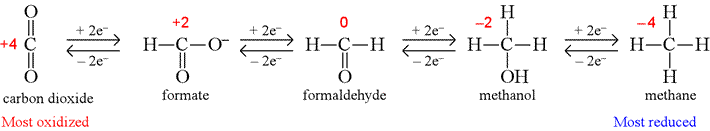
How do you determine oxidation states?
To calculate the oxidation state for carbon, use the following guidelines:
- In a C-H bond, the H is treated as if it has an oxidation state of +1. ...
- For carbon bonded to a more electronegative non-metal X, such as nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur or the halogens, each C-X bond will increase the oxidation state of the carbon by 1. ...
- For carbon bonded to another carbon, the oxidation state is unaffected. ...
What are the rules for oxidation states?
- The oxidation state of an atom in any pure element, whether monatomic, diatomic, or polyatomic, is zero.
- The oxidation state of a monatomic ion is the same as its charge—for example, Na + = +1, Cl − = −1.
- The oxidation state of fluorine in chemical compounds is always −1. ...
What are oxidation states?
Oxidation state indicates the degree of oxidation for an atom in a chemical compound; it is the hypothetical charge that an atom would have if all bonds to atoms of different elements were completely ionic. Oxidation states are typically represented by integers, which can be positive, negative, or zero.
What does oxidation state mean?
Oxidation state is also known as oxidation number. Oxidation state shows the total number of electrons which have been removed from an element (a positive oxidation state) or added to an element (a negative oxidation state) to get to its present state. It is an indicator of the degree of oxidation or reduction of an atom in a chemical compound.
What are the rules used to assign oxidation number?
Assigning Oxidation Numbers Using Rules The oxidation number of a free, neutral element is zero. The oxidation number of a monoatomic ion is equal to the charge of the ion. The oxidation number of Group IA elements is always +1. The oxidation number of Group IIA elements is always +2.
How do you determine oxidation number and state?
Calculating Oxidation NumbersAny free element has an oxidation number equal to zero.For monoatomic ions, the oxidation number always has the same value as the net charge corresponding to the ion.The hydrogen atom (H) exhibits an oxidation state of +1. ... Oxygen has an oxidation of -2 in most of its compounds.More items...•
How is the oxidation state trick determined?
Just follow the steps: Determine whether the substance in question is elemental. Free, uncombined elemental atoms always have an oxidation number of 0. This is true both for atoms whose elemental form is composed of a lone atom, as well as atoms whose elemental form is diatomic or polyatomic.
What determines the most likely oxidation state of an element?
The oxidation state of an element is related to the number of electrons that an atom loses, gains, or appears to use when joining with another atom in compounds. It also determines the ability of an atom to oxidize (to lose electrons) or to reduce (to gain electrons) other atoms or species.
How do you determine the oxidation state of a redox reaction?
We can identify redox reactions using oxidation numbers, which are assigned to atoms in molecules by assuming that all bonds to the atoms are ionic. An increase in oxidation number during a reaction corresponds to oxidation, while a decreases corresponds to reduction.
What is the fastest way to find the oxidation number?
The oxidation numbers of all the atoms in a compound must add up to the charge of that compound. For example, if a compound has no charge, the oxidation numbers of each of its atoms must add up to zero; if the compound is a polyatomic ion with a charge of -1, the oxidation numbers must add up to -1, etc.
How do you find the oxidation number in a structure?
For each atom in the structure:Break all 2-electron bonds and give both electrons to the more electronegative of the bonding pair.Sum all electrons around the atom.Compare that number to the number of valence electrons of that atom. ... Use Roman Numerals to indicate the oxidation state.
How do you find the oxidation number of an ion?
0:061:34How to Find Oxidation Numbers for an Ion - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipNumber the chlorine in the center that's normally minus one except when it's bonded to things likeMoreNumber the chlorine in the center that's normally minus one except when it's bonded to things like well chlorine bromine iodine and then oxygen. So it this chlorine it's bonded to oxygen.
How do you find the oxidation number in a structure?
