Which phase of glycolysis is energy-requiring?
Glycolysis consists of an energy-requiring phase followed by an energy-releasing phase. Suppose that we gave one molecule of glucose to you and one molecule of glucose to Lactobacillus acidophilus —the friendly bacterium that turns milk into yogurt.
What is the first step of glycolysis of glucose?
Yet, the first steps would be the same in both cases: both you and the bacterium would need to split the glucose molecule in two by putting it through glycolysis. What is glycolysis? Glycolysis is a series of reactions that extract energy from glucose by splitting it into two three-carbon molecules called pyruvates.
What is the net ATP yield of glycolysis?
Glycolysis requires the input of 2 ATP molecules for each molecule of glucose. However, 4 ATP molecules will be produced directly from glycolysis for each molecule of glucose. Therefore, the net ATP yield of glycolysis is 2 ATP. Why can glycolysis supply energy to cells when oxygen is not avalable? Glycolysis can occur without oxygen.
What is glycolysis and how does it work?
Glycolysis is a series of reactions that extract energy from glucose by splitting it into two three-carbon molecules called pyruvates. Glycolysis is an ancient metabolic pathway, meaning that it evolved long ago, and it is found in the great majority of organisms alive today .

What is the energy input and output of glycolysis?
Input for the breakdown of 1 glucose molecule in glycolysis is 2 ATP and the output is 4 ATP, 2 NADH and 2 pyruvate molecules. Metabolic pathway which provides anaerobic source of energy in all organisms is glycolysis.
Does glycolysis require oxygen as an input?
Glycolysis requires no oxygen. It is an anaerobic type of respiration performed by all cells, including anaerobic cells that are killed by oxygen. For these reasons, glycolysis is believed to be one of the first types of cell respiration and a very ancient process, billions of years old.
What is needed to run glycolysis?
Glycolysis requires two molecules of NAD+ per glucose molecule, producing two NADHs as well as two hydrogen ions and two molecules of water. The end product of glycolysis is pyruvate, which the cell can further metabolize to yield a large amount of additional energy.
Where does glycolysis get its energy?
During glycolysis, a glucose molecule with six carbon atoms is converted into two molecules of pyruvate, each of which contains three carbon atoms. For each molecule of glucose, two molecules of ATP are hydrolyzed to provide energy to drive the early steps, but four molecules of ATP are produced in the later steps.
Does glycolysis need ATP?
Energy is needed at the start of glycolysis to split the glucose molecule into two pyruvate molecules. These two molecules go on to stage II of cellular respiration. The energy to split glucose is provided by two molecules of ATP.
Why is ATP required for glycolysis?
Why is ATP required for glycolysis? ATP makes it easier to break apart glucose into two three-carbon molecules.
What is the input in glycolysis?
Overall, the input for glycolysis is one glucose, two ATP and two NAD+ molecules giving rise to two pyruvate molecules, four ATP and two NADH.
What is the source of energy for the first step of glycolysis?
In the process of glycolysis, glucose, a six-carbon molecule, is split into two pyruvates (three-carbon molecules). The first stage of glycolysis involves an energy investment of two ATP.
Which steps in glycolysis require ATP?
Key Points. ATP molecules donate high energy phosphate groups during the two phosphorylation steps, step 1 with hexokinase and step 3 with phosphofructokinase, in the first half of glycolysis.
What is the role of oxygen in glycolysis?
Aerobic glycolysis is a series of reactions wherein oxygen is required to reoxidize NADH to NAD+, hence the name. This ten-step process begins with a molecule of glucose and ends up with two molecules of pyruvate[1].
What happens if oxygen is not present in glycolysis?
When oxygen is not present, pyruvate will undergo a process called fermentation. In the process of fermentation the NADH + H+ from glycolysis will be recycled back to NAD+ so that glycolysis can continue. In the process of glycolysis, NAD+ is reduced to form NADH + H+.
How is glycolysis affected by the absence of oxygen?
When oxygen is absent, the end product of glycolysis, i.e. pyruvate is converted to lactic acid or ethanol and CO2 by fermentation. It is called anaerobic respiration.
