh, or have any joy in their response. Flat affect is more common among men than women and is often present during the onset of schizophrenia. 1 .
Can a person with schizophrenia express their emotions?
While they may be unable to express their emotions, your emotions are likely in overdrive as you struggle to come to terms with this symptom of schizophrenia. Continuing to educate yourself on the condition and the experiences your loved one will face is one of the most important ways to cope.