For each atom in the structure:Break all 2-electron bonds and give both electrons to the more electronegative of the bonding pair.Sum all electrons around the atom.Compare that number to the number of valence electrons of that atom. ... Use Roman Numerals to indicate the oxidation state.
What is the difference between oxidation state and oxidation number?
6 days agoThe main difference between oxidation number and oxidation state is that oxidation number is the charge of the central atom of a coordination complex if all the bonds around it were ionic bonds whereas oxidation state is the number of electrons that a particular atom can lose, gain or share with another atom.
How do you find the oxidation number of an ion?
0:061:34How to Find Oxidation Numbers for an Ion - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipNumber the chlorine in the center that's normally minus one except when it's bonded to things likeMoreNumber the chlorine in the center that's normally minus one except when it's bonded to things like well chlorine bromine iodine and then oxygen. So it this chlorine it's bonded to oxygen.
How do you find the oxidation state of oxygen?
- If we have a monatomic ion then its oxidation number is equal to the charge on it. It can be positive, negative or neutral. - Oxidation number of oxygen is generally -2 but in some cases it can be -1or (−12) too. The sum of oxidation numbers of all the atoms in a neutral compound is 0.
1. How similar are the Oxidation States and numbers?
Although often used interchangeably, oxidation states differ from oxidation numbers in meaning, utility, representation, and charge indication. Whi...
2. What maximum positive OS is possible for an element?
The maximum OS that can be assigned to an element can go up to +9 and not beyond.
3. What uses can the OS be put to?
Alongside helping determine the charge of an atom in a chemical reaction, OS is also useful in the determination of the strength of acids and bases...
4. What is the OS for Nitrogen?
As nitrogen is a Group 5 element, the oxidation state for nitrogen can range anywhere between -3 and +5 based on the compound it has reacted to for...
5. How can Vedantu make a difference in your learning process?
Vedantu has the most updated and detailed set of topics available for students. Which can be accessed for free. So students can learn and understan...
6. How can I download reading material from Vedantu?
Accessing material from Vedantu is extremely easy and student-friendly. Students have to simply visit the website of Vedantu and create an account....
Which atom has an oxidation state?
solving for gives , giving us the answer we need. Therefore the nitrogen atom in has an oxidation state of , which is the correct answer.
What is reduction in chemistry?
Reduction is defined as the gain of electrons so we want to find the element that gains electrons/becomes negatively charged.
How to determine the total charge of all hydrogens together?
Using our knowledge of oxidation states of hydrogen and oxygen and counting the number of hydrogens and oxygen in this compound, we can determine that the total charge of all the hydrogens together is equal to , and that the total charge of the one oxygen is .
Does fluorine have an oxidation number?
Finally, let's look . We can once again use the general rule of oxidation numbers that fluorine has a oxidation number to simplify this. Therefore
Can we create an equation and solve for our unknown?
Just as we did above we can create an equation and solve for our unknown.
Is nitrogen a neutral oxidation state?
We know this compound as a whole is neutrally charged (equal to overall charge), and applying our knowledge of the general oxidation state of hydrogen in a compound and knowing there are hydrogens we know that the hydrogens have a total charge of together, and nitrogen has an unknown oxidation state , so for our equation we have:
What does Oxidation Entail?
The contact between the oxygen molecules and substances causes an Oxidation reaction. It can be simply described as an atom's enhanced oxidation state through a chemical reaction. It’s the exact contrary part of the reduction reaction. In both reactions, the transfer of electrons is required.
How to define oxidation number?
One could thus define oxidation number or state by putting a value to such electron losses during a reaction, which usually stood as integers. At times, the OS can also be represented as a fraction. For instance, the OS of iron in Fe3O4 is valued at 8/3.
What is the chemical reaction that involves electron movement between the elements of any compound?
Oxidation refers to a chemical reaction that involves electron movement between the elements of any compound. The process’s character is exhibited when an element donates electrons. It is also denoted by an increased oxidation state. A common example of oxidation is the reaction of iron (Fe) with oxygen (O2).
What is the OS of iron in Fe3O4?
At times, the OS can also be represented as a fraction. For instance, the OS of iron in Fe3O4 is valued at 8/3. Before moving on to more about oxidation number or state, take a brief look at the process of oxidation.
