How are valleys and gorges formed?
How are valleys and gorges formed? When a river is near its source, it often develops a V-shaped valley as the river erodes down (this is called vertical erosion). The gorge owes its existence to the vertical erosion of the river which flows through it. A gorge of recession is formed eg.
How many major ocean gyres are there on Earth?
What are the 6 gyres?
- Indian Ocean Gyre.
- North Atlantic Gyre.
- North Pacific Gyre.
- South Atlantic Gyre.
- South Pacific Gyre.
What direction do gyres flow?
the Northern Hemisphere, the gyres flow clockwise. In the Southern Hemisphere, they flow counterclockwise. The Coriolis effect is the main factor that determines the direction in which a gyre flows. 3.
How many gyres are in the northern hemisphere?
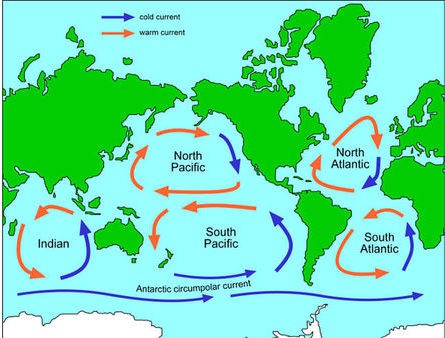
how many gyres are there? five . ... In oceanography, a subtropical gyre is a ring-like system of ocean currents rotating clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and counterclockwise in the Southern Hemisphere caused by the Coriolis Effect. They generally form in large open ocean areas that lie between land masses.
Are gyres caused by the Coriolis effect?
In oceanography, a gyre (/ˈdʒaɪər/) is any large system of circulating ocean currents, particularly those involved with large wind movements. Gyres are caused by the Coriolis effect; planetary vorticity, horizontal friction and vertical friction determine the circulatory patterns from the wind stress curl (torque).
What is the result of a gyre?
Each gyre has a major effect on ocean circulation in that part of the ocean basin. As surface winds push the surface layer of the ocean with them, the surface wind gyres result in surface ocean current gyres. Along coastlines, the direction of movement of a gyre has a significant impact on continental climate.
What are gyres and how are they formed quizlet?
An ocean gyre is a system of circular ocean currents formed by the Earth's wind patterns and the forces created by the rotation of the planet. The circular motion of the gyre draws debris into this stable center, where it becomes trapped.
How is a subtropical gyre formed?
In oceanography, a subtropical gyre is a ring-like system of ocean currents rotating clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and counterclockwise in the Southern Hemisphere caused by the Coriolis Effect. They generally form in large open ocean areas that lie between land masses.
What is a gyre simple definition?
A gyre is a large system of rotating ocean currents. The ocean churns up various types of currents. Together, these larger and more permanent currents make up the systems of currents known as gyres. Wind, tides, and differences in temperature and salinity drive ocean currents.
What is another term for gyre?
Definitions of gyre. a round shape formed by a series of concentric circles (as formed by leaves or flower petals) synonyms: coil, curl, curlicue, ringlet, roll, scroll, whorl.
What causes the circulation of the gyres in the ocean basins?
Three forces cause the circulation of a gyre: global wind patterns, Earth's rotation, and Earth's landmasses. Wind drags on the ocean surface, causing water to move in the direction the wind is blowing. Earth's rotation deflects, or changes the direction of, these wind-driven currents.
What two forces contribute to the creation of an ocean gyre quizlet?
What factors lead to the world wide gyres? Atmospheric circulation drives ocean surface currents: Wind "pulls" water due to friction. This causes the formation of gyres = flow of currents around the periphery of an ocean. Warm water is transported away from the equator and cold water is transported towards the equator.
What direction do gyres turn in the Northern Hemisphere why quizlet?
What is a gyre? Large, circular-moving loops of water driven by wind belts. They rotate clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and counterclockwise in the Southern Hemisphere.
Where are ocean gyres found?
Five permanent subtropical gyres can be found in the major ocean basins—two each in the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans and one in the Indian Ocean—turning clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and counterclockwise in the Southern.
Are gyres surface currents?
These currents come from high latitude areas, so they deliver cold water to the lower latitudes. Together, these currents combine to create large-scale circular patterns of surface circulation called gyres .
How many gyres are there in the world's oceans?
five gyresThere are five gyres to be exact—the North Atlantic Gyre, the South Atlantic Gyre, the North Pacific Gyre, the South Pacific Gyre, and the Indian Ocean Gyre—that have a significant impact on the ocean. The big five help drive the so-called oceanic conveyor belt that helps circulate ocean waters around the globe.
