How is peat soil made?
Peat soil is a type of soil made from decomposed organic materials that form over thousands of years. Peat soil has a high percentage of organic matter content from plant materials like decaying sphagnum peat moss. Peat soil accumulates in wetland ecosystems called peatlands or peat bogs.
What is a peat and how is it formed?
Peat is a soft, crumbly, dark brown substance that is formed from generations of dead and partially decaying organic matter. To form peat, the vegetation must fall and be buried in a relatively oxygen poor environment so that it can be incorporated into layers of the soil without completely decomposing.
Where does peat usually form?
wetlandspeat, spongy material formed by the partial decomposition of organic matter, primarily plant material, in wetlands such as swamps, muskegs, bogs, fens, and moors.
What is peat in soils?
Peat is the surface organic layer of a soil that consists of partially decomposed organic matter, derived mostly from plant material, which has accumulated under conditions of waterlogging, oxygen deficiency, high acidity and nutrient deficiency.
How long does it take peat to form?
10 yearsPeat, or turf, as it is often referred to in Ireland, is a type of soil that contains a high amount of dead organic matter, mainly plants that have accumulated over thousands of years. It takes approximately a staggering 10 years for 1cm of peat to form!
What are the characteristics of peat soil?
Peat has typical characteristics, which include high natural moisture content, high compressibility and water-holding capacity, low specific gravity, low bearing capacity, and medium-to-low permeability [3].
How can you tell if soil is peat?
Squeeze the soil ball. If it feels spongy, it is most likely peat. If the soil forms a loose ball when squeezed, it is probably loam.
Why is peat soil important?
Peat is hugely important to our planet for lots of reasons. It acts as a carbon store, it is a great habitat for wildlife, it has a role in water management, and preserves things well for archaeology.
What is the difference between peat and soil?
Tip. The main difference between peat moss and potting soil is that peat moss is soilless and potting soil contains soil mixed with a few other ingredients. Of course, peat moss can be added to a potting soil to benefit moisture-loving plants.
Why is peat soil bad?
It contains little to no nutrients and growing in peat-based mixes ties the grower to constantly applying fertilisers to keep plants healthy.
Which of the following is responsible for peat formation?
Sphagnum accumulations can store water, since both living and dead cells can hold water and living matter for very long distance transport inside their cells. Hence, sphagnum is responsible for peat formation.
Is peat soil good for agriculture?
It can accelerate plant growth, adsorb heavy metals well and reduce the damage of heavy metals to plants. Therefore, it is a good plant soil amendment. 3. The Role of Peat in Fertilizer Application As a fertilizer, peat has become a mature technology in the world.
What is peat and why is it important?
It acts as a carbon store, it is a great habitat for wildlife, it has a role in water management, and preserves things well for archaeology. Peat is of great importance to our planet: as a carbon store – peat holds more carbon than the combined forests of Britain, France and Germany.
How is peat formed IB Biology?
Peat formation Peat is formed when partially decomposed organic matter is compressed in anaerobic waterlogged soils to form a brown soil like carbon rich matter. In aerobic conditions organic matter is eventually digested by saprotrophic bacteria and fungi.
How do you make peat?
Peat forms when plant material does not fully decay in acidic and anaerobic conditions. It is composed mainly of wetland vegetation: principally bog plants including mosses, sedges, and shrubs. As it accumulates, the peat holds water. This slowly creates wetter conditions that allow the area of wetland to expand.
What is peat and why does it burn?
What is peat burning? Peat burning is not actually burning of peat, it's burning of the vegetation that grows on top of peat. This is usually heather or grasses, such as purple moor grass. It has been done traditionally to provide new growth of heather (for grouse) or grasses (for sheep).
How is peat soil formed?
Peat soils are formed from partially decomposed plant material under anaerobic water saturated conditions. They are found in peatlands (also called bogs or mires). Peatlands cover about 3% of the earth’s land mass; they are found in the temperate (Northern Europe and America) and tropical regions (South East Asia, South America, South Africa and the Caribbean) 1.#N#Peat soils are classified as histosols. These are soils high in organic matter content. Peat formation is influenced by moisture and temperature. In highly saturated anaerobic soils, decomposition of plant material by micro organisms is slowed down, resulting in high carbon accumulation. In colder climates decomposition of plant material by micro organisms is slowed down leading to quicker peat formation. The carbon content of peat soils makes peatland a major storage of carbon on the earth surface. This is why its importance in fighting climate change can never be overemphasized.