What is the oxidation number used for?
Also interchangeably used with oxidation number, it is used for the determination of changes which are taking place in a redox reaction. It has a similar numerical representation as valence electrons, but is typically differentiated from formal charge.
What is the chemical process of oxidation?
It is also an essential contributor to the metabolic process, whereby nutrient oxidation leads to energy release and enables life forms to thrive. Exposure of various elements, as well as compounds, causes combustion and release of water, carbon dioxide and energy.
What is OS in chemistry?
OS refers to a specific number assigned to elements in different chemical combinations. These numbers are a representation of electron quantity lost or gained by an element’s atom to result in a chemical bond with another element.
How to find the oxidation state of an atom?
Oxidation state is obtained by summing the heteronuclear-bond orders at the atom as positive if that atom is the electropositive partner in a particular bond and as negative if not , and the atom’s formal charge (if any) is added to that sum.
How is the oxidation state calculated in chemistry?
Introductory chemistry uses postulates: the oxidation state for an element in a chemical formula is calculated from the overall charge and postulated oxidation states for all the other atoms.
What does OS stand for in chemistry?
where OS stands for oxidation state . This approach yields correct oxidation states in oxides and hydroxides of any single element, and in acids such as H 2 SO 4 or H 2 Cr 2 O 7. Its coverage can be extended either by a list of exceptions or by assigning priority to the postulates. The latter works for H 2 O 2 where the priority of rule 1 leaves both oxygens with oxidation state −1.
How many bonds does oxygen have to the auride anion?
We see that the oxygen atom bonds to the six nearest rubidium cations, each of which has 4 bonds to the auride anion. The bond graph summarizes these connectivities. The bond orders (also called bond valences) sum up to oxidation states according to the attached sign of the bond's ionic approximation (there are no formal charges in bond graphs).
What is the increase in oxidation state?
The increase in the oxidation state of an atom, through a chemical reaction, is known as oxidation; a decrease in oxidation state is known as a reduction. Such reactions involve the formal transfer of electrons: a net gain in electrons being a reduction, and a net loss of electrons being oxidation. For pure elements, the oxidation state is zero. ...
What is the oxidation state of an element?
In inorganic nomenclature, the oxidation state is represented by a Roman numeralplaced after the element name inside the parenthesis or as a superscript after the element symbol, e.g. Iron(III) oxide. The term oxidationwas first used by Antoine Lavoisierto signify the reaction of a substance with oxygen.
What is the oxidation number?
The oxidation state, sometimes referred to as oxidation number, describes the degree of oxidation(loss of electrons) of an atomin a chemical compound. Conceptually, the oxidation state, which may be positive, negative or zero, is the hypothetical chargethat an atom would have if all bondsto atoms of different elements were 100% ionic, ...
What is the oxidation state of an atom?
The oxidation state of an atom can be defined as the hypothetical charge that would be held by that atom if all of its bonds to other atoms were completely ionic in nature. For example, the oxidation state of carbon in CO 2 would be +4 since the hypothetical charge held by the carbon atom if both of the carbon-oxygen double bonds were completely ...
How to calculate Oxidation Number?
To calculate oxidation number we need to understand and follow certain rules. There are six rules:
What is the oxidation number?
The oxidation state of an atom (sometimes referred to as the oxidation number) in a chemical compound provides insight into the number of electrons lost it and, therefore, describes the extent of oxidation of the atom. The oxidation state of an atom can be defined as the hypothetical charge that would be held by that atom if all of its bonds to other atoms were completely ionic in nature. For example, the oxidation state of carbon in CO 2 would be +4 since the hypothetical charge held by the carbon atom if both of the carbon-oxygen double bonds were completely ionic would be equal to +4 (each oxygen atom would hold a charge of -2 since oxygen is more electronegative than carbon).
What happens if the oxidation number is positive?
If the oxidation number is positive, the atom loses electrons; if the oxidation number is negative, the atom acquires electrons. Calcium has a charge of +2, indicating that it has lost two electrons. The -2 charge of oxygen indicates that it has gained two electrons.