Where are the subtropical gyres located?
subtropical gyre, an area of anticyclonic ocean circulation that sits beneath a region of subtropical high pressure. The movement of ocean water within the Ekman layer of these gyres forces surface water to sink, giving rise to the subtropical convergence near 20°–30° latitude.
What is the subtropical convergence?
The Subtropical Convergence Zone is delimited to the north by the subtropical gyres and to the south by the northernmost current band of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current. The area has high productivity compared with the oligotrophic waters to the north and supports a significant diversity of biota.
What causes Western intensification of surface ocean currents in the subtropical gyres?
0:006:46Western Boundary Intensification | Ocean currents - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipOcean gyres are asymmetric their centers are shifted to the west in all ocean basins. This shiftMoreOcean gyres are asymmetric their centers are shifted to the west in all ocean basins. This shift causes currents on the western side of the basins to be more concentrated. Than those on the eastern.
Is the Kuroshio Current A subtropical gyre?
Similar to the Gulf Stream in the North Atlantic, the Kuroshio is a powerful western boundary current that transports warm equatorial water poleward and forms the western limb of the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre.
Do all oceans have gyres?
Yes, all of the oceans on earth have at least one gyre. There are four named oceans: The Atlantic, Pacific, Indian, and Arctic. In addition, there...
What current flows around the center of gyres?
The subtropical gyres are encircled by four linked currents: two boundary currents aligned roughly north-south at their eastern and western margins...
Where are the 5 major ocean gyres?
There are five identified permanent oceanic gyre currents: the North Atlantic, the South Atlantic, the North Pacific, the South Pacific, and the In...
Why do gyres spin in different directions?
Gyres are primarily created by global wind patterns, and the Coriolis effect shifts the winds that affect the water 45o to form the gyres. To the r...
Why do gyres exist?
The gyres exist because strong winds exert a mechanical force, or stress, on the oceans, causing the water to accelerate. The imposed forces must b...
How are gyres created?
Gyres are created by three forces: the rotation of the Earth, wind patterns, and the landmasses of the Earth. The wind blows across the ocean’s surface, causing the water to move in the direction of the wind.
What Is A Gyre?
A gyre is a series of ocean currents that move in a circular pattern. Winds formed as the earth spins and shifting wind patterns help create them.
Where Are the 5 Major Ocean Gyres?
There are five identified permanent oceanic gyre currents: the North Atlantic, the South Atlantic, the North Pacific, the South Pacific, and the Indian Ocean.
Why Do Gyres Spin in Different Directions?
Gyres are primarily created by global wind patterns , and the Coriolis effect shifts the winds that affect the water 45o to form the gyres .
Why Do Ocean Gyres Exist?
The gyres exist because strong winds exert a mechanical force, or stress, on the oceans, causing the water to accelerate.
What is the Beaufort gyre?
The Beaufort Gyre is a massive swirl of water produced by high winds that force currents clockwise.
How is the Ekman spiral created?
The Ekman spiral is created beneath the water’s surface by the Coriolis force.
Where do gyres form?
Most of the world’s major gyres are subtropical gyre s. These form between the polar and equatorial regions of Earth. Subtropical gyres circle areas beneath regions of high atmospheric pressure. These are placid ocean areas thousands of kilometers in diameter. Unlike coastal zones, these central regions are relatively stable. The ocean water generally stays in one place while the currents of the gyre circulate around it.
What is a gyre?
Gyres are comprise d of ocean currents that link up as they follow the coastlines of the Earth’s continents. Each gyre has a powerful western boundary current and a weaker eastern boundary current. The North Atlantic Gyre begins with the northward flow of the Gulf Stream along the East Coast of the United States.
Where do subpolar gyres form?
Subpolar gyre s form in the polar regions of the planet. They sit beneath an area of low atmospheric pressure. Wind drives the currents in subpolar gyres away from coastal areas. These surface currents are replaced by cold, nutrient-rich water in a process called upwelling. The Northern Hemisphere has several subpolar gyres, bounded by islands such as Iceland, Greenland, and the Aleutians; and the northern reaches of Scandinavia, Asia, and North America.
Which direction does the North Atlantic Ocean gyre flow?
The North Atlantic Ocean Gyre always flows in a steady, clockwise path around the North Atlantic Ocean. Some gyres experience seasonal variation, however. The Indian Ocean Gyre is a complex system of many currents extending from the eastern coast of Africa to the western coast of Australia.