Why is peat soil more vulnerable to erosion?
Peat soils drained for agricultural purposes are more vulnerable to wind and water erosion when the topsoil is severely dry. 5. Drainage of peatland can lead to peat fires which destroy forestland and habitation and further increase the emission of CO2 to the atmosphere.
Why is peat used in agriculture?
Peat use for forestry and agriculture are beneficial but it alters the natural peatland hydrology. This causes oxidation of stored carbon therefore declining its organic matter content. During peat extraction, peat is drained and dried before storage or transportation for sale. These processes reduce the water content and encourage microbial decomposition of organic matter. The result of this is the release of greenhouse gasses such as CO2 and N2O.3, 4
Why are peatlands important?
Peatlands bring enormous economic benefits to regions where they are found. 1. Peat is extracted for use as horticultural compost. It is highly sought after in commercial horticulture because of its high water retaining ability and flow of air.1. 2.
What are the causes of the decline of biodiversity in peatland?
1. Drainage of peatland causes decline in biodiversity because its natural hydrological habitat is disturb ed. Peatlands provide habitation for diverse species of meadow birds, animals, vegetation and insects. 2. Peat oxidation can lead to release of dissolved organic matter and peat particles into surface waters. 3.
How to preserve peatlands?
1. Conserve wet peatlands: This approach is preventive and avoids the expensive cost of restoring peatlands to their natural hydrological state. This is simply putting a stop to the drainage of peatlands. There is no need for soil restoration projects if efforts are made to keep the soil in its natural state. People in surrounding communities must be educated on the benefits of conserving the peatland natural ecosystem.
How long can peat soil store human remains?
Peat soils have the ability to store human remains or ancient artefacts for thousands of years; since they have very minimal microbial decomposition. A good example of this is the 4000 year old body of a man found in peat from Cashel-Central Ireland. 4.
Why is peat formed in waterlogged soils?
The presence of oxygen (aerobic conditions) is necessary for fungal and microbial activity that promotes decomposition, but peat is formed in waterlogged soils with little or no access to oxygen (anaerobic conditions), largely preventing the complete decomposition of organic material.
What is peat made of?
peat, fuel consisting of spongy material formed by the partial decomposition of organic matter, primarily plant material, in wetlands such as swamps, muskegs, bogs, fens, and moors. The development of peat is favoured by warm moist climatic conditions; however, peat can develop even in cold regions such as Siberia, Canada, and Scandinavia.
How are peats different from coal?
Peat may be distinguished from lower-ranked coals on the basis of four characteristics: peats generally contain free cellulose, more than 75 percent moisture, and less than 60 percent carbon, and they can be cut with a knife. The transition to brown coal takes place slowly and is usually reached at depths ranging from 100 to 400 metres (approximately 330 to 1,300 feet).
How is peat pumped into a sump?
Hydraulic excavating can also be used, particularly in bogs that contain roots and tree trunks. The peat is washed down by a high-pressure water jet, and the pulp runs to a sump. There, after slight maceration, it is pumped to a draining ground in a layer, which, after partial drying, is cut up and dried further.
What is dried peat used for?
Peat is used for domestic heating purposes as an alternative to firewood and forms a fuel suitable for boiler firing in either briquetted or pulverized form. Peat is also used for household cooking in some places and has been used to produce small amounts of electricity.
What is the first step in the formation of coal?
The formation of peat is the first step in the formation of coal. With increasing depth of burial and increasing temperature, peat deposits are gradually changed to lignite. With increased time and higher temperatures, these low-rank coals are gradually converted to subbituminous and bituminous coal and under certain conditions to anthracite.
How does peatification occur?