What is the reaction between iron and oxygen?
For example, The reaction between iron and oxygen – When iron (Fe) reacts with oxygen it forms rust because iron loses electrons and oxygen gains electrons.
What is the lowest oxidation state?
The lowest known oxidation state is −4, for carbon in CH 4 (methane).
What is the term used to describe the interaction of a material with oxygen?
Antoine Lavoisier used the term “oxidation” to describe the interaction of a material with oxygen. Much later, it was discovered that the material loses electrons when oxidised, and the definition was expanded to encompass any process in which electrons are lost, regardless of whether oxygen is present.
What is the oxidation number of a monatomic ion?
The oxidation number of a monatomic ion equals the charge of the ion. For example, the oxidation number of Na + is +1; the oxidation number of N 3- is -3. The usual oxidation number of hydrogen is +1. The oxidation number of hydrogen is -1 in compounds containing elements that are less electronegative than hydrogen, as in CaH 2.
What is the sum of the oxidation numbers of all of the atoms in a neutral compound?
The sum of the oxidation numbers of all of the atoms in a neutral compound is 0.
What is the oxidation number of a Group IIA element in a compound?
The oxidation number of a Group IIA element in a compound is +2.
What is electrochemical reaction?
She has taught science courses at the high school, college, and graduate levels. Electrochemical reactions involve the transfer of electrons. Mass and charge are conserved when balancing these reactions, but you need to know which atoms are oxidized and which atoms are reduced during the reaction.
What is the convention for cation?
The convention is that the cation is written first in a formula, followed by the anion. For example, in NaH, the H is H-; in HCl, the H is H+.
Is F more electronegative than O?
Exceptions include OF 2 because F is more electronegative than O, and BaO 2, due to the structure of the peroxide ion, which is [O-O] 2-. The oxidation number of a Group IA element in a compound is +1. The oxidation number of a Group IIA element in a compound is +2.
What is the oxidation state of an atom?
If you want to use the IUPAC definition, here it is: “ Oxidation state of an atom is the charge of this atom after ionic approximation of its heteronuclear bonds “
What is the oxidation state of an atom in its elemental state?
The oxidation state of an atom in its elemental state is zero. Forexample, He, O 2, S 8
What is the oxidation state & number of sulfur in the Tetrathionate Ion?
In the tetrathionate ion, S 4 O 6-2, two of the sulfurs have oxidation state of 0, and two have an oxidation state of +5. The “average” oxidation number of sulfur in the molecule is (0+0+5+5)/4 = 2.5. It is only in these mixed oxidation state compounds that the concept of oxidation number being different than oxidation state may come up
What does the oxidation number represent?
The oxidation number represents how many electrons an atom has gained or lost in a molecule. Elements have an oxidation state of zero, and atoms in ionic compounds are usually assigned a positive or negative oxidation state. Organic compounds and some covalent compounds do not have oxidation states assigned to the atoms in the compounds.