Does glycolysis require co2?
The answer is C, carbon dioxide only. Glucose is a reactant of cellular respiration (and of glycolysis, the first step), while the others are intermediates along the way from deriving a total of 36 to 38 ATP from glucose so long as oxygen is present.
How many ATP molecules are produced in the last step of glycolysis?
In the last steps of glycolysis 4 ATP molecules are produced. Analyze Model 1 to find the source of the four inorganic phosphates (Pi) that are added to the ADP molecules to make the four ATP molecules. Describe the origins of the four inorganic phosphates here.
Which has less potential energy, pyruvate or glucose?
Pyruvate is at a lower point than glucose in Model 1, and 4 ATP molecules are made as PGAL is converted to pyruvate, so pyruvate has less potential energy than glucose.
How many ATP molecules are needed to convert glucose to PGAL?
Yes. 2 ATP molecules are needed to convert a glucose molecule to 2 PGAL molecules.
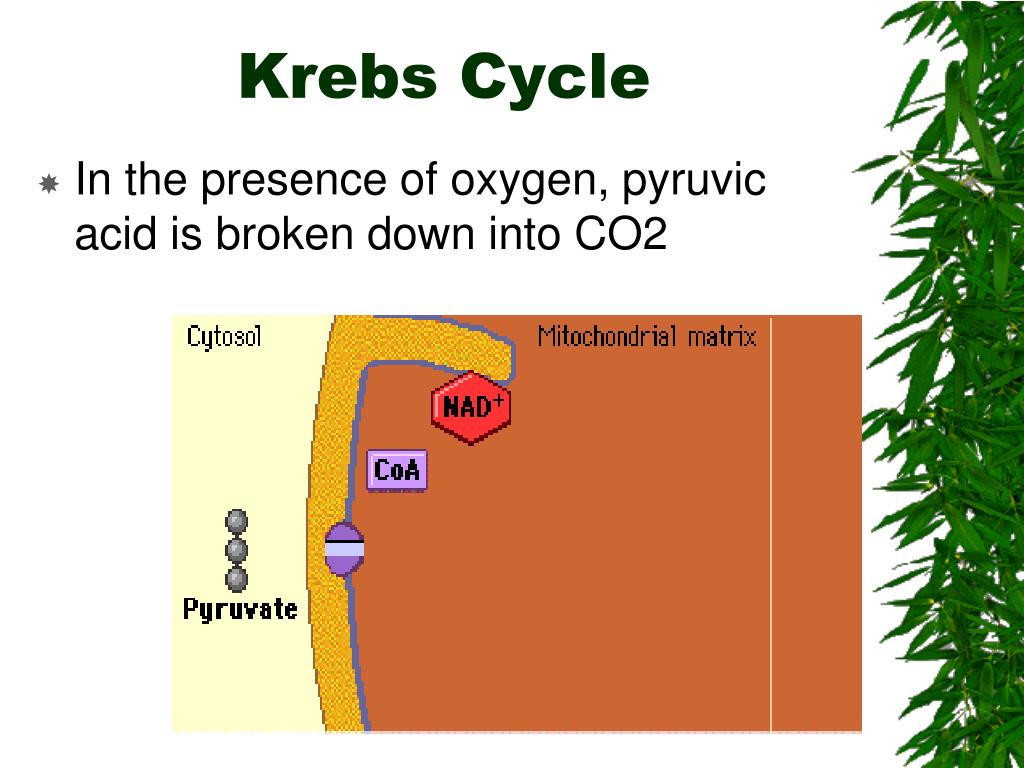
Which carbons enter the Krebs cycle from the link reaction?
2 carbons are in acetyl group that enters the Krebs cycle from the link reaction.
Where does pyruvate move?
The pyruvate probably moves across the membrane through a protein carrier.
Which molecule has higher potential energy?
The PGAL molecule has higher potential energy than the glucose molecule. The energy from the ATP molecule converting to ADP has increased the potential energy of the PGAL.