How does wind affect the ocean?
Wind drags on the ocean surface, causing water to move in the direction the wind is blowing. The Earth’s rotation deflect s, or changes the direction of, these wind-driven currents. This deflection is a part of the Coriolis effect. The Coriolis effect shifts surface currents by angles of about 45 degrees.
Why are ocean gyres considered oligotrophic?
Their calm centers have traditionally been regarded as oligotrophic, or nutrient-poor, because they have few concentrations of the organic chemicals that support producer s, such as algae and plankton, in the ocean food web.
Where does the Canary Current flow?
Still flowing in a circular pattern, the current flows south as far as the northwestern coast of Africa, where it is known as the Canary Current—the gyre’s eastern boundary current. The gyre is completed as the North Atlantic Equatorial Current crosses the Atlantic Ocean to the Caribbean Sea.
How are Ocean Gyres Formed?
Ocean gyres are caused by two different forces acting on the water: the wind and the Coriolis effect. Earth’s wind patterns grab the ocean water and push it forward, however, these wind patterns are deflected by the earth’s rotation (the Coriolis effect) causing both the winds and the water they are pushing to swirl around in a circular pattern.
What causes gyres in the ocean?
Ocean gyres are caused by two different forces acting on the water: the wind and the Coriolis effect . Earth’s wind patterns grab the ocean water and push it forward, however, these wind patterns are deflected by the earth’s rotation (the Coriolis effect) causing both the winds and the water they are pushing to swirl around in a circular pattern.
Why are ocean gyres bad?
Though the ocean gyres themselves are constantly circulating, the area of water that they surround is actually calm and stationary. This creates a bit of a problem when it comes to environmental pollution. When garbage that has made its way into the ocean is carried into the center of an ocean gyre, there are no more outside forces acting on the garbage to move it any further. The result is that garbage will often collect at the center of ocean gyres and stay there for many years.
Why are there no life in the ocean gyres?
Not a lot of life exists within the major ocean gyres. This, however, is not because of the garbage that gathers there but rather because the water itself is so calm. Without currents within the gyres to bring in fresh nutrients, the centers become oligotrophic, or nutrient poor. Without these key nutrients, plankton and algae are not able to thrive, and it is plankton and algae that serve as the base of the food chain for most all other ocean creatures.
How many different ocean gyres are there?
There are five different major ocean gyres on the planet. The five are named based on their locations:
How many gyres are there in the ocean?
There are five different major ocean gyres on the planet. The five are named based on their locations: North Pacific Gyre. South Pacific Gyre. North Atlantic Gyre. South Atlantic Gyre. Indian Gyre. However, there are also a large number of smaller ocean gyres, including gyres in the Arctic Ocean.
Where do tropical gyres occur?
Tropical gyres occur near the equator of the earth. Since the Coriolis effect is not observed at the earth’s equator, the main force acting on the ocean water near the equator of the earth is straight-line winds. For this reason, tropical ocean gyres are much more elongated in their shape. As the name suggests, subpolar ocean gyres form near ...
What is an ocean gyre?
An ocean gyre is an area of ocean that slowly rotates in an enormous circle.
How are tides formed?
Tides are formed by the differential nature of (primarily) the moon's gravitational pull on the earth.
What is the term for the border between water of different temperature, like the warm water of Gulf Stream and much cold?
2. Thermoclines - border between water of different temperature, like the warm water of Gulf Stream and much colder North Atlantic ocean.
Is the Indian Ocean a gyre?
In contrast, the northern Indian Ocean Gyre is a much smaller ocean gyre. Unlike the South Pacific Gyre, its extent is determined largely by landmasses. The Equator forms its southern boundary, but it is bounded elsewhere by the Horn of Africa, Sri Lanka and the Indian subcontinent, as well as the Indonesian archipelago.
What is a gyre in the ocean?
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) defines a gyre as a large system of swirling ocean currents. Increasingly, however, it also refers to the garbage patch as a vortex of plastic waste and debris broken down into small particles in the ocean.
What is the center of a gyre?