Peatification is influenced by several factors, including the nature of the plant material deposited, the availability of nutrients to support bacterial life, the availability of oxygen, the acidity of the peat , and temperature. Some wetlands result from high groundwater levels, whereas some elevated bogs are the result of heavy rainfall. Although the rate of plant growth in cold regions is very slow, the rate of decomposition of organic matter is also very slow. Plant material decomposes more rapidly in groundwater rich in nutrients than in elevated bogs with heavy rainfall. The presence of oxygen (aerobic conditions) is necessary for fungal and microbial activity that promotes decomposition, but peat is formed in waterlogged soils with little or no access to oxygen (anaerobic conditions), largely preventing the complete decomposition of organic material. The formation of abundant peat was not possible before land plants spread widely during and after the Devonian Period (beginning approximately 419.2 million years ago). Peat moss ( Sphagnum) is one of the most common constituents of peat.
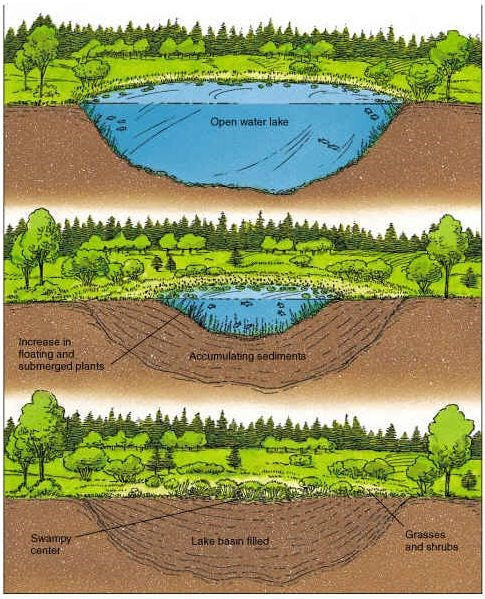
How is peat soil formed?
Peat soil is formed over time in areas such as lakes and swamps when plants remain underwater and decay over the years.
What is peat soil?
Peat soil, which is recommended for many plants, is a type of soil that is often heard by those who want to grow flowers at home and indoors. Now, in this article, we will answer the questions about what peat means and peat soil.
How to Make Peat Soil at Home?
Peat soil requires a long time and a natural environment to form. However, in some cases, a soil type with properties very close to peat soil can be prepared at home. Let us explain to you how to make natural peat soil at home.
How is Peat Used?
If you have peat soil and you think if peat can be used alone; Let us give you information about the usage areas of this land:
How to prepare a large number of seedlings?
If you are going to prepare a large number of seedlings; You can make a productive start by choosing peat soil for seedlings.
Why do we need to know what kind of soil we need for plants?
If you are interested in plant care and cultivation; You need to know which plant wants what kind of soil. Because every plant wants to hold on to the soil that is suitable for its own structure. Climate, roots and branches, watering demand, pot size, and seed type are all important factors for a plant.
Why is soil important for plants?
Both soils are mineral sources of plants. It helps the plant to grow healthily.
How long does it take for soil to form?
Soil formation happens over hundreds, sometimes thousands, of years, but you can still see evidence of that formation today. You can see the soft, dark topsoil layer and every layer underneath, all the way down to the impenetrable bedrock. These layers are called soil horizons.
When will soil formation start?
April 9, 2021. June 7, 2020. The soil formation process has to start somewhere – whether it is from the erosion of rocks near a body of water or the destructive effects of an environmental disaster.
Why do microorganisms play a role in soil formation?
Microorganisms play an even greater role in soil formation because of how they guide the soil nitrogen process, which is essential for the balance of minerals and chemical reactions in the soil. Without the soil nitrogen process, the ocean and other bodies of water would become inhabitable for sea life.
What are the three stages of soil formation?
Soil formation can vary depending on what type of soil is forming – clay, sand, or silt . But generally, these are the three stages that most soils go through on their way to full formation.
What is the definition of soil formation?
Encyclopedia Britannica defines soil formation as “The evolution of soils and their properties.”
Why is it important to classify soil types?
Classifying soil types helps farmers when conducting a soil survey on their fields, or gardeners when they wish to plant only the best species of plants that will thrive in the soil.
What are the horizons of soil?
Deeper horizons usually remain unmoving until someone digs into the ground. The soil horizons are O, A, E, B, C, and R. Many factors go into soil formation, and how the soil turns out in appearance and feel depends entirely upon them.
