
What do chondrocytes do?
So what, exactly, do chondrocytes do? Since chondrocytes are the only cells located in cartilage, they produce and maintain the cartilage matrix. So what is a cartilage matrix?
How does the number of chondrocytes affect cartilage shape?
The number of chondrocytes found in cartilage determines how 'bendy' the cartilage is. When looking through a microscope, chondrocytes look similar to eyeballs floating in goo.
What is the function of The chondroblast?
Chondrocyte. They produce and maintain the cartilaginous matrix, which consists mainly of collagen and proteoglycans. Although the word chondroblast is commonly used to describe an immature chondrocyte, the term is imprecise, since the progenitor of chondrocytes (which are mesenchymal stem cells) can differentiate into various cell types,...
What happens during terminal differentiation of chondrocytes?
Chondrocytes undergo terminal differentiation when they become hypertrophic, which happens during endochondral ossification. This last stage is characterized by major phenotypic changes in the cell. Structure The chondrocyte in cartilage matrix has rounded
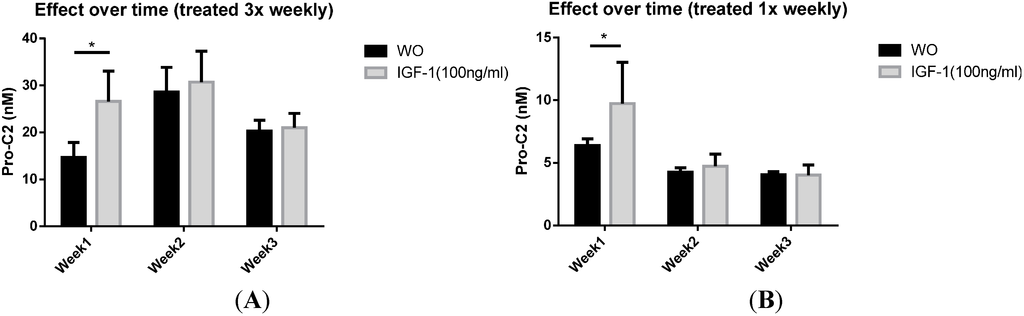
How do chondrocytes get their nutrients?
nutrient acquisition Cartilage cells, called chondrocytes, occur at scattered sites through the cartilage and receive nutrition by diffusion through the gel; cartilage contains no blood vessels or nerves, unlike bone.
How is cartilage nourished?
Cartilage is nourished by long range diffusion from nearby capillaries in the perichondrium. Therefore, cartilage can never become very thick, as diffusion would not be sufficient to supply the cartilage with nutrients and oxygen. (This is in contrast to bone, because bone has a very good blood supply).
How are the chondrocytes in articular cartilage nourished?
Articular cartilage is an avascular tissue [15] nourished by two potential pathways: diffusion from subchondral bone vessels and diffusion from the synovial fluid.
How do chondrocytes get nutrients and eliminate waste products?
Access to nutrients and elimination of waste products occur via diffusion through the extracellular matrix.
Are chondrocytes nourished by synovial fluid?
Chondrocytes within the cartilage matrix are responsible for forming and maintaining the matrix. Articular cartilage is avascular, so chondrocytes are nourished by synovial fluid diffusion through the matrix by mechanical forces.
How are nutrients and oxygen transported to the chondrocytes?
There are no blood vessels in cartilage to supply the chondrocytes with nutrients. Instead, nutrients diffuse through a dense connective tissue surrounding the cartilage (called the perichondrium) and into the core of the cartilage.
How does cartilage receive its nutrients quizlet?
Unlike other connective tissues, cartilage has no blood vessels or nerves within it. Chondrocytes receive nutrients and oxygen via diffusion through the matrix from the perichondrium.
What are chondrocytes made of?
Chondrocytes (/ˈkɒndrəsaɪt, -droʊ-/, from Greek χόνδρος, chondros = cartilage + κύτος, kytos = cell) are the only cells found in healthy cartilage. They produce and maintain the cartilaginous matrix, which consists mainly of collagen and proteoglycans.
What nutrients does cartilage need?
Vitamin C. Vitamin C is a vitamin and an antioxidant. Your body needs it to make cartilage, which protects the bones in your knee joint. It can also help remove free radicals.
How do chondrocytes work?