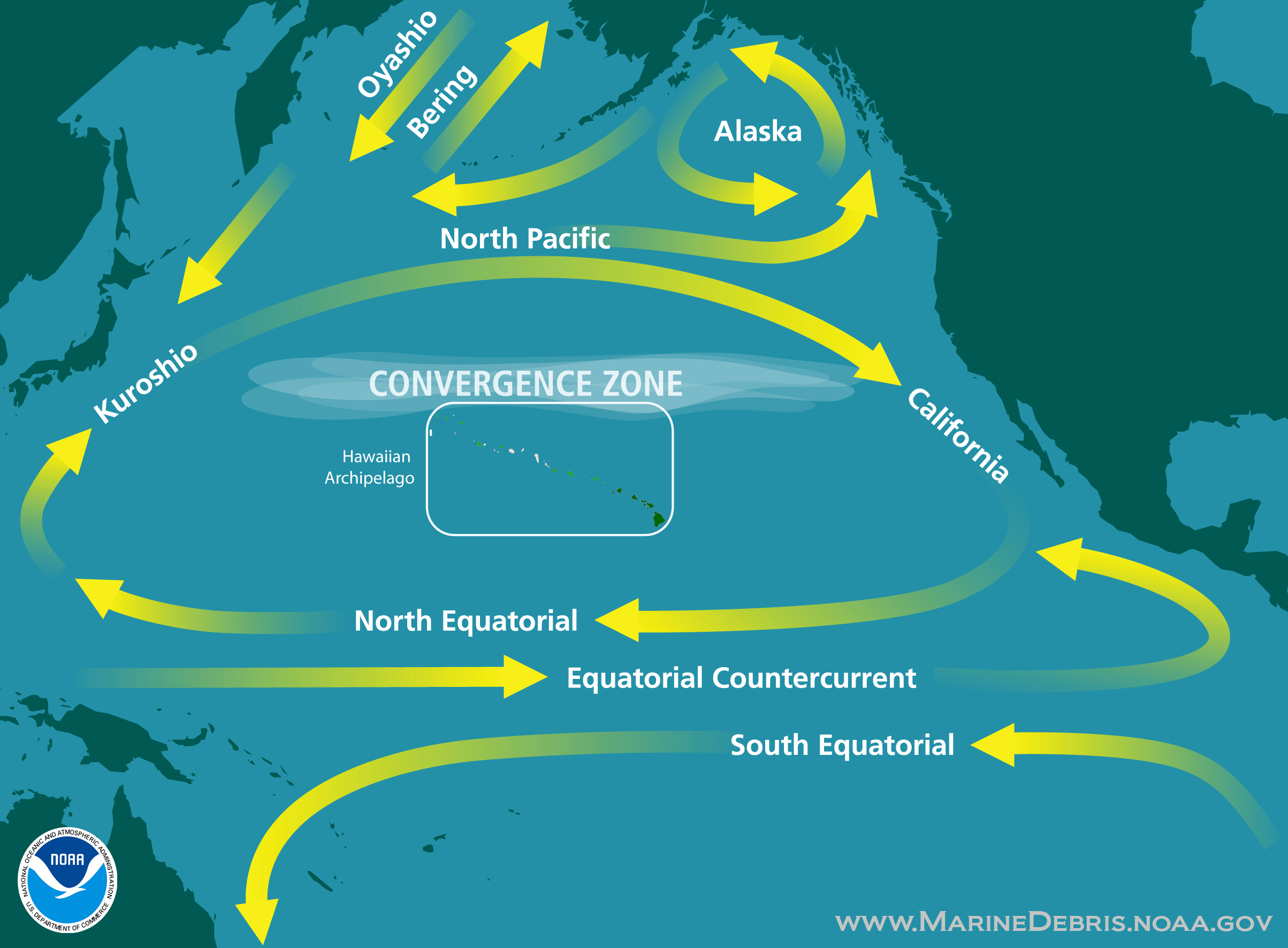
The area in the center of a gyre tends to be very calm and stable . The circular motion of the gyre draws debris into this stable center, where it becomes trapped. A plastic water bottle discarded off the coast of California, for instance, takes the California Current south toward Mexico. There, it may catch the North Equatorial Current, which crosses the vast Pacific. Near the coast of Japan, the bottle may travel north on the powerful Kuroshiro Current. Finally, the bottle travels eastward on the North Pacific Current. The gently rolling vortexes of the Eastern and Western Garbage Patches gradually draw in the bottle.
Why does the Great Pacific Garbage Patch accumulate?
The gently rolling vortexes of the Eastern and Western Garbage Patches gradually draw in the bottle. The amount of debris in the Great Pacific Garbage Patch accumulates because much of it is not biodegradable. Many plastics, for instance, do not wear down; they simply break into tinier and tinier pieces. For many people, the idea of ...