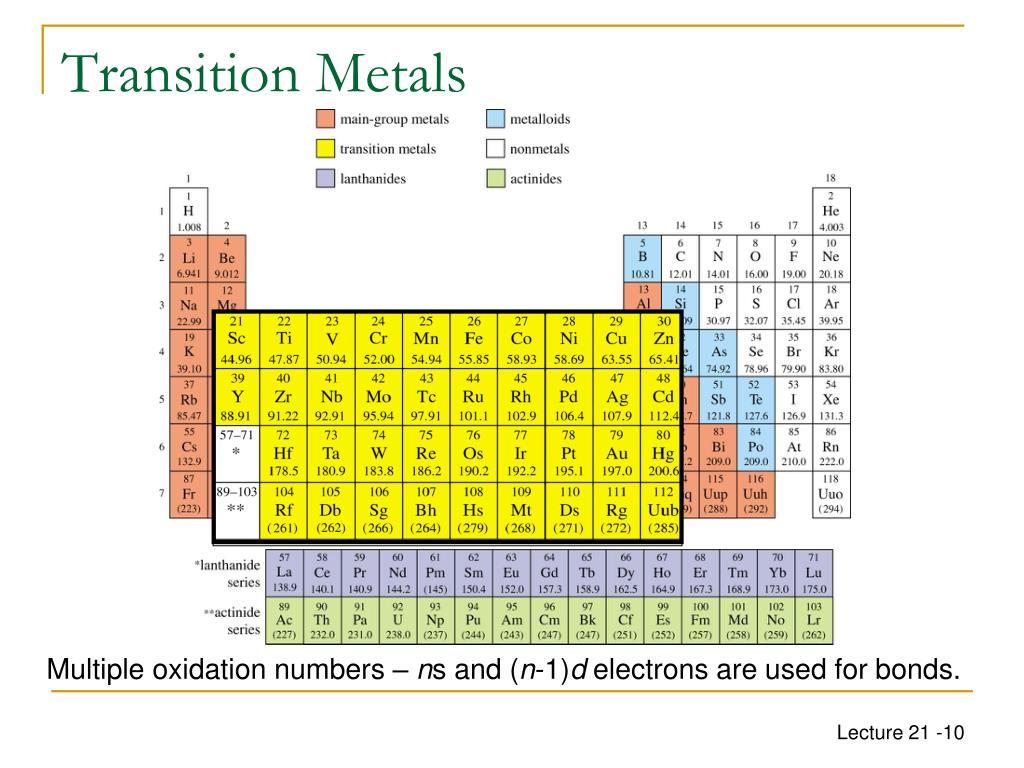
Which metal has the most stable oxidation states?
Vanadium, manganese, and chromium have the greatest variety of stable oxidation states and colors. The cover photo for this article, taken by Wilco Oelen (who was one of the many inspirations for ChemTalk), shows the colors of vanadium compounds in the +2, +3, +4 and +5 oxidation states. Tungsten and molybdenum also have several oxidation states, some of which are less studied than other transition metals.

Overview
Determination
While introductory levels of chemistry teaching use postulated oxidation states, the IUPAC recommendation and the Gold Book entry list two entirely general algorithms for the calculation of the oxidation states of elements in chemical compounds.
Introductory chemistry uses postulates: the oxidation state for an element in a …
IUPAC definition
IUPAC has published a "Comprehensive definition of the term oxidation state (IUPAC Recommendations 2016)". It is a distillation of an IUPAC technical report "Toward a comprehensive definition of oxidation state" from 2014. The current IUPAC Gold Book definition of oxidation state is:
Oxidation state of an atom is the charge of this atom after ionic approximation of its heteronucle…
Appearances
A nominal oxidation state is a general term with two different definitions:
• Electrochemical oxidation state represents a molecule or ion in the Latimer diagram or Frost diagram for its redox-active element. An example is the Latimer diagram for sulfur at pH 0 where the electrochemical oxidation state +2 for sulfur puts HS 2O 3 between S and H2SO3:
List of oxidation states of the elements
This is a list of known oxidation states of the chemical elements, excluding nonintegral values. The most common states appear in bold. The table is based on that of Greenwood and Earnshaw, with additions noted. Every element exists in oxidation state 0 when it is the pure non-ionized element in any phase, whether monatomic or polyatomic allotrope. The column for oxidation state 0 o…
Use in nomenclature
The oxidation state in compound naming for transition metals and lanthanides and actinides is placed either as a right superscript to the element symbol in a chemical formula, such as Fe or in parentheses after the name of the element in chemical names, such as iron(III). For example, Fe 2(SO 4) 3 is named iron(III) sulfate and its formula can be shown as Fe 2(SO 4) 3. This is because a sulfate ion has a charge of −2, so each iron atom takes a charge of +3.
History of the oxidation state concept
Oxidation itself was first studied by Antoine Lavoisier, who defined it as the result of reactions with oxygen (hence the name). The term has since been generalized to imply a formal loss of electrons. Oxidation states, called oxidation grades by Friedrich Wöhler in 1835, were one of the intellectual stepping stones that Dmitri Mendeleev used to derive the periodic table. William B. Jensen gives an overview of the history up to 1938.
See also
• Electronegativity
• Electrochemistry
• Atomic orbital
• Atomic shell
• Quantum numbers