Chondrocytes in the AC proliferate and secrete extracellular matrix to maintain and sustain the cartilage. The cells themselves are separated from each other by cartilage matrix [2]. They respond to outside stimuli and tissue damage, and are also responsible for degenerative conditions, such as osteoarthritis (OA).
What is the source of oxygen and nutrients for articular cartilage?
Articular cartilage does not have a blood supply. Rather it gets it oxygen and nutrients from the surrounding joint fluid. When a joint is loaded, the pressure squeezes fluid including waste products out of the cartilage, and when the pressure is relieved, the fluid seeps back in together with oxygen and nutrients.
What is the source of oxygen and nutrients for articular cartilage quizlet?
Articular cartilage is nourished by oxygen and nutrients in synovial fluid.
What nutrients does cartilage need?
Vitamin C. Vitamin C is a vitamin and an antioxidant. Your body needs it to make cartilage, which protects the bones in your knee joint. It can also help remove free radicals.
Can you rebuild cartilage naturally?
Q: Can cartilage repair itself? A: Though it is made of cells and tissues, cartilage cannot repair itself due to the lack of blood vessels and enough blood supply to create and duplicate new cells.
Can you regenerate cartilage?
Cartilage Regeneration Options MACI is a surgical procedure that uses cartilage-forming cells from your body to restore damaged cartilage in the knees. It involves a biopsy to harvest chondrocytes (cartilage-forming cells), which are allowed to multiply in a lab, and surgery to implant them into the damaged area.
What is the best supplement to rebuild cartilage?
Dietary supplements: Dietary supplements such as glucosamine and chondroitin are the non-surgical treatment options for cartilage restoration. Chrondroitin sulphate and glucosamine are naturally occurring substances in the body that prevent degradation of cartilage and promote formation of new cartilage.
characteristics
Chondrocytes are present in all three types of cartilage. They are cells derived from mesenchymal cells, which in the areas where cartilage is formed, lose their extensions, round up and congregate forming dense masses called “chondrification” centers.
Cartilage growth and chondroblast differentiation
As each cell in each cluster or isogenic group forms a matrix, they move away from each other and form their own separate gaps. As a consequence, the cartilage grows from the inside, calling this form of cartilage growth interstitial growth.
Histology
Three types of chondrogenic cells can be found in cartilage: chondroblasts and chondrocytes.
Chondrocytes in cartilage tissue
Chondrocytes are chondroblasts surrounded by extracellular matrix. They can have an ovoid shape when they are near the periphery, and a more rounded shape with about 20 to 30μm in diameter when they are in deeper regions of the cartilage.
Chondrocytes and types of cartilage
The arrangement of chondrocytes varies according to the type of cartilage where they are found. In hyaline cartilage, which has a translucent, pearly white appearance, chondrocytes are found in many isogenic groups and arranged in large gaps with very few fibers in the matrix.
Features
The fundamental function of chondrocytes is to synthesize the extracellular matrix of the different types of cartilage. Like chondrocytes, together with the matrix, they are the constitutive elements of cartilage and share its functions with it (as a whole).
Crops
Hyaline cartilage, which is the most abundant in the human body, can be subject to multiple injuries due to diseases, but, above all, due to sports practice.
What are Chondrocytes?
Chondrocytes, or chondrocytes in lacunae, are cells found in cartilage connective tissue. The number of chondrocytes found in cartilage determines how 'bendy' the cartilage is. When looking through a microscope, chondrocytes look similar to eyeballs floating in goo. Remember the movie Indiana Jones and the Temple of Doom? That section of the movie when they are eating eyeball soup? That's the easiest way to determine what type of cartilage you're talking about, the number of 'eyeballs' in the soup.
Where are chondrocytes found?
Chondrocytes, or chondrocytes in lacunae, are cells found in cartilage connective tissue. They are the only cells located in cartilage. They produce and maintain the cartilage matrix, which is a type of lake in which the chondrocytes swim. There are three types of cartilage found in the human body, including elastic cartilage, ...
What happens when cartilage doesn't form?
Dysfunctional Chondrocytes. Sometimes chondrocytes don't function properly, which means the cartilage isn't formed correctly, or cartilage gets damaged by an accident. When elastic cartilage doesn't form right or is damaged, it's not too big of a deal.
Why is cartilage important?
This may lead you to ask why cartilage is important in the first place. One of the principal functions of some cartilage types is to keep bones from rubbing together. We call this reducing friction. Imagine rubbing two pieces of sandpaper together. The pieces of sand in the paper rub against one another and, after a while, you get a pile of dust, right? Imagine the two pieces of sandpaper were the ends of your bones. That would start to hurt! Now imagine putting a piece of regular paper in between the two pieces of sandpaper. Now the friction is reduced, and the sandpaper moves much easier.
What is cartilage matrix?
That's exactly what the matrix is - a type of lake in which the chondrocytes 'swim.'. This may lead you to ask why cartilage is important in the first place.
What are the cells in cartilage called?
In cartilage connective tissues there are cells called chondrocytes. Understand the definition and function of chondrocytes, examine the three cartilage types, and what it looks like when chondrocytes disfunction. Updated: 09/09/2021
What does it mean when there is no cartilage?
But think of the other places where we find hyaline and fibro-cartilage. If there's no cartilage, that means there's nothing to decrease friction between our bones. Think of the sandpaper example. No cartilage would mean no regular paper to decrease friction between our two pieces of sandpaper.
Where do cartilage cells get nutrients?
Cartilage cells, called chondrocytes, occur at scattered sites through the cartilage and receive nutrition by diffusion through the gel; cartilage contains no blood vessels or nerves, unlike bone.
What is the component of cartilage?
component of cartilage. In connective tissue: Cartilage. The cells of cartilage, called chondrocytes, are isolated in small lacunae within the matrix. Although cartilage is avascular, gaseous metabolites and nutrients can diffuse through the aqueous phase of the gel-like matrix to reach the cells.
Does metabolism of carbohydrates decrease with age?
metabolism. …that of its cells (chondrocytes). Carbohydrate metabolism in these cells is similar to that of cells elsewhere and is unaffected by age. The oxygen consumption of the chondrocytes, on the other hand, decreases with age once the cells have matured.
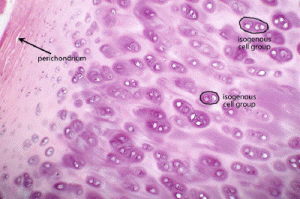
Overview
Chondrocytes are the only cells found in healthy cartilage. They produce and maintain the cartilaginous matrix, which consists mainly of collagen and proteoglycans. Although the word chondroblast is commonly used to describe an immature chondrocyte, the term is imprecise, since the progenitor of chondrocytes (which are mesenchymal stem cells) can differentiate into vario…
Development
From least- to terminally-differentiated, the chondrocytic lineage is:
1. Colony-forming unit-fibroblast
2. Mesenchymal stem cell / marrow stromal cell
3. Chondrocyte
4. Hypertrophic chondrocyte
Structure
The chondrocyte in cartilage matrix has rounded or polygonal structure. The exception occurs at tissue boundaries, for example the articular surfaces of joints, in which chondrocytes may be flattened or discoid. Intra-cellular features are characteristic of a synthetically active cell. The cell density of full-thickness, human, adult, femoral condyle cartilage is maintained at 14.5 (±3.0) × 10 cells/ mm from age 20 to 30 years. Although chondrocyte senescence occurs with aging, mitoti…
Genetics
The number of chondrocyte cells created and their maturation process can be influenced by multiple different genes and proteins. Two proteins, bone morphogenetic protein 4(BMP-4) and fibroblast growth factor 2(FGF2) have been seen to influence the amount of differentiation into chondrocytes. Both proteins are known to play a role in embryonic stem cell differentiation into mesodermal cells, through signaling with BMP-4 and as FGF2 acting as a stimulator. From the m…
Gallery
• Chondrocytes in hyaline cartilage
• Transmission electron micrograph of a chondrocyte, stained for calcium, showing its nucleus (N) and mitochondria (M).
See also
• Chondronectin
• Endochondral ossification
• Intramembranous ossification
• List of human cell types derived from the germ layers
Further reading
• Dominici M, Hofmann TJ, Horwitz EM (2001). "Bone marrow mesenchymal cells: biological properties and clinical applications". Journal of Biological Regulators and Homeostatic Agents. 15 (1): 28–37. PMID 11388742.
• Bianco P, Riminucci M, Gronthos S, Robey PG (2001). "Bone marrow stromal stem cells: nature, biology, and potential applications". Stem Cells. 19 (3): 180–92. doi:10.1634/stemcells.19-3-180. PMID 11359943. S2CID 12197415.
External links
• Histology image: 03317loa – Histology Learning System at Boston University
• Stem